Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.9: Symmetrical Distortions"
m |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | [[File:P_ID1040__Mod_Z_2_8.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID1040__Mod_Z_2_8.png|right|frame|Transmitter and receiver spectrum in the equivalent low-pass region]] |
| − | + | The source signal made up of two components | |
:$$q(t) = A_1 \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_1 t ) + A_2 \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_2 t )$$ | :$$q(t) = A_1 \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_1 t ) + A_2 \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_2 t )$$ | ||
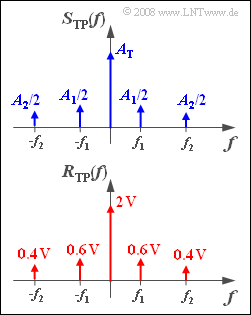
| − | + | is amplitude modulated and transmitted through a linearly distorting transmission channel. The carrier frequency is $f_{\rm T}$ and the added DC component $A_{\rm T}$. Thus, a ''Double-sideband amplitudemoduluation'' $\rm (DSB–AM)$ ''with carrier'' is present. | |
| − | + | The upper graph shows the spectrum $S_{\rm TP}(f)$ of the equivalent low-pass signal in schematic form. This means, that the lengths of the Dirac lines drawn do not correspond to the actual values of $A_{\rm T}$, $A_1/2$ and $A_2/2$ . | |
| − | + | The spectral function $R(f)$ of the received signal was measured. In the lower graph we can observe the equivalent low-pass spectrum $R_{\rm TP}(f)$ calculated from this. | |
| − | + | The channel frequency response is characterised with sufficient accuracy with a few auxiliary values: | |
:$$ H_{\rm K}(f = f_{\rm T}) = 0.5,$$ | :$$ H_{\rm K}(f = f_{\rm T}) = 0.5,$$ | ||
:$$H_{\rm K}(f = f_{\rm T} \pm f_1) = 0.4,$$ | :$$H_{\rm K}(f = f_{\rm T} \pm f_1) = 0.4,$$ | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Hints:'' |
| − | * | + | *This exercise belongs to the chapternbsp; [[Modulation_Methods/Envelope_Demodulation|Envelope Demodulation]]. |
| − | * | + | *Particular reference is made to the page [[Modulation_Methods/Envelope_Demodulation#Description_using_the_equivalent_low-pass_signal|Description using the equivalent low-pass signal]]. |
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {Give the amplitudes of the carrier and source signal. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$A_{\rm T} \ = \hspace{0.17cm} $ { 4 3% } $\ \rm V$ | $A_{\rm T} \ = \hspace{0.17cm} $ { 4 3% } $\ \rm V$ | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
$A_2 \ = \ $ { 4 3% } $\ \rm V$ | $A_2 \ = \ $ { 4 3% } $\ \rm V$ | ||
| − | { | + | {Which kind of distortion would the application of an envelope demodulator in an ideal channel ⇒ $H_{\rm K}(f) = 1$ lead to? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
| − | - | + | - No distortion. |
| − | - | + | - Linear distortions. |
| − | + | + | + Nonlinear distortions. |
| − | { | + | {Calculate the equivalent lowpass signal and answer the following questions. Is it true that... |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + $r_{\rm TP}(t)$ | + | + $r_{\rm TP}(t)$ is always real, |
| − | + $r_{\rm TP}(t)$ | + | + $r_{\rm TP}(t)$ is always greater than or equal to zero, |
| − | - | + | - the phase function $ϕ(t)$ can take on the values $0^\circ$ and $180^\circ$ . |
| − | { | + | {Which kind of distortion does the envelope demodulator in the observed transmission channel lead to? |
|type="()"} | |type="()"} | ||
| − | - | + | - No distortion. |
| − | + | + | + Linear distortions. |
| − | - | + | - Nonlinear distortions. |
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
'''(1)''' Anhand der Grafiken auf der Angabenseite sind folgende Aussagen möglich: | '''(1)''' Anhand der Grafiken auf der Angabenseite sind folgende Aussagen möglich: | ||
Revision as of 22:13, 20 December 2021
The source signal made up of two components
- $$q(t) = A_1 \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_1 t ) + A_2 \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_2 t )$$
is amplitude modulated and transmitted through a linearly distorting transmission channel. The carrier frequency is $f_{\rm T}$ and the added DC component $A_{\rm T}$. Thus, a Double-sideband amplitudemoduluation $\rm (DSB–AM)$ with carrier is present.
