Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.13: Threshold Decision vs. DFE vs. Maximum Likelihood"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Digital_Signal_Transmission/Viterbi_Receiver}} |
| − | [[File:P_ID1479__Dig_A_3_13.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID1479__Dig_A_3_13.png|right|frame|Error probabilities in comparison: <br>SE: Threshold Decision, <br>DFE: Decision Feedback Equalization, <br>ML: Maximum Likelihood Detection]] |
| − | + | Error probabilities of different receiver types are to be compared. Considered in detail are: | |
| − | * | + | * Threshold Decision (SE) ⇒ error probability $p_{\rm SE}$, |
| − | * Decision Feedback Equalization (DFE) ⇒ | + | * Decision Feedback Equalization (DFE) ⇒ error probability $p_{\rm DFE}$ and |
| − | * Maximum | + | * Maximum Likelihood Detection (ML) ⇒ error probability $p_{\rm ML}$. |
| − | + | The "main value" $g_0$, the precursor $g_{\rm –1}$ and the postcursor $g_1$ of the basic detection pulse, as well as the detection coefficient before the respective decision ($\sigma_d$) are given for four different parameter sets $\rm A$, $\rm B$, $\rm C$ and $\rm D$ in the table. | |
| − | + | Bipolar amplitude coefficients are assumed, so that, for example, for the worst-case error probability of the receiver with single threshold decision, the following applies: | |
:$$p_{\rm U,\hspace{0.05cm} SE } = \left\{ \begin{array}{c} {\rm Q}\big [ ({g_0-|g_{-1}|-|g_{1}|})/{\sigma_d} \big ]\\ | :$$p_{\rm U,\hspace{0.05cm} SE } = \left\{ \begin{array}{c} {\rm Q}\big [ ({g_0-|g_{-1}|-|g_{1}|})/{\sigma_d} \big ]\\ | ||
\\{\rm Q}(0) = 0.5 \end{array} \right.\quad | \\{\rm Q}(0) = 0.5 \end{array} \right.\quad | ||
| − | \begin{array}{*{1}c} {\rm | + | \begin{array}{*{1}c} {\rm with }\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm open }\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm eye }, |
| − | \\ \\{\rm | + | \\ \\{\rm with }\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm closed }\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm eye }. \\ \end{array}\begin{array}{*{20}c} |
\\ | \\ | ||
\end{array}$$ | \end{array}$$ | ||
| − | + | For the Nyquist system $\rm A$, the mean error probability is exactly the same, viz. | |
:$$p_{\rm SE } =p_{\rm U,\hspace{0.05cm} SE } = {\rm Q}\left( {g_0}/{\sigma_d} \right)= {\rm | :$$p_{\rm SE } =p_{\rm U,\hspace{0.05cm} SE } = {\rm Q}\left( {g_0}/{\sigma_d} \right)= {\rm | ||
Q}(5) \approx 2.87 \cdot 10^{-7}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | Q}(5) \approx 2.87 \cdot 10^{-7}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | For the other system variants $\rm B$, $\rm C$ and $\rm D$ considered here, the intersymbol interferences are so strong and the given noise rms value is so small that the following approximation can be applied: | |
:$$p_{\rm SE } \approx {1}/{4} \cdot p_{\rm U,\hspace{0.05cm} SE } | :$$p_{\rm SE } \approx {1}/{4} \cdot p_{\rm U,\hspace{0.05cm} SE } | ||
= {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm Q}\left( \frac {{\rm Max }\hspace{0.05cm}\big [0, \hspace{0.05cm}g_0-|g_{-1}|-|g_{1}|\big ]}{\sigma_d} \right)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | = {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm Q}\left( \frac {{\rm Max }\hspace{0.05cm}\big [0, \hspace{0.05cm}g_0-|g_{-1}|-|g_{1}|\big ]}{\sigma_d} \right)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | Except for the Nyquist system $\rm A$ $($here $p_{\rm DFE} = p_{\rm SE})$, the following approximation applies to the DFE receiver instead: | |
:$$p_{\rm DFE } \approx {1}/{2} \cdot p_{\rm U,\hspace{0.05cm} DFE } | :$$p_{\rm DFE } \approx {1}/{2} \cdot p_{\rm U,\hspace{0.05cm} DFE } | ||
= {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm Q}\left( \frac{{\rm Max }\hspace{0.05cm}\big [0, \hspace{0.05cm}g_0-|g_{-1}|\big ]}{\sigma_d} \right)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm Q}\left( \frac{{\rm Max }\hspace{0.05cm}\big [0, \hspace{0.05cm}g_0-|g_{-1}|\big ]}{\sigma_d} \right)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | In contrast, it was shown in the [[Digital_Signal_Transmission/Viterbi_Receiver#Error_probability_in_maximum_likelihood_decision|"last theory section"]] for this chapter that for a receiver with ML decision, the following approximation holds: | |
:$$p_{\rm ML } | :$$p_{\rm ML } | ||
= {\rm Q}\left( \frac{{\rm Max }\hspace{0.05cm}[g_{\nu}]}{\sigma_d} \right)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | = {\rm Q}\left( \frac{{\rm Max }\hspace{0.05cm}[g_{\nu}]}{\sigma_d} \right)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Notes:'' |
| − | * | + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Digital_Signal_Transmission/Viterbi_Receiver|"Viterbi Receiver"]]. |
| − | * | + | *Reference is also made to the chapters [[Digital_Signal_Transmission/Linear_Nyquist_Equalization|"Linear Nyquist Equalization"]] and [[Digital_Signal_Transmission/Decision_Feedback|"Decision Feedback"]]. |
| − | * | + | * DYou can determine the numerical values of the Q-function using the interaction module [[Applets:Komplementäre_Gaußsche_Fehlerfunktionen|"Complementary Gaussian Error Functions"]]. |
| − | * | + | * To apply the algorithm given in the theory section for two precursors, you would have to make the following renamings (which, however, has no meaning for the calculation of the error probabilities): |
:$$g_{1 }\hspace{0.1cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm}g_{0 },\hspace{0.4cm} | :$$g_{1 }\hspace{0.1cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm}g_{0 },\hspace{0.4cm} | ||
g_{0 }\hspace{0.1cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm}g_{-1 },\hspace{0.4cm} | g_{0 }\hspace{0.1cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm}g_{-1 },\hspace{0.4cm} | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
{Welche Fehlerwahrscheinlichkeit ergibt sich bei System $\rm A$ mit Maximum–Likelihood–Detektion (ML)? | {Welche Fehlerwahrscheinlichkeit ergibt sich bei System $\rm A$ mit Maximum–Likelihood–Detektion (ML)? | ||
Revision as of 11:50, 8 June 2022
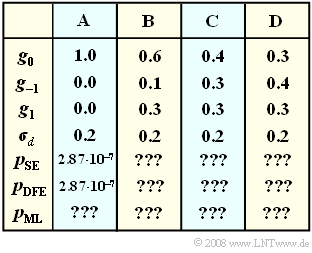
Error probabilities of different receiver types are to be compared. Considered in detail are:
- Threshold Decision (SE) ⇒ error probability $p_{\rm SE}$,
- Decision Feedback Equalization (DFE) ⇒ error probability $p_{\rm DFE}$ and
- Maximum Likelihood Detection (ML) ⇒ error probability $p_{\rm ML}$.
The "main value" $g_0$, the precursor $g_{\rm –1}$ and the postcursor $g_1$ of the basic detection pulse, as well as the detection coefficient before the respective decision ($\sigma_d$) are given for four different parameter sets $\rm A$, $\rm B$, $\rm C$ and $\rm D$ in the table.
Bipolar amplitude coefficients are assumed, so that, for example, for the worst-case error probability of the receiver with single threshold decision, the following applies:
- $$p_{\rm U,\hspace{0.05cm} SE } = \left\{ \begin{array}{c} {\rm Q}\big [ ({g_0-|g_{-1}|-|g_{1}|})/{\sigma_d} \big ]\\ \\{\rm Q}(0) = 0.5 \end{array} \right.\quad \begin{array}{*{1}c} {\rm with }\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm open }\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm eye }, \\ \\{\rm with }\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm closed }\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm eye }. \\ \end{array}\begin{array}{*{20}c} \\ \end{array}$$
For the Nyquist system $\rm A$, the mean error probability is exactly the same, viz.
- $$p_{\rm SE } =p_{\rm U,\hspace{0.05cm} SE } = {\rm Q}\left( {g_0}/{\sigma_d} \right)= {\rm Q}(5) \approx 2.87 \cdot 10^{-7}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
For the other system variants $\rm B$, $\rm C$ and $\rm D$ considered here, the intersymbol interferences are so strong and the given noise rms value is so small that the following approximation can be applied:
- $$p_{\rm SE } \approx {1}/{4} \cdot p_{\rm U,\hspace{0.05cm} SE } = {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm Q}\left( \frac {{\rm Max }\hspace{0.05cm}\big [0, \hspace{0.05cm}g_0-|g_{-1}|-|g_{1}|\big ]}{\sigma_d} \right)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Except for the Nyquist system $\rm A$ $($here $p_{\rm DFE} = p_{\rm SE})$, the following approximation applies to the DFE receiver instead:
- $$p_{\rm DFE } \approx {1}/{2} \cdot p_{\rm U,\hspace{0.05cm} DFE } = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm Q}\left( \frac{{\rm Max }\hspace{0.05cm}\big [0, \hspace{0.05cm}g_0-|g_{-1}|\big ]}{\sigma_d} \right)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
In contrast, it was shown in the "last theory section" for this chapter that for a receiver with ML decision, the following approximation holds:
- $$p_{\rm ML } = {\rm Q}\left( \frac{{\rm Max }\hspace{0.05cm}[g_{\nu}]}{\sigma_d} \right)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Notes:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter "Viterbi Receiver".
- Reference is also made to the chapters "Linear Nyquist Equalization" and "Decision Feedback".
