Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.15: Block Error Probability with AWGN"
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
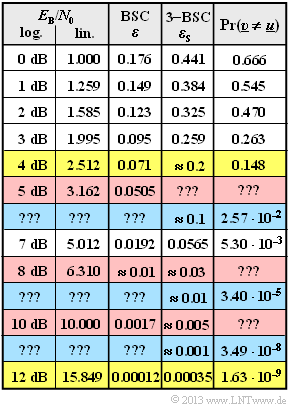
[[File:P_ID2571__KC_A_2_15neu.png|right|frame|Incomplete table of results]] | [[File:P_ID2571__KC_A_2_15neu.png|right|frame|Incomplete table of results]] | ||
| − | Using the example of $\rm RSC \, (7, \, 3, \, 5)_8$ with | + | Using the example of $\rm RSC \, (7, \, 3, \, 5)_8$ with parameters |
| − | * $n = 7$ (number of code symbols) | + | * $n = 7$ $($number of code symbols$)$, |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | * $k =3$ $($number of information symbols$)$, | ||
| − | the calculation of the block error probability in [[Channel_Coding/Error_Probability_and_Areas_of_Application#Block_error_probability_for_RSC_and_BDD|"Bounded Distance Decoding"]] (BDD) shall be shown. The corresponding equation is: | + | * $t = 2$ $($correction capability$)$. |
| − | :$${\rm Pr( | + | |
| + | |||
| + | the calculation of the block error probability in [[Channel_Coding/Error_Probability_and_Areas_of_Application#Block_error_probability_for_RSC_and_BDD|"Bounded Distance Decoding"]] $\rm (BDD)$ shall be shown. The corresponding equation is: | ||
| + | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} = {\rm Pr}(\underline{v} \ne \underline{u}) = | ||
\sum_{f = t + 1}^{n} {n \choose f} \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^f \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{n-f} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \sum_{f = t + 1}^{n} {n \choose f} \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^f \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{n-f} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | The calculation is performed for the [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Gaussian_Distributed_Random_Variables#Exceedance_probability|"AWGN channel" | + | ⇒ The calculation is performed for the [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Gaussian_Distributed_Random_Variables#Exceedance_probability|"AWGN channel" |
| − | ]] characterized by the parameter $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ | + | ]] characterized by the parameter $E_{\rm B}/N_0$: |
*The quotient $E_{\rm B}/{N_0}$ can be expressed by the relation | *The quotient $E_{\rm B}/{N_0}$ can be expressed by the relation | ||
:$$\varepsilon = {\rm Q} \big (\sqrt{{2 \cdot R \cdot E_{\rm B}}/{N_0}} \big ) $$ | :$$\varepsilon = {\rm Q} \big (\sqrt{{2 \cdot R \cdot E_{\rm B}}/{N_0}} \big ) $$ | ||
| − | into the [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Binary_Symmetric_Channel_.E2.80. 93_BSC|"BSC model"]] where $R$ denotes the code rate $($here: $R = 3/7)$ and ${\rm Q}(x)$ indicates the [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Gaussian_Distributed_Random_Variables#Exceedance_probability|"complementary Gaussian error integral"]] | + | :into the [[Channel_Coding/Channel_Models_and_Decision_Structures#Binary_Symmetric_Channel_.E2.80. 93_BSC|"BSC model"]] where $R$ denotes the code rate $($here: $R = 3/7)$ and ${\rm Q}(x)$ indicates the [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Gaussian_Distributed_Random_Variables#Exceedance_probability|"complementary Gaussian error integral"]]. |
| − | *But since in the considered code the symbols come from $\rm GF(2^3)$ | + | |
| − | *For the | + | *But since in the considered code the symbols come from $\rm GF(2^3)$, the BSC model with parameter $\varepsilon$ must also still be adapted to the task. |
| + | |||
| + | *For the falsification probability of the [[Channel_Coding/Error_Probability_and_Areas_of_Application#Block_error_probability_for_RSC_and_BDD|"''m''– BSC" model]] applies: | ||
:$$\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 1 - (1 - \varepsilon)^m | :$$\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 1 - (1 - \varepsilon)^m | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | :Here it is to be set $m = 3$ $($three bits per code symbol$)$. | ||