The upper graph shows the spectrum $S_{\rm TP}(f)$ of the equivalent low-pass signal in schematic form. This means, that the lengths of the Dirac lines drawn do not correspond to the actual values of $A_{\rm T}$, $A_1/2$ and $A_2/2$ .
The spectral function $R(f)$ of the received signal was measured. In the lower graph we can observe the equivalent low-pass spectrum $R_{\rm TP}(f)$ calculated from this.
The channel frequency response is characterised with sufficient accuracy with a few auxiliary values:
- $$ H_{\rm K}(f = f_{\rm T}) = 0.5,$$
- $$H_{\rm K}(f = f_{\rm T} \pm f_1) = 0.4,$$
- $$ H_{\rm K}(f = f_{\rm T} \pm f_2) = 0.2 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapternbsp; Envelope Demodulation.
- Particular reference is made to the page Description using the equivalent low-pass signal.
Questions
Solution
- $${A_{\rm T}} \cdot 0.5 = 2 \,{\rm V}\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}A_{\rm T} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 4 \,{\rm V}},$$
- $${A_{\rm 1}}/{2} \cdot 0.4 = 0.6\,{\rm V}\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}A_{\rm 1} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 3 \,{\rm V}},$$
- $${A_{\rm 2}}/{2} \cdot 0.2 = 0.4\,{\rm V}\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}A_{\rm 2} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 4 \,{\rm V}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) Richtig ist der Lösungsvorschlag 3:
- Der Modulationsgrad ergibt sich zu $m = (A_1 + A_2)/A_T = 1.75$.
- Damit ergeben sich bei Verwendung eines Hüllkurvendemodulators starke nichtlineare Verzerrungen.
- Ein Klirrfaktor kann aber nicht angegeben werden, da das Quellensignal zwei Frequenzanteile beinhaltet.
(3) Richtig sind die Aussagen 1 und 2:
- Die Fourierrücktransformation von $R_{\rm TP}(f)$ führt zum Ergebnis:
- $$ r_{\rm TP}(t) = 2 \,{\rm V} + 1.2 \,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_1 t ) + 0.8 \,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_2 t )\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Diese Funktion ist stets reell und nicht–negativ.
- Damit gilt gleichzeitig $ϕ(t) = 0$. Dagegen ist $ϕ(t) = 180^\circ$ nicht möglich.
(4) Ein Vergleich der beiden Signale
- $$q(t) = 3 \,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_1 t ) + 4 \,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_2 t ),$$
- $$ v(t) = 0.4 \cdot 3 \,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_1 t ) + 0.2 \cdot 4 \,{\rm V} \cdot \cos(2 \pi f_2 t )$$
- zeigt, dass nun lineare Verzerrungen – genauer gesagt Dämpfungsverzerrungen – auftreten ⇒ Lösungsvorschlag 2.
- Der Kanal $H_{\rm K}(f)$ hat hier den positiven Effekt, dass anstelle von irreversiblen nichtlinearen Verzerrungen nun lineare Verzerrungen entstehen, die durch ein nachgeschaltetes Filter eliminiert werden können.
- Dies ist darauf zurückzuführen, dass durch die stärkere Dämpfung des Quellensignals $q(t)$ im Vergleich zum Trägersignal $z(t)$ der Modulationsgrad von $m = 1.75$ auf $m = (0.4 · 3 \ \rm V + 0.2 · 4 \ \rm V)/(0.5 · 4 \ \rm V) = 1$ herabgesetzt wird.