Exercise 3.3: Entropy of Ternary Quantities
From LNTwww
(Redirected from Aufgabe 3.3: Entropie von Ternärgrößen)
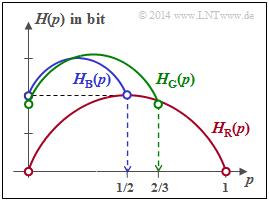
On the right you see the entropy functions $H_{\rm R}(p)$, $H_{\rm B}(p)$ and $H_{\rm G}(p)$, where $\rm R$ stands for "red", $\rm B$ for "blue" and $\rm G$ for "green". The probability functions are for all random variables:
- $$P_X(X) = [\hspace{0.05cm}p_1\hspace{0.05cm},\ p_2\hspace{0.05cm},\ p_3\hspace{0.05cm}]\hspace{0.3cm}\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} |X| = 3\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
For the questionnaire, the relationship $p_1 = p$ and $p_2 = 1 - p_3- p$.
The probability function of a random variable
- $$X = \big \{\hspace{0.05cm}x_1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.15cm} x_2\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.15cm} \text{...}\hspace{0.1cm} ,\hspace{0.15cm} x_{\mu}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.1cm} , \hspace{0.15cm} x_{M}\hspace{0.05cm}\big \}$$
with the symbolic range $|X| = M$ is generally:
- $$P_X(X) = [\hspace{0.05cm}p_1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.15cm} p_2\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} ...\hspace{0.1cm} ,\hspace{0.15cm} p_{\mu}\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.05cm}...\hspace{0.1cm} , \hspace{0.15cm} p_{M}\hspace{0.05cm}]\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The entropy (uncertainty) of this random variable is calculated according to the equation
- $$H(X) = {\rm E} \big [\log_2 \hspace{0.05cm} {1}/{P_X(X)} \big ]\hspace{0.05cm},$$
and always lies in the range $0 \le H(X) \le \log_2 \hspace{0.05cm} |X|$.
- The lower bound $H(X) = 0$ results when any probability $p_\mu = 1$ and all others are zero.
- The upper bound is to be derived here as in the lecture "Information Theory" by Gerhard Kramer at the TU Munich:
- By extending the above equation by $|X|$ in the numerator and denominator, using $\log_2 \hspace{0.05cm}x= \ln(x)/\ln(2)$, we obtain:
- $$H(X) = \frac{1}{{\rm ln}(2)}\cdot {\rm E} \left [{\rm ln} \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{|X| \cdot P_X(X)} \right ] + {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm}|X| \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
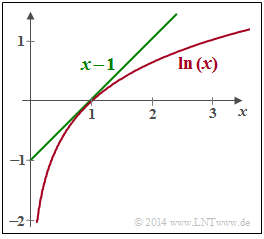
- As can be seen from the graph opposite, the estimation $\ln(x) \le x-1$ holds with the identity for $x=1$. Thus, it can be written:
- $$H(X) \le \frac{1}{{\rm ln}(2)}\cdot {\rm E} \left [\frac{1}{|X| \cdot P_X(X)} -1 \right ] + {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm}|X| \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- In Exercise 3.2 the expected value ${\rm E} \big [\log_2 \hspace{0.05cm} {1}/{P_X(X)} \big ] =|X|$ was calculated for the case $p_\mu \ne 0$ for all $\mu$ . Thus, the first term disappears and the known result is obtained:
- $$H(X) \le {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm}|X| \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Some preliminary remarks on 2D random variables.
- In particular, reference is made to the page Probability function and entropy.
- The same constellation is assumed here as in Exercise 3.2.