| − | For some $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ values the results are entered in the table above. The two rows with yellow background are briefly explained here: | + | ⇒ For some $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ values the results are entered in the table above. The two rows with yellow background are briefly explained here: |
| − | * For $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} = 4 \ \rm dB$ we get $\varepsilon \approx {\rm Q}(1.47) \approx 0.071$ and $\varepsilon_{\rm S} \approx 0.2$. The block error probability here can most easily be calculated using the complement: | + | * For $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} = 4 \ \rm dB$ we get $\varepsilon \approx {\rm Q}(1.47) \approx 0.071$ and $\varepsilon_{\rm S} \approx 0.2$. The block error probability here can most easily be calculated using the complement: |
| − | :$${\rm Pr( | + | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} = 1 - \left [ {7 \choose 0} \cdot 0.8^7 + {7 \choose 1} \cdot 0.2 \cdot 0.8^6 + {7 \choose 2} \cdot 0.2^2 \cdot 0.8^5\right ] |
\approx 0.148 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \approx 0.148 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * For $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} = 12 \ \rm dB$ one gets $\varepsilon \approx 1.2 \cdot 10^{-4}$ and $\varepsilon_{\rm S} \approx 3.5 \cdot 10^{-4}$. With this very small | + | |
| − | :$${\rm Pr( | + | * For $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} = 12 \ \rm dB$ one gets $\varepsilon \approx 1.2 \cdot 10^{-4}$ and $\varepsilon_{\rm S} \approx 3.5 \cdot 10^{-4}$. With this very small falsification probability, the $f = 3$ term dominates, and we obtain: |
| + | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \approx {7 \choose 3} \cdot (3.5 \cdot 10^{-4})^3 \cdot (1- 3.5 \cdot 10^{-4})^4 | ||
\approx 1.63 \cdot 10^{-9} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \approx 1.63 \cdot 10^{-9} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | ⇒ You are to calculate the block error probabilities for the rows highlighted in red $(10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} = 5 \ \rm dB, \ 8 \rm dB$, $10 \ \rm dB)$. | |
| − | *The rows with blue background show some results of [[Aufgaben:Exercise_2.15Z:_Block_Error_Probability_once_more|"Exercise 2.15Z"]]. There ${\rm Pr}(\underline{v} ≠ \underline{u})$ is calculated for $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 10\%, \ 1\%$ $0.1\%$. | + | :*The rows with blue background show some results of [[Aufgaben:Exercise_2.15Z:_Block_Error_Probability_once_more|"Exercise 2.15Z"]]. There ${\rm Pr}(\underline{v} ≠ \underline{u})$ is calculated for $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 10\%, \ 1\%$ $0.1\%$. |
| − | *In subtasks '''(4)''' and '''(5)''' you are to establish the relationship between the | + | :*In subtasks '''(4)''' and '''(5)''' you are to establish the relationship between the quantity $\varepsilon_{\rm S}$ and the AWGN parameter $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ thus completing the above table. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 42: | Line 46: | ||
| + | <u>Hints:</u> | ||
| + | * The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Channel_Coding/Error_Probability_and_Areas_of_Application| "Error Probability and Application Areas"]]. | ||
| − | + | * We refer you here to the two interactive HTML5/JavaScript applets | |
| − | + | :*[[Applets:Complementary_Gaussian_Error_Functions|"Complementary Gaussian error functions"]], and | |
| − | * We refer you here to the two interactive applets | + | :*[[Applets:Binomial_and_Poisson_Distribution_(Applet)|"Binomial and Poisson Distribution"]]. |
| − | : | ||
| − | : | ||
| Line 57: | Line 61: | ||
{What is the block error probability for $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 5 \ \rm dB}$? | {What is the block error probability for $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 5 \ \rm dB}$? | ||
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | ${\rm Pr( | + | ${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \ = \ ${ 6.66 3% } $\ \cdot 10^{-2}$ |
{What is the block error probability for $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 8 \ \rm dB}$? | {What is the block error probability for $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 8 \ \rm dB}$? | ||
