Exercise 4.09: Decision Regions at Laplace
We consider a transmission system based on the basis functions $\varphi_1(t)$ and $\varphi_2(t)$. The two equally probable transmitted signals are given by the signal points
- $$\boldsymbol{ s }_0 = (-\sqrt{E}, \hspace{0.1cm}-\sqrt{E})\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm} \boldsymbol{ s }_1 = (+\sqrt{E}, \hspace{0.1cm}+\sqrt{E})\hspace{0.05cm}$$.
In the following we normalize the energy parameter to $E = 1$ for simplification and thus obtain
- $$\boldsymbol{ s }_0 \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} (-1, \hspace{0.1cm}-1) \hspace{0.2cm} \Leftrightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} m_0\hspace{0.05cm}, $$
- $$ \boldsymbol{ s }_1 \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} (+1, \hspace{0.1cm}+1)\hspace{0.2cm} \Leftrightarrow \hspace{0.2cm} m_1\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The messages $m_0$ and $m_1$ are uniquely assigned to the signals $\boldsymbol{s}_0$ and $\boldsymbol{s}_1$ defined in this way.
Let the two noise components $n_1(t)$ and $n_2(t)$ be independent of each other and each be Laplace distributed with parameter $a = 1$:
- $$p_{n_1} (\eta_1) = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm e}^{- | \eta_1|} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm} p_{n_2} (\eta_2) = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm e}^{- | \eta_2|} \hspace{0.05cm} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \boldsymbol{ p }_{\boldsymbol{ n }} (\eta_1, \eta_2) = {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm e}^{- | \eta_1|- | \eta_2|} \hspace{0.05cm}. $$
The properties of such a Laplace noise will be discussed in detail in "Exercise 4.9Z".
The received signal $\boldsymbol{r}$ is composed additively of the transmitted signal $\boldsymbol{s}$ and the noise signal $\boldsymbol{n}$:
- $$\boldsymbol{ r } \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \boldsymbol{ s } + \boldsymbol{ n } \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.45cm}\boldsymbol{ r } = ( r_1, r_2) \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.45cm} \boldsymbol{ s } \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} ( s_1, s_2) \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.8cm}\boldsymbol{ n } = ( n_1, n_2) \hspace{0.05cm}. $$
The corresponding realizations are denoted as follows:
- $$\boldsymbol{ s }\text{:} \hspace{0.4cm} (s_{01},s_{02}){\hspace{0.15cm}\rm and \hspace{0.15cm}} (s_{11},s_{12}) \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.8cm} \boldsymbol{ r }\text{:} \hspace{0.4cm} (\rho_{1},\rho_{2}) \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.8cm}\boldsymbol{ n }\text{:} \hspace{0.4cm} (\eta_{1},\eta_{2}) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The decision rule of the MAP and ML receivers (both are identical due to the same symbol probabilities) are:
- Decide for the symbol $m_0$, if $p_{\boldsymbol{ r} \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}m } ( \rho_{1},\rho_{2} |m_0 ) > p_{\boldsymbol{ r} \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}m } (\rho_{1},\rho_{2} |m_1 ) \hspace{0.05cm}.$
With the further conditions for this $($decision for $m_0)$ can also be written:
- $${1}/{4} \cdot {\rm exp}\left [- | \rho_1 +1|- | \rho_2 +1| \hspace{0.1cm} \right ] > {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm exp}\left [- | \rho_1 -1|- | \rho_2 -1| \hspace{0.1cm} \right ] $$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | \rho_1 +1|+ | \rho_2 +1| < | \rho_1 -1|+ | \rho_2 -1|$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} L (\rho_1, \rho_2) = | \rho_1 +1|+ | \rho_2 +1| - | \rho_1 -1|- | \rho_2 -1| < 0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
This function $L(\rho_1, \rho_2)$ is frequently referred to in the questions.
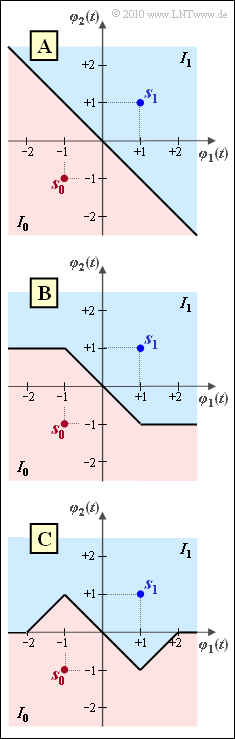
The graph shows three different decision regions $(I_0, \ I_1)$.
- For AWGN noise, only the upper variant $\rm A$ would be optimal.
- Also for the considered Laplace noise, variant $\rm A$ leads to the smallest possible error probability, see "Exercise 4.9Z":
- $$p_{\rm min} = {\rm Pr}({\cal{E}} \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm} {\rm optimal\hspace{0.15cm} receiver}) = {\rm e}^{-2} \approx 13.5\,\%\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- It is to be examined whether variant $\rm B$ or variant $\rm C$ is also optimal, i.e. whether their error probabilities are also as small as possible equal to $p_{\rm min}$.
Note:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter "Approximation of the Error Probability".
