Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.5: "Binomial" or "Poisson"?"
| (22 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Poisson_Distribution |
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID104__Sto_A_2_5_neu.png|right| | + | [[File:P_ID104__Sto_A_2_5_neu.png|right|frame|Characteristics of $z_1$ and $z_2$]] |
| − | + | Consider two discrete random variables $z_1$ and $z_2$ that can take (at least) all integer values between $0$ and $5$ (including these limits). | |
| − | + | The probabilities of these random variables are given in the adjacent table. However, one of the two random variables is not limited to the given range of values. | |
| − | + | Furthermore it is known that | |
| − | * | + | * one of the variables is binomially distributed, and |
| + | * the other describes a Poisson distribution. | ||
| − | |||
| + | However, it is not known which of the two variables $(z_1$ or $z_2)$ is binomially distributed and which is Poisson distributed. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | |
| + | |||
| + | Hints: | ||
| + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Poisson_Distribution|Poisson distribution]]. | ||
| + | *But also refers to the previous chapter [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Binomial_Distribution|Binomial Distribution]]. | ||
| + | *To check your results you can use the interactive HTML5/JavaScript applet [[Applets:Binomial_and_Poisson_Distribution_(Applet)|Binomial and Poisson distribution]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Find out from the probabilities, means, and standard deviations whether $z_1$ or $z_2$ is Poisson distributed. |
| − | |type=" | + | |type="()"} |
| − | + $z_1$ | + | + $z_1$ is Poisson distributed and $z_2$ is binomially distributed. |
| − | - $z_1$ | + | - $z_1$ is binomially distributed and $z_2$ is Poisson distributed. |
| − | { | + | {What rate $\lambda$ does the Poisson distribution exhibit? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $\lambda \ =$ | + | $\lambda \ = \ $ { 2 3% } |
| − | { | + | {The values of the Poisson distribution are not limited to the range $0$, ... , $5$ . <br>What are the probabilities that the Poisson distributed size is exactly equal to $6$ or is greater than $6$ ? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $\rm Pr(6)$ = { 0. | + | ${\rm Pr}(z_{\rm Poisson} = 6) \ = \ $ { 0.012 3% } |
| + | ${\rm Pr}(z_{\rm Poisson} > 6) \ = \ $ { 0.004 3% } | ||
| − | { | + | {Now consider the binomial distribution. Give its characteristic probability&. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $p \ =$ { 0.4 3% } | + | $p \ = \ $ { 0.4 3% } |
| − | { | + | {What is the size of the parameter $I$ of the binomial distribution? Check your result using the probability $\rm Pr(0)$. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
| − | $I \=$ { 5 3% } | + | $I \ = \ $ { 5 3% } |
| − | |||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | + | '''(1)''' Correct is the <u>proposed solution 1</u>: | |
| + | *In the Poisson distribution, mean $m_1$ and variance $\sigma^2$ are equal. | ||
| + | *The random variable $z_1$ satisfies this condition in contrast to the random variable $z_2$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(2)''' Moreover, in the Poisson distribution, the mean is equal to the rate. Therefore, $\underline{\lambda = 2}$ must hold. | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | '''(3)''' The corresponding probability is with $z_{\rm Poisson} = z_1$: | |
| + | :$${\rm Pr}(z_1 = 6)=\frac{2^6}{6!}\cdot e^{-2}\hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 0.012}$$ | ||
| + | :$${\rm Pr}(z_1 > 6)=1 -{\rm Pr}(0) -{\rm Pr}(1) - \ \text{...} \ -{\rm Pr}(6)\hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 0.004}.$$ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''(4)''' For the variance of the binomial distribution holds: | |
| + | :$$\sigma^{2}= I\cdot p\cdot (1- p)= m_{\rm 1}\cdot ( 1- p).$$ | ||
| − | + | *The characteristic probability of the binomial distribution is obtained from the variance $\sigma^2 = 1.095$ and the mean $m_1 = 2$ according to the equation: | |
| − | :$$\sigma^{\ | + | :$$ 1- p = \frac{\sigma^{2}}{m_1}= \frac{1.2}{2} = 0.6\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} p \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{= 0.4}.$$ |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''(5)''' From the mean $m_1 = 2$ it further follows $\underline{I= 5}.$ | |
| − | :$$\rm Pr(z_2 = 0)=\left({5 \atop {0}}\right)\cdot | + | *The probability for the outcome "0" would have to be as follows with these parameters: |
| + | :$${\rm Pr}(z_2 = 0)=\left({5 \atop {0}}\right)\cdot p^{\rm 0}\cdot (1 - p)^{\rm 5-0}=0.6^5=0.078.$$ | ||
| − | : | + | *This means: <u>Our results are correct</u>. |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Theory of Stochastic Signals: Exercises|^2.4 Poisson Distribution^]] |
Latest revision as of 16:10, 16 February 2022
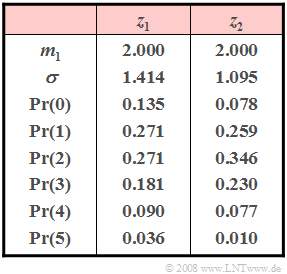
Consider two discrete random variables $z_1$ and $z_2$ that can take (at least) all integer values between $0$ and $5$ (including these limits).
The probabilities of these random variables are given in the adjacent table. However, one of the two random variables is not limited to the given range of values.
Furthermore it is known that
- one of the variables is binomially distributed, and
- the other describes a Poisson distribution.
However, it is not known which of the two variables $(z_1$ or $z_2)$ is binomially distributed and which is Poisson distributed.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Poisson distribution.
- But also refers to the previous chapter Binomial Distribution.
- To check your results you can use the interactive HTML5/JavaScript applet Binomial and Poisson distribution.
Questions
Solution
- In the Poisson distribution, mean $m_1$ and variance $\sigma^2$ are equal.
- The random variable $z_1$ satisfies this condition in contrast to the random variable $z_2$.
(2) Moreover, in the Poisson distribution, the mean is equal to the rate. Therefore, $\underline{\lambda = 2}$ must hold.
(3) The corresponding probability is with $z_{\rm Poisson} = z_1$:
- $${\rm Pr}(z_1 = 6)=\frac{2^6}{6!}\cdot e^{-2}\hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 0.012}$$
- $${\rm Pr}(z_1 > 6)=1 -{\rm Pr}(0) -{\rm Pr}(1) - \ \text{...} \ -{\rm Pr}(6)\hspace{0.15cm} \underline{\approx 0.004}.$$
(4) For the variance of the binomial distribution holds:
- $$\sigma^{2}= I\cdot p\cdot (1- p)= m_{\rm 1}\cdot ( 1- p).$$
- The characteristic probability of the binomial distribution is obtained from the variance $\sigma^2 = 1.095$ and the mean $m_1 = 2$ according to the equation:
- $$ 1- p = \frac{\sigma^{2}}{m_1}= \frac{1.2}{2} = 0.6\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} p \hspace{0.15cm} \underline{= 0.4}.$$
(5) From the mean $m_1 = 2$ it further follows $\underline{I= 5}.$
- The probability for the outcome "0" would have to be as follows with these parameters:
- $${\rm Pr}(z_2 = 0)=\left({5 \atop {0}}\right)\cdot p^{\rm 0}\cdot (1 - p)^{\rm 5-0}=0.6^5=0.078.$$
- This means: Our results are correct.