Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 4.16: Comparison between Binary PSK and Binary FSK"
m (Textersetzung - „*Sollte die Eingabe des Zahlenwertes „0” erforderlich sein, so geben Sie bitte „0.” ein.“ durch „ “) |
|||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
}} | }} | ||
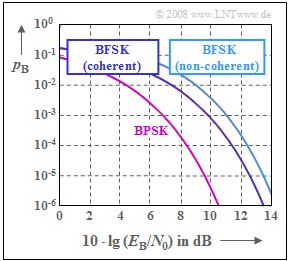
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:EN_Mod_A_4_15_neu.png|right|frame|Bit error probability curves: <br>Binary PSK and binary FSK]] |
| − | + | The graph shows the bit error probability for binary [[Modulation_Methods/Nonlinear_Digital_Modulation#FSK_.E2.80.93_Frequency_Shift_Keying| FSK modulation]] $\rm (BFSK)$ in | |
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Modulation_Methods/Nonlinear_Digital_Modulation#Coherent_demodulation_of_FSK|coherent demodulation]] , as well as in |
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Modulation_Methods/Nonlinear_Digital_Modulation#Error_probability_of_orthogonal_FSK|non-coherent demodulation]] |
| − | |||
| − | + | in comparison with [[Modulation_Methods/Lineare_digitale_Modulation#BPSK_.E2.80.93_Binary_Phase_Shift_Keying|binary phase modulation]] $\rm (BPSK)$. | |
| − | + | Orthogonality is always assumed. For coherent demodulation, the modulation index can be a multiple of $h = 0.5$ , so that the middle plot can also apply to [[Modulation_Methods/Nonlinear_Digital_Modulation#MSK_.E2.80.93_Minimum_Shift_Keying|Minimum Shift Keying]] $\rm (MSK)$ . In contrast, for non-coherent demodulation of BFSK, the modulation index must be a multiple of $h = 1$ . | |
| − | * ''Binary Phase Shift Keying'' (BPSK): | + | |
| − | :$$p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{ | + | This system comparison is once again based on the [[Modulation_Methods/Quality_Criteria#Some_remarks_on_the_AWGN_channel_model|AWGN channel]] , characterized by the relationship $E_{\rm B}/N_0$. The equations for the bit error probabilities are as follows |
| − | * ''Binary Frequency Shift Keying'' (BFSK) | + | * for ''Binary Phase Shift Keying'' $\rm (BPSK)$: |
| − | :$$p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{{E_{\rm B}}/{N_0 }} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ) = {1}/{2}\cdot {\rm erfc}\left ( \sqrt{ | + | :$$p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{{2 \cdot E_{\rm B}}/{N_0 }} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ) = {1}/{2}\cdot {\rm erfc}\left ( \sqrt{{E_{\rm B}}/{N_0 }} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ),$$ |
| − | * ''Binary Frequency Shift Keying'' (BFSK) | + | * for ''Binary Frequency Shift Keying'' $\rm (BFSK)$ with ''coherent'' demodulation: |
| + | :$$p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{{E_{\rm B}}/{N_0 }} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ) = {1}/{2}\cdot {\rm erfc}\left ( \sqrt{{E_{\rm B}}/(2 N_0 )} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ),$$ | ||
| + | * for ''Binary Frequency Shift Keying'' $\rm (BFSK)$ with ''incoherent'' demodulation: | ||
:$$p_{\rm B} = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm e}^{- E_{\rm B}/{(2N_0) }}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$p_{\rm B} = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm e}^{- E_{\rm B}/{(2N_0) }}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | It was shown in [[Aufgaben:Exercise_4.8:_Different_Error_Probabilities|Exercise 4.8]] , that for BPSK, the log ratio $10 · \lg \ E_{\rm B}/N_0$ must be at least $9.6 \ \rm dB$ so that the bit error probability does not exceed $p_{\rm B} = 10^{–5}$ . | |
| − | '' | + | |
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''Hints:'' | ||
| + | *This exercise belongs to the chapter [[Modulation_Methods/Nonlinear_Digital_Modulation|Nonlinear_Digital_Modulation]]. | ||
| + | *However, reference is also made to the page [[Modulation_Methods/Lineare_digitale_Modulation|Linear Digital Modulation]]. | ||