- DYou can determine the numerical values of the Q-function using the interaction module "Complementary Gaussian Error Functions".
- To apply the algorithm given in the theory section for two precursors, you would have to make the following renamings (which, however, has no meaning for the calculation of the error probabilities):
- $$g_{1 }\hspace{0.1cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm}g_{0 },\hspace{0.4cm} g_{0 }\hspace{0.1cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm}g_{-1 },\hspace{0.4cm} g_{-1 }\hspace{0.1cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.1cm}g_{-2 } \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Questions
Musterlösung
- $$ p_{\rm DFE } = p_{\rm ML } = p_{\rm SE } \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 2.87 \cdot 10^{-7}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) Mit $g_0 = 0.6$, $g_{\rm –1} = 0.1$ und $g_1 = 0.3$ $\text{(System B)}$ erhält man näherungsweise:
- $$p_{\rm SE } \ \approx \ {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm Q}\left( \frac{0.6-0.1-0.3}{0.2} \right)= {1}/{4} \cdot{\rm Q}(1) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 4\% \hspace{0.05cm}},$$
- $$ p_{\rm DFE } \ \approx \ {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm Q}\left( \frac{0.6-0.1}{0.2} \right)= {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm Q}(2.5) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 0.31\%} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ p_{\rm ML } \ \approx \ {\rm Q}\left( \frac{0.6}{0.2} \right) = {\rm Q}(3) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 0.135\%} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) Die Fehlerwahrscheinlichkeiten lauten mit $g_0 = 0.4$ und $g_1 = g_{\rm –1} = 0.3$ $\text{(System C)}$:
- $$p_{\rm SE } \ \approx \ {1}/{4} \cdot{\rm Q}(0) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 12.5\%} \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm geschlossenes }\hspace{0.15cm}{\rm Auge } \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ p_{\rm DFE } \ \approx \ {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm Q}\left( \frac{0.4-0.3}{0.2} \right)= {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm Q}(0.5) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 15\% \hspace{0.05cm}},$$
- $$ p_{\rm ML } \ \approx \ {\rm Q}\left( \frac{0.4}{0.2} \right) = {\rm Q}(2) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {\approx 2.27\%} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Interessant – und nicht etwa ein Rechenfehler – ist, dass die DFE schlechter ist als der herkömmliche Schwellenwertentscheider, wenn die Fehlerwahrscheinlichkeit $10\%$ oder mehr beträgt.
- Siehe dazu auch die Musterlösung zur Teilaufgabe (4).
(4) Bei System $\text{D}$ ergibt sich auch für den DFE–Empfänger ein geschlossenes Auge.
- Die Fehlerwahrscheinlichkeit $p_{\rm DFE}$ ist größer als $p_{\rm SE}$, da nun die ungünstigste Symbolfolge häufiger auftritt. Nach der angegebenen einfachen Näherung gilt:
- $$p_{\rm SE } = {1}/{4} \cdot{\rm Q}(0) = 0.125\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm} p_{\rm DFE } = {1}/{2} \cdot{\rm Q}(0) \hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 0.250} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Bei exakter Rechnung erhält man dagegen:
- $$p_{\rm SE } \ = \ {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm Q}\left( \frac{0.3-0.4-0.3}{0.2}\right) + {1}/{4} \cdot{\rm Q}\left( \frac{0.3-0.4+0.3}{0.2}\right)+ \ {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm Q}\left( \frac{0.3+0.4-0.3}{0.2}\right) +{1}/{4} \cdot{\rm Q}\left( \frac{0.3+0.4+0.3}{0.2}\right)$$
- $$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}p_{\rm SE } \ = \ {1}/{4} \cdot \left[ {\rm Q}(-2) + {\rm Q}(1) +{\rm Q}(2) +{\rm Q}(5) \right] ={1}/{4} \cdot \left[ 1+ {\rm Q}(1) +{\rm Q}(5) \right] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Wegen ${\rm Q}(–2) + {\rm Q}(2) = 1$ und ${\rm Q}(5) \approx 0$ erhält man daraus $p_{\rm SE} \approx 25.5\%$.
- Entsprechend gilt für den DFE–Empfänger:
- $$p_{\rm DFE } \ = \ {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm Q}\left( \frac{0.3-0.4}{0.2}\right) + {1}/{2} \cdot{\rm Q}\left( \frac{0.3+0.4}{0.2}\right)= \ {1}/{2} \cdot \left[ {\rm Q}(-0.5) + {\rm Q}(3.5) \right] \approx\frac{1- {\rm Q}(0.5)}{2}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline {= 35\%} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Dagegen beträgt die Fehlerwahrscheinlichkeit $p_{\rm ML}$ eines Maximum–Likelihood–Empfängers weiterhin ${\rm Q}(2) \hspace{0.15cm} \underline {= 2.27\%}$.
- Die Reihenfolge der Detektionsgrundimpulswerte ist für die Fehlerwahrscheinlichkeit des Viterbi–Empfängers (nahezu) nicht von Bedeutung.