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | ${\rm Pr( | + | ${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \ = \ ${ 8.63 3% } $\ \cdot 10^{-4}$ |
{What is the block error probability for $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 10 \ \rm dB}$? | {What is the block error probability for $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 10 \ \rm dB}$? | ||
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | ${\rm Pr( | + | ${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \ = \ ${ 4.3 3% } $\ \cdot 10^{-6}$ |
| − | {How is $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.1$ related to $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0}$ ? | + | {How is $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.1$ related to $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0}$ ? <u>Note:</u> Use the given applet to calculate ${\rm Q}(x)$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 10^{-1} \text{:} \hspace{0.4cm} 10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} \ = \ ${ 5.87 3% } $\ \rm dB$ | $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 10^{-1} \text{:} \hspace{0.4cm} 10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} \ = \ ${ 5.87 3% } $\ \rm dB$ | ||
| − | {Find also the $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ values $($in $\rm dB)$ for $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.01$ and $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.001$. Complete the table | + | {Find also the $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ values $($in $\rm dB)$ for $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.01$ and $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.001$. Complete the table. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 10^{-2} \text{:} \hspace{0.4cm} 10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} \ = \ $ { 9.32 3% } $\ \rm dB$ | $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 10^{-2} \text{:} \hspace{0.4cm} 10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} \ = \ $ { 9.32 3% } $\ \rm dB$ | ||
| Line 79: | Line 83: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' From the table on the information page, the BSC parameter $\varepsilon = 0.0505$ can be read. | + | '''(1)''' From the table on the information page, the BSC parameter $\varepsilon = 0.0505$ can be read. |
| − | *This gives $\varepsilon_{\rm S}$ for the symbol | + | *This gives $\varepsilon_{\rm S}$ for the symbol error probability with $m = 3$: |
:$$1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S} = (1 - 0.0505)^3 \approx 0.856 | :$$1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S} = (1 - 0.0505)^3 \approx 0.856 | ||
\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| Line 86: | Line 90: | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | *The fastest way to calculate the block error probability here | + | *The fastest way to calculate the block error probability is here to use the formula |
| − | :$${\rm Pr( | + | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 1 - {\rm Pr}(f=0) - {\rm Pr}(f=1) - {\rm Pr}(f=2) = 1 - 1 \cdot 0.856^7 - |
7 \cdot 0.144^1 \cdot 0.856^6 - 21 \cdot 0.144^2 \cdot 0.856^5$$ | 7 \cdot 0.144^1 \cdot 0.856^6 - 21 \cdot 0.144^2 \cdot 0.856^5$$ | ||
| − | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm Pr( | + | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm Pr(block\:error)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {\rm Pr}(\underline{v} \ne \underline{u}) =1 - 0.3368 - 0.3965 - 0.2001 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{=0.0666} |
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(2)''' Following the same calculation procedure as in subtask '''(1)''', | + | '''(2)''' Following the same calculation procedure as in subtask '''(1)''', we obtain with $\varepsilon_{\rm S} \approx 0.03 \ \Rightarrow \ 1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.97$: |
| − | :$${\rm Pr( | + | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} |
\hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 1 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 1 \cdot 0.97^7 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} | \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 1 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 1 \cdot 0.97^7 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} | ||
7 \cdot 0.03^1 \cdot 0.97^6 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 21 \cdot 0.03^2 \cdot 0.97^5 =1 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.8080 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.1749\hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.0162= 1 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.9991 = 9 \cdot 10^{-4} | 7 \cdot 0.03^1 \cdot 0.97^6 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 21 \cdot 0.03^2 \cdot 0.97^5 =1 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.8080 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.1749\hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.0162= 1 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.9991 = 9 \cdot 10^{-4} | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | *You can see that here the difference between two numbers of almost the same size must be formed, so that the result could be affected by an error. | + | *You can see that here the difference between two numbers of almost the same size must be formed, so that the result could be affected by an error. |
| + | |||
*Therefore we still calculate the following quantities: | *Therefore we still calculate the following quantities: | ||
:$${\rm Pr}(f=3) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} | :$${\rm Pr}(f=3) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} | ||
| Line 107: | Line 112: | ||
:$${\rm Pr}(f=5) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} | :$${\rm Pr}(f=5) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} | ||
{7 \choose 5} \cdot \varepsilon_{\rm S}^5 \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^2 = 21 \cdot 0.03^5 \cdot 0.97^2 = 0.005 \cdot 10^{-4}$$ | {7 \choose 5} \cdot \varepsilon_{\rm S}^5 \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^2 = 21 \cdot 0.03^5 \cdot 0.97^2 = 0.005 \cdot 10^{-4}$$ | ||
| − | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm Pr( | + | :$$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm Pr(block\:error)} = {\rm Pr}(\underline{v} \ne \underline{u}) \approx {\rm Pr}(f=3) + {\rm Pr}(f=4) + {\rm Pr}(f=5) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{=8.63 \cdot 10^{-4}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | *The terms for $f = 6$ and $f = 7$ can be omitted here. They do not provide a relevant contribution. | + | *The terms for $f = 6$ and $f = 7$ can be omitted here. They do not provide a relevant contribution. |
| − | '''(3)''' Here $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.005 \ \Rightarrow \ 1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.995$ is already given in the table. | + | '''(3)''' Here $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.005 \ \Rightarrow \ 1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.995$ is already given in the table. |
| − | *The (by far) dominant term in the calculation of the block error probability is ${\rm Pr}(f = 3)$: | + | *The (by far) dominant term in the calculation of the block error probability is ${\rm Pr}(f = 3)$: |
| − | :$${\rm Pr( | + | :$${\rm Pr(block\:error)} = {\rm Pr}(\underline{v} \ne \underline{u}) \approx {\rm Pr}(f=3) = {7 \choose 3} \cdot 0.005^3 \cdot 0.995^4 |
\hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 4.3 \cdot 10^{-6}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 4.3 \cdot 10^{-6}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(4)''' For the BSC parameter $\varepsilon$ holds with $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.1$: | + | '''(4)''' For the BSC parameter $\varepsilon$ holds with $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.1$: |
:$$\varepsilon = 1 -(1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{1/3} = 1 - 0.9^{1/3} \approx 0.0345 | :$$\varepsilon = 1 -(1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{1/3} = 1 - 0.9^{1/3} \approx 0.0345 | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | *The relation between $\varepsilon$ and $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ is: | + | *The relation between $\varepsilon$ and $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ is: |