Questions
Solution
- The joint probability densities under conditions $m_0$ and $m_1$, respectively, are:
- $$p_{\boldsymbol{ r} \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}m } ( \rho_{1},\rho_{2} |m_0 ) \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm exp}\left [- | \rho_1 +1|- | \rho_2 +1| \hspace{0.05cm} \right ]\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$p_{\boldsymbol{ r} \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}m } ( \rho_{1},\rho_{2} |m_1 ) \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm exp}\left [- | \rho_1 -1|- | \rho_2 -1| \hspace{0.05cm} \right ]\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- For equally probable symbols ⇒ ${\rm Pr}(m_0) = {\rm Pr}(m_1) = 0.5$, the MAP decision rule is: Decide for symbol $m_0$ ⇔ signal $s_0$, if
- $$p_{\boldsymbol{ r} \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}m } ( \rho_{1},\rho_{2} |m_0 ) > p_{\boldsymbol{ r} \hspace{0.05cm}|\hspace{0.05cm}m } (\rho_{1},\rho_{2} |m_1 ) \hspace{0.05cm}\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm exp}\left [- | \rho_1 +1|- | \rho_2 +1| \hspace{0.05cm} \right ] > {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm exp}\left [- | \rho_1 -1|- | \rho_2 -1|\hspace{0.05cm} \right ] $$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | \rho_1 +1|+ | \rho_2 +1| < | \rho_1 -1|+ | \rho_2 -1|\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} L (\rho_1, \rho_2) = | \rho_1 +1|- | \rho_1 -1|+ | \rho_2 +1| - | \rho_2 -1| < 0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) All statements are true: For $x ≥ 1$
- $$| x +1|- | x -1| = x +1 -x +1 =2 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Similarly, for $x ≤ \, –1$, for example, $x = \, –3$:
- $$| x +1|- | x -1| = | -3 +1|- | -3 -1| = 2-4 = -2 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- On the other hand, in the middle range $–1 ≤ x ≤ +1$:
- $$| x+1|- | x -1| = x +1 -1 +x =2x \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(3) Solution 1 is correct:
- The result of subtask (1) was: Decide for the symbol $m_0$, if
- $$L (\rho_1, \rho_2) = | \rho_1 +1| - | \rho_1 -1|+ | \rho_2 +1| - | \rho_2 -1| < 0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- In the considered (inner) range $-1 ≤ \rho_1 ≤ +1$, $-1 ≤ \rho_2 ≤ +1$ holds with the result of subtask (2):
- $$| \rho_1+1| - | \rho_1 -1| = 2\rho_1 \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm} | \rho_2+1| - | \rho_2 -1| = 2\rho_2 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- If we insert this result above, we have to decide for $m_0$ exactly if
- $$L (\rho_1, \rho_2) = 2 \cdot ( \rho_1+\rho_2) < 0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \rho_1+\rho_2 < 0\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) Correct is here solution 2:
- For $\rho_1 > 1$, $|\rho_1+1| \, -|\rho_1 \, -1| = 2$, while for $D_2 = |\rho_2+1| \,-|\rho_2 \, -1|$ all values between $-2$ and $+2$ are possible.
- Thus, the decision variable is $L(\rho_1, \rho_2) = 2 + D_2 ≥ 0$. In this case, the rule leads to an $m_1$ decision.
(5) Solution 1 is correct:
- After similar calculation as in subtask (3), one arrives at the result:
- $$L (\rho_1, \rho_2) = -2 + D_2 \le 0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm decision\hspace{0.15cm} on\hspace{0.15cm}} m_0\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(6) Solution 2 is correct: decision on $m_1$.
- Similar to subtask (4), the following holds here:
- $$D_1 = | \rho_1 +1| - | \rho_1 -1| \in \{-2, ... \hspace{0.05cm} , +2 \} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}L (\rho_1, \rho_2) = 2 + D_1 \ge 0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(7) Solution 1 is correct: decision on $m_0$.
- After similar reasoning as in the last subtask, we arrive at the result:
- $$L (\rho_1, \rho_2) = -2 + D_1 \le 0 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} {\rm decision\hspace{0.15cm} on\hspace{0.15cm}} m_0\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
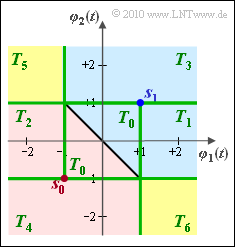
(8) The results of subtasks (3) to (7) are summarized in the graph:
- Subarea $T_0$: decision on $m_0$ or $m_1$ according to task (3).
- Subarea $T_1$: decision on $m_1$ according to task (4).
- Subarea $T_2$: decision on $m_0$ according to task (5).
- Subarea $T_3$: decision on $m_1$ according to task (6).
- Subarea $T_4$: decision on $m_0$ according to task (7).
- Subarea $T_5$: Decision on $m_0$ according to task (5), and on $m_1$ according to task (6)
⇒ For Laplace noise, it does not matter whether one assigns $T_5$ to region $I_0$ or $I_1$. - Subarea $T_6$: Again, based on the results of task (4) and (7), one can assign this region to both region $I_0$ and region $I_1$.
It can be seen:
- For subtask $T_0$, ... $T_4$ there is a fixed assignment to the decision regions $I_0$ (red) and $I_1$ (blue).
- In contrast, the two regions $T_5$ and $T_6$ marked in yellow can be assigned to both $I_0$ and $I_1$ without loss of optimality.
Comparing this graph with variants A, B and C on the specification page, we see that suggestions 1 and 2 are correct:
- Variants A and B are equally good. Both are optimal. The error probability in both cases is $p_{\rm min} = {\rm e}^{\rm -2}$.
- Variant C is not optimal; with respect to the subareas $T_1$ and $T_2$ there are mismatches. The error probability is therefore greater than $p_{\rm min}$.