- The equation of the binary entropy function is:
- $$H_{\rm bin}(p) = p \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{p} + (1-p) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{1-p} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Questions
Solution
(1) Both statements are correct:
- If we set $p_3 = 0$ and formally $p_1 = p$ ⇒ $p_2 = 1- p$, we get the binary entropy function
- $$H_{\rm bin}(p) = p \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{p} + (1-p) \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1}{1-p} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) Only the proposed solution 1 is correct:
- One can also put the binary entropy function into the following form because of $\log(x) = \ln(x)/\ln(2)$ :
- $$H_{\rm bin}(p) = \frac{-1}{{\rm ln}(2)} \cdot \big [ p \cdot {\rm ln}(p) + (1-p) \cdot {\rm ln}(1-p) \big ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The first derivation leads to the result
- $$\frac {{\rm d}H_{\rm bin}(p)}{{\rm d}p} = \frac{-1}{{\rm ln}(2)} \cdot \big [ {\rm ln}(p) + p \cdot \frac{1}{p} - {\rm ln}(1-p) - (1-p) \cdot \frac{1}{1-p} \big ] = \frac{1}{{\rm ln}(2)} \cdot \big [ {\rm ln}(1-p) - {\rm ln}(p) \big ] = {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.1cm} \frac{1-p}{p} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
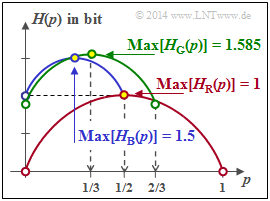
- By setting this derivative to zero, we obtain the abscissa value $p = 0.5$, which leads to the maximum of the entropy function: $H_{\rm bin}(p =0.5) = 1$ bit
⇒ the proposed solution 2 is wrong. - By differentiating again, one obtains for the second derivative
- $$\frac {{\rm d}^2H_{\rm bin}(p)}{{\rm d}p^2} = \frac{1}{{\rm ln}(2)} \cdot \left [ \frac{-1}{1-p} - \frac{1}{p} \right ] = \frac{-1}{{\rm ln}(2) \cdot p \cdot (1-p)} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This function is negative in the entire definition domain $0 ≤ p ≤ 1$ ⇒ $H_{\rm bin}(p)$ is concave ⇒ the proposed solution 1 is correct.
(3) Propositions 1 and 2 are correct here:
- For $p = 0$ one obtains the probability function $P_X(X) = \big [\hspace{0.05cm}0\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.15cm} 1/2\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.15cm} 1/2 \hspace{0.05cm} \big ]$ ⇒ $H(X) = 1$ bit.
- The maximum under the condition $p_3 = 1/2$ is obtained for $p_1 = p_2 = 1/4$:
- $$P_X(X) = \big [\hspace{0.05cm}1/4\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.05cm} 1/4\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.05cm} 1/2 \hspace{0.05cm} \big ] \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm Max} \ [H_{\rm B}(p)] = 1.5 \ \rm bit \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- In compact form, $H_{\rm B}(p)$ with the constraint $0 ≤ p ≤ 1/2$ can be represented as follows:
- $$H_{\rm B}(p) = 1.0\,{\rm bit} + {1}/{2} \cdot H_{\rm bin}(2p) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) The first and last statements are correct here::
- The green curve with $p = 1/3$ also contains the equal distribution of all probabilities
- $$ {\rm Max} \ [H_{\rm G}(p)] = \log_2 (3)\ \text{bit}.$$
- In general, the entire curve in the range $0 ≤ p ≤ 2/3$ can be expressed as follows:
- $$H_{\rm G}(p) = H_{\rm G}(p= 0) + {2}/{3} \cdot H_{\rm bin}(3p/2) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- From the graph on the information page, one can also see that the following condition must be fulfilled:
- $$H_{\rm G}(p = 0) + {2}/{3}= {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.01cm} (3) \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} H_{\rm G}(p= 0) = 1.585 - 0.667 = 0.918 \,{\rm bit} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The second suggested solution is therefore wrong. The same result can be obtained with the equation
- $$H_{\rm G}(p = 0) = {1}/{3} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.01cm} (3) +{2}/{3} \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.01cm} (3/2) = {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.01cm} (3) -2/3 \cdot {\rm log}_2 \hspace{0.01cm} (2) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$