:$$\varepsilon = {\rm Q}(x)\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.5cm} x = \sqrt{2 \cdot R \cdot E_{\rm B}/N_0}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$\varepsilon = {\rm Q}(x)\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.5cm} x = \sqrt{2 \cdot R \cdot E_{\rm B}/N_0}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | *The inverse $x = {\rm Q}^{-1}(0.0345)$ is obtained with the applet [[Applets:QFunction|"Complementary Gaussian Error Functions"]] to $x = 1.82$. | + | *The inverse $x = {\rm Q}^{-1}(0.0345)$ is obtained with the applet [[Applets:QFunction|"Complementary Gaussian Error Functions"]] to $x = 1.82$. This further gives: |
| − | |||
:$$E_{\rm B}/N_0 = \frac{x^2}{2R} = \frac{1.82^2}{2R \cdot 3/7} \approx 3.864 | :$$E_{\rm B}/N_0 = \frac{x^2}{2R} = \frac{1.82^2}{2R \cdot 3/7} \approx 3.864 | ||
\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| Line 136: | Line 140: | ||
'''(5)''' After the same calculation one obtains | '''(5)''' After the same calculation one obtains | ||
| − | * | + | * for $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 10^{-2} \ \Rightarrow \ \varepsilon \approx 0.33 \cdot 10^{-2} \ \Rightarrow \ x = {\rm Q}^{-1}(\varepsilon) = 2.71$ |
:$$E_{\rm B}/N_0 = \frac{x^2}{2R} = \frac{2.71^2}{2R \cdot 3/7} \approx 8.568 | :$$E_{\rm B}/N_0 = \frac{x^2}{2R} = \frac{2.71^2}{2R \cdot 3/7} \approx 8.568 | ||
\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
| Line 148: | Line 152: | ||
\hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 11.3 \,\, {\rm dB}} \hspace{0.05cm}. $$ | \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 11.3 \,\, {\rm dB}} \hspace{0.05cm}. $$ | ||
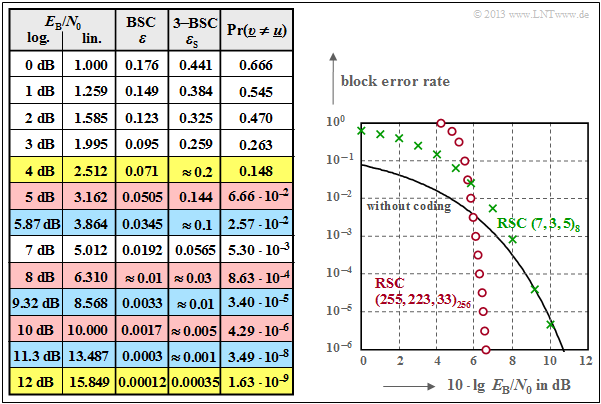
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:EN_KC_A_2_15e.ng.png|right|frame|Results for $\rm RSC \, (7, \, 3, \, 5)_8$ decoding]] |
| − | + | ||
| − | The graph shows the course of the block error probability as | + | The graph shows |
| + | *the course of the block error probability as function of $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0}$, | ||
| + | |||
| + | * and the completely filled result table. | ||
| − | |||
| + | One can see the clearly less favorable (asymptotic) behavior of the (green) code $\rm RSC \, (7, \, 5, \, 3)_8$ compared to the (red) comparison code $\rm RSC \, (255, \, 223, \, 33)_8$: | ||
| − | + | # For abscissa values smaller than $10 \ \rm dB$ the result is even worse than without coding. | |
| − | + | # It should be pointed out again that the $\rm RSC \, (7, \, 3, \, 5)_8$ has only little practical meaning. | |
| − | + | # It was chosen for this exercise only to be able to demonstrate with reasonable effort the calculation of the block error probability for "Bounded Distance Decoding" $\rm (BDD)$. | |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
[[Category:Channel Coding: Exercises|^2.6 Block Error Probability of RS Codes^]] | [[Category:Channel Coding: Exercises|^2.6 Block Error Probability of RS Codes^]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:12, 13 March 2023
Using the example of $\rm RSC \, (7, \, 3, \, 5)_8$ with parameters
- $n = 7$ $($number of code symbols$)$,
- $k =3$ $($number of information symbols$)$,
- $t = 2$ $($correction capability$)$.
the calculation of the block error probability in "Bounded Distance Decoding" $\rm (BDD)$ shall be shown. The corresponding equation is:
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} = {\rm Pr}(\underline{v} \ne \underline{u}) = \sum_{f = t + 1}^{n} {n \choose f} \cdot {\varepsilon_{\rm S}}^f \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{n-f} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
⇒ The calculation is performed for the "AWGN channel" characterized by the parameter $E_{\rm B}/N_0$:
- The quotient $E_{\rm B}/{N_0}$ can be expressed by the relation
- $$\varepsilon = {\rm Q} \big (\sqrt{{2 \cdot R \cdot E_{\rm B}}/{N_0}} \big ) $$
- into the "BSC model" where $R$ denotes the code rate $($here: $R = 3/7)$ and ${\rm Q}(x)$ indicates the "complementary Gaussian error integral".
