Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 1.6: Rectangular-in-Time Low-Pass Filter"
From LNTwww
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
| − | { | + | {Let the input signal $x(t)$ be a rectangle symmetric about $t = 0$ of duration $T = 2 \ \rm ms$ and height $1 \, \rm V$. Let $τ = 0$ hold. <br>Which statements are true? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - $y(t)$ | + | - $y(t)$ is rechteckförmig. |
| − | + $y(t)$ | + | + $y(t)$ is dreieckförmig. |
| − | - $y(t)$ | + | - $y(t)$ is trapezförmig. |
+ Der Maximalwert von $y(t)$ beträgt $ 1\hspace{0.05cm} \rm V$. | + Der Maximalwert von $y(t)$ beträgt $ 1\hspace{0.05cm} \rm V$. | ||
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true, if $x(t)$ has a rectangle width of $T = 1 \ \rm ms$ ? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - $y(t)$ ist | + | - $y(t)$ ist rectangular. |
| − | - $y(t)$ ist | + | - $y(t)$ ist triangular. |
| − | + $y(t)$ ist | + | + $y(t)$ ist trapezoidal. |
| − | - | + | - The maximum value of $y(t)$ is $1\hspace{0.05cm} \rm V$. |
| − | { | + | {The following still holds: $τ = 0$. Compute the output signal $z(t)$, if $x(t)$ jumps from zero to $1\hspace{0.05cm} \rm V$ at time $t = 0$ . <br>Which statements are true? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - $z(t)$ | + | - $z(t)$ is an even function of time. |
| − | + $z(t)$ | + | + $z(t)$ has a jump discontinuity at $t = 0$ . |
| − | + | + | + At time $t = 0$ , $z(t) = 0$ holds. |
| − | + | + | + For $t > 1 \ \rm ms$ , $z(t) = 0$ is true. |
| − | { | + | {What is the curve shape of $z(t)$ in response to the step-shaped input signal $x(t)$, if the runtime is $τ =1 \hspace{0.05cm} \rm ms$ ? <br>What signal value occurs at $t =1 \hspace{0.05cm} \rm ms$ ? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$z(t = 1 \rm \ ms) =\ $ { 0.5 3% } $\ \rm V$ | $z(t = 1 \rm \ ms) =\ $ { 0.5 3% } $\ \rm V$ | ||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' The condition $H(f = 0) = 1$ means that the area of the impulse response is equal to $1$ . From this it follows that: |
:$$k = {1}/{\Delta t} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 500\hspace{0.1cm}{ 1/{\rm s}}} .$$ | :$$k = {1}/{\Delta t} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 500\hspace{0.1cm}{ 1/{\rm s}}} .$$ | ||
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' <u>Approaches 2 and 4</u> are correct: |
| − | * | + | *The output signal $y(t)$ is obtained as the convolution product of $x(t)$ and $h(t)$. |
| − | * | + | *Convolution of two rectangles of equal width results in a triangle with its maximum at $t = 0$: |
:$$y(t = 0 ) = 1\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V}\cdot \int_{ - 1\,{\rm ms} }^{ 1\,{\rm ms} } {k \hspace{0.1cm}}{\rm d}\tau = | :$$y(t = 0 ) = 1\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V}\cdot \int_{ - 1\,{\rm ms} }^{ 1\,{\rm ms} } {k \hspace{0.1cm}}{\rm d}\tau = | ||
1\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V}\cdot \int_{ - 1\,{\rm ms} }^{ 1\,{\rm ms} } {\frac{1}{2\,{\rm ms}} \hspace{0.1cm}}{\rm d}\tau= 1\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V}.$$ | 1\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V}\cdot \int_{ - 1\,{\rm ms} }^{ 1\,{\rm ms} } {\frac{1}{2\,{\rm ms}} \hspace{0.1cm}}{\rm d}\tau= 1\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V}.$$ | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
| − | [[File: P_ID859__LZI_A_1_6_c.png | | + | [[File: P_ID859__LZI_A_1_6_c.png | Trapezoid pulse| rechts|frame]] |
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' <u>Approach 3</u> is correct: |
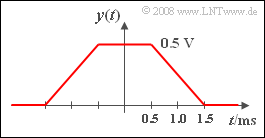
| − | * | + | *Convolution of two rectangles of different widths results in the trapezoidal output signal as shown in the sketch. |
| − | * | + | *The maximum value occurs in the constant range of $-0.5 \hspace{0.05cm} \rm ms$ to $+0.5 \hspace{0.05cm} \rm ms$ and is |
:$$y(t = 0 ) = 1\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V} \cdot \frac{1}{2\,{\rm | :$$y(t = 0 ) = 1\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V} \cdot \frac{1}{2\,{\rm | ||
ms}} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot 1\,{\rm ms} = 0.5\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V}.$$ | ms}} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot 1\,{\rm ms} = 0.5\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V}.$$ | ||
Revision as of 16:54, 7 September 2021
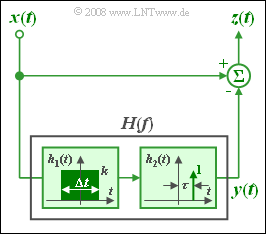
We consider below the constellation shown in the graph:
- The frequency response $H(f) = H_1(f) · H_2(f)$ in the lower branch is determined by the impulse responses of its two subcomponents.