- But since in the considered code the symbols come from $\rm GF(2^3)$, the BSC model with parameter $\varepsilon$ must also still be adapted to the task.
- For the falsification probability of the "m– BSC" model applies:
- $$\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 1 - (1 - \varepsilon)^m \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Here it is to be set $m = 3$ $($three bits per code symbol$)$.
⇒ For some $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ values the results are entered in the table above. The two rows with yellow background are briefly explained here:
- For $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} = 4 \ \rm dB$ we get $\varepsilon \approx {\rm Q}(1.47) \approx 0.071$ and $\varepsilon_{\rm S} \approx 0.2$. The block error probability here can most easily be calculated using the complement:
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} = 1 - \left [ {7 \choose 0} \cdot 0.8^7 + {7 \choose 1} \cdot 0.2 \cdot 0.8^6 + {7 \choose 2} \cdot 0.2^2 \cdot 0.8^5\right ] \approx 0.148 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- For $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} = 12 \ \rm dB$ one gets $\varepsilon \approx 1.2 \cdot 10^{-4}$ and $\varepsilon_{\rm S} \approx 3.5 \cdot 10^{-4}$. With this very small falsification probability, the $f = 3$ term dominates, and we obtain:
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \approx {7 \choose 3} \cdot (3.5 \cdot 10^{-4})^3 \cdot (1- 3.5 \cdot 10^{-4})^4 \approx 1.63 \cdot 10^{-9} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
⇒ You are to calculate the block error probabilities for the rows highlighted in red $(10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0} = 5 \ \rm dB, \ 8 \rm dB$, $10 \ \rm dB)$.
- The rows with blue background show some results of "Exercise 2.15Z". There ${\rm Pr}(\underline{v} ≠ \underline{u})$ is calculated for $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 10\%, \ 1\%$ $0.1\%$.
- In subtasks (4) and (5) you are to establish the relationship between the quantity $\varepsilon_{\rm S}$ and the AWGN parameter $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ thus completing the above table.
Hints:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter "Error Probability and Application Areas".
- We refer you here to the two interactive HTML5/JavaScript applets
Questions
Solution
- This gives $\varepsilon_{\rm S}$ for the symbol error probability with $m = 3$:
- $$1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S} = (1 - 0.0505)^3 \approx 0.856 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \varepsilon_{\rm S} \approx 0.144 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The fastest way to calculate the block error probability is here to use the formula
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 1 - {\rm Pr}(f=0) - {\rm Pr}(f=1) - {\rm Pr}(f=2) = 1 - 1 \cdot 0.856^7 - 7 \cdot 0.144^1 \cdot 0.856^6 - 21 \cdot 0.144^2 \cdot 0.856^5$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm Pr(block\:error)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {\rm Pr}(\underline{v} \ne \underline{u}) =1 - 0.3368 - 0.3965 - 0.2001 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{=0.0666} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) Following the same calculation procedure as in subtask (1), we obtain with $\varepsilon_{\rm S} \approx 0.03 \ \Rightarrow \ 1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.97$:
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} 1 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 1 \cdot 0.97^7 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 7 \cdot 0.03^1 \cdot 0.97^6 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 21 \cdot 0.03^2 \cdot 0.97^5 =1 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.8080 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.1749\hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.0162= 1 \hspace{-0.05cm}-\hspace{-0.05cm} 0.9991 = 9 \cdot 10^{-4} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- You can see that here the difference between two numbers of almost the same size must be formed, so that the result could be affected by an error.
- Therefore we still calculate the following quantities:
- $${\rm Pr}(f=3) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {7 \choose 3} \cdot \varepsilon_{\rm S}^3 \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^4 = 35 \cdot 0.03^3 \cdot 0.97^4 = 8.366 \cdot 10^{-4}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $${\rm Pr}(f=4) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {7 \choose 4} \cdot \varepsilon_{\rm S}^4 \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^3 = 35 \cdot 0.03^4 \cdot 0.97^3 = 0.259 \cdot 10^{-4}\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $${\rm Pr}(f=5) \hspace{-0.15cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.15cm} {7 \choose 5} \cdot \varepsilon_{\rm S}^5 \cdot (1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^2 = 21 \cdot 0.03^5 \cdot 0.97^2 = 0.005 \cdot 10^{-4}$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm Pr(block\:error)} = {\rm Pr}(\underline{v} \ne \underline{u}) \approx {\rm Pr}(f=3) + {\rm Pr}(f=4) + {\rm Pr}(f=5) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{=8.63 \cdot 10^{-4}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The terms for $f = 6$ and $f = 7$ can be omitted here. They do not provide a relevant contribution.
(3) Here $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.005 \ \Rightarrow \ 1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.995$ is already given in the table.
- The (by far) dominant term in the calculation of the block error probability is ${\rm Pr}(f = 3)$:
- $${\rm Pr(block\:error)} = {\rm Pr}(\underline{v} \ne \underline{u}) \approx {\rm Pr}(f=3) = {7 \choose 3} \cdot 0.005^3 \cdot 0.995^4 \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 4.3 \cdot 10^{-6}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) For the BSC parameter $\varepsilon$ holds with $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 0.1$:
- $$\varepsilon = 1 -(1 - \varepsilon_{\rm S})^{1/3} = 1 - 0.9^{1/3} \approx 0.0345 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The relation between $\varepsilon$ and $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ is:
- $$\varepsilon = {\rm Q}(x)\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.5cm} x = \sqrt{2 \cdot R \cdot E_{\rm B}/N_0}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The inverse $x = {\rm Q}^{-1}(0.0345)$ is obtained with the applet "Complementary Gaussian Error Functions" to $x = 1.82$. This further gives:
- $$E_{\rm B}/N_0 = \frac{x^2}{2R} = \frac{1.82^2}{2R \cdot 3/7} \approx 3.864 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm}(E_{\rm B}/N_0) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 5.87 \,\, {\rm dB}} \hspace{0.05cm}. $$
(5) After the same calculation one obtains
- for $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 10^{-2} \ \Rightarrow \ \varepsilon \approx 0.33 \cdot 10^{-2} \ \Rightarrow \ x = {\rm Q}^{-1}(\varepsilon) = 2.71$
- $$E_{\rm B}/N_0 = \frac{x^2}{2R} = \frac{2.71^2}{2R \cdot 3/7} \approx 8.568 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm}(E_{\rm B}/N_0) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 9.32 \,\, {\rm dB}} \hspace{0.05cm}, $$
- for $\varepsilon_{\rm S} = 10^{-3} \ \Rightarrow \ \varepsilon \approx 0.33 \cdot 10^{-3} \ \Rightarrow \ x = {\rm Q}^{-1}(\varepsilon) = 3.4$:
- $$E_{\rm B}/N_0 = \frac{x^2}{2R} = \frac{3.4^2}{2R \cdot 3/7} \approx 13.487 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.15cm}(E_{\rm B}/N_0) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 11.3 \,\, {\rm dB}} \hspace{0.05cm}. $$
The graph shows
- the course of the block error probability as function of $10 \cdot \lg {E_{\rm B}/N_0}$,
- and the completely filled result table.
One can see the clearly less favorable (asymptotic) behavior of the (green) code $\rm RSC \, (7, \, 5, \, 3)_8$ compared to the (red) comparison code $\rm RSC \, (255, \, 223, \, 33)_8$:
- For abscissa values smaller than $10 \ \rm dB$ the result is even worse than without coding.
- It should be pointed out again that the $\rm RSC \, (7, \, 3, \, 5)_8$ has only little practical meaning.
- It was chosen for this exercise only to be able to demonstrate with reasonable effort the calculation of the block error probability for "Bounded Distance Decoding" $\rm (BDD)$.