- Here, $h_1(t)$ is constantly equal to $k$ in the reange from $-1\ \rm ms$ to $+1\ \rm ms$ and zero outside.
- At the range limits, half the value is valid in each case.
- The time variable drawn in the figure is thus $Δt = 2 \ \rm ms$.
The impulse response of the second system function $H_2(f)$ is:
- $$h_2(t) = \delta(t - \tau).$$
The frequency response between the signals $x(t)$ and $z(t)$ is of high-pass character and generally:
- $$H_{\rm HP}(f) = 1 - H_1(f) \cdot {\rm e}^{-{\rm j\hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm}2 \pi}f \tau}.$$
- For the subtasks (1) to (4) the following holds: $τ = 0$ ⇒ $H(f) = H_1(f)$.
- However, using $τ = 0$ this can also be formulated as follows $(Δt = 2 \ \rm ms)$:
- $$H_{\rm HP}(f) = 1 - {\rm si}( \pi \cdot {\rm \Delta}t \cdot f).$$
- With no effect on the solution of the problem, note that this equation is not applicable for $τ ≠ 0$ because of:
- $$|H_{\rm HP}(f)|\hspace{0.09cm} \ne \hspace{0.09cm}1 - |H_1(f)| .$$
Please note:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Some Low-Pass Functions in Systems Theory.
- Reference is made especially to the page Slit low-pass filter.
Questions
Solution
(1) The condition $H(f = 0) = 1$ means that the area of the impulse response is equal to $1$ . From this it follows that:
- $$k = {1}/{\Delta t} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 500\hspace{0.1cm}{ 1/{\rm s}}} .$$
(2) Approaches 2 and 4 are correct:
- The output signal $y(t)$ is obtained as the convolution product of $x(t)$ and $h(t)$.
- Convolution of two rectangles of equal width results in a triangle with its maximum at $t = 0$:
- $$y(t = 0 ) = 1\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V}\cdot \int_{ - 1\,{\rm ms} }^{ 1\,{\rm ms} } {k \hspace{0.1cm}}{\rm d}\tau = 1\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V}\cdot \int_{ - 1\,{\rm ms} }^{ 1\,{\rm ms} } {\frac{1}{2\,{\rm ms}} \hspace{0.1cm}}{\rm d}\tau= 1\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V}.$$
(3) Approach 3 is correct:
- Convolution of two rectangles of different widths results in the trapezoidal output signal as shown in the sketch.
- The maximum value occurs in the constant range of $-0.5 \hspace{0.05cm} \rm ms$ to $+0.5 \hspace{0.05cm} \rm ms$ and is
- $$y(t = 0 ) = 1\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V} \cdot \frac{1}{2\,{\rm ms}} \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot 1\,{\rm ms} = 0.5\hspace{0.05cm}{\rm V}.$$
(4) Richtig sind die Lösungsvorschläge 2, 3 und 4:
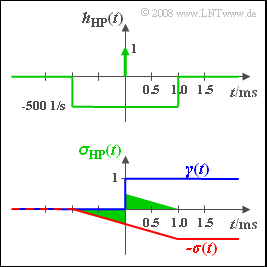
- Die Impulsantwort des Gesamtsystems lautet: $h_{\rm HP}(t) = \delta(t) - h(t).$ Beide Anteile sind in der Skizze dargestellt.
- Durch Integration über $h_{\rm HP}(t)$ und Multiplikation mit $1 \hspace{0.05cm} \rm V$ kommt man zum gesuchten Signal $z(t)$.
In der unteren Skizze sind dargestellt:
- das Integral über $δ(t)$ blau,
- die Funktion $-σ(t)$ rot, und
- das gesamte Signal $z(t)$ grün.
- $z(t)$ ist eine ungerade Funktion in $t$ mit einer Sprungstelle bei $t = 0$: Der Signalwert bei $t = 0$ liegt genau in der Mitte zwischen dem links– und dem rechteckseitigem Grenzwert und ist somit Null.
- Für $t > 1 \hspace{0.05cm} \rm ms$ gilt ebenfalls $z(t) = 0$, da das Gesamtsystem eine Hochpass-Charakteristik aufweist.
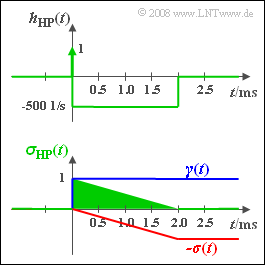
(5) Die untere Grafik zeigt die resultierende Impulsantwort $h_{\rm HP}(t)$ und die Sprungantwort $σ_{\rm HP}(t)$.
- Diese springt bei $t = 0$ auf $1$ und klingt bis zum Zeitpunkt $t = 2 \hspace{0.05cm} \rm ms$ auf den Endwert "Null" ab.
- Zum Zeitpunkt $t = 1\ \rm ms$ ergibt sich $σ_{\rm HP}(t) = 0.5$.
- Das Signal $z(t)$ ist formgleich mit der Sprungantwort $σ_{\rm HP}(t)$, ist jedoch noch mit $1 \hspace{0.05cm} \rm V$ zu multiplizieren.
- Der gesuchte Signalwert zur Zeit $t_1 = 1 \hspace{0.05cm} \rm ms$ ergibt sich also zu $z(t_1) \; \rm \underline{ = \ 0.5 \: {\rm V}}$.