| − | * | + | *Use the approximation $\lg(2) ≈ 0.3$. |
| − | === | + | ===Questions=== |
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {What $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ (in dB) is required in for MSK and coherent demodulation to satisfy $p_{\rm B} \le 10^{–5}$ ? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$10 · \lg \ E_{\rm B}/N_0 \ = \ $ { 12.6 3% } $\ \rm dB$ | $10 · \lg \ E_{\rm B}/N_0 \ = \ $ { 12.6 3% } $\ \rm dB$ | ||
| − | { | + | {Which of the following statements is correct: The same result is obtained for |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - FSK with modulation index $h = 0.7$, |
| − | + | + | + FSK with modulation index $h = 1$? |
| − | { | + | {What $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ (in dB) is required for BFSK with $h = 1$ and incoheren demodulation to satisfy $p_{\rm B} \le 10^{–5}$ ? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$10 · \lg \ E_{\rm B}/N_0 \ = \ $ { 13.4 3% } $\ \rm dB$ | $10 · \lg \ E_{\rm B}/N_0 \ = \ $ { 13.4 3% } $\ \rm dB$ | ||
| − | { | + | {What is the bit error probability $p_{\rm B}$ results from incoherent BFSK demodulation when $10 · \lg \ E_{\rm B}/N_0 = 12.6 \ \rm dB$? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$p_{\rm B} \ = \ $ { 1.12 3% } $\ \cdot 10^{-4}$ | $p_{\rm B} \ = \ $ { 1.12 3% } $\ \cdot 10^{-4}$ | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' A comparison of the first two equations on the exercise page makes it clear that for MSK with coherent demodulation, the AWGN ratio $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ must be doubled to achieve the same error probability as for BPSK. |
| − | In | + | *In other words: the coherent BFSK curve is $10 · \lg (2) ≈ 3 \ \rm dB$ to the right of the the BPSK curve. |
| + | *Thus, to guarantee $p_{\rm B} \le 10^{–5}$ it must hold that: | ||
:$$10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.05cm}{E_{\rm B}} /{N_{\rm 0}}= 9.6\,\,{\rm dB} + 3\,\,{\rm dB} = \underline{12.6\,\,{\rm dB}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.05cm}{E_{\rm B}} /{N_{\rm 0}}= 9.6\,\,{\rm dB} + 3\,\,{\rm dB} = \underline{12.6\,\,{\rm dB}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(2)''' | + | |
| − | * | + | '''(2)''' <u>Answer 2</u> is correct: |
| − | * | + | *The equation given does not just hold for MSK $($this is a FSK with $h = 0.5)$, but also for every form of orthogonal FSK. |
| − | * | + | *This is the case whenever the modulation index $h$ is an integer multiple of $0.5$ , such as when $h = 1$. |
| − | + | *When $h = 0.7$ , there is no orthogonal FSK. | |
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' From the inverse function of the equation given we get: |
:$$\frac{E_{\rm B}} {2 \cdot N_{\rm 0}}= {\rm ln}\hspace{0.05cm}\frac{1}{2 p_{\rm B}}= {\rm ln}(50000)\approx 10.82 \hspace{0.3cm} | :$$\frac{E_{\rm B}} {2 \cdot N_{\rm 0}}= {\rm ln}\hspace{0.05cm}\frac{1}{2 p_{\rm B}}= {\rm ln}(50000)\approx 10.82 \hspace{0.3cm} | ||
\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}{E_{\rm B}} /{N_{\rm 0}}= 21.64 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.05cm}{E_{\rm B}}/ {N_{\rm 0}}\approx \underline{13.4\,\,{\rm dB}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}{E_{\rm B}} /{N_{\rm 0}}= 21.64 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.05cm}{E_{\rm B}}/ {N_{\rm 0}}\approx \underline{13.4\,\,{\rm dB}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(4)''' | + | |
| + | '''(4)''' From $10 · \lg \ E_{\rm B}/N_0 = 12.6 \ \rm dB$ it follows that: | ||
:$${E_{\rm B}} /{N_{\rm 0}}= 10^{1.26} \approx 16.8 \hspace{0.25cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.25cm} ({E_{\rm B}} /{N_{\rm 0}})/2 \approx 8.4 \hspace{0.25cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.25cm} p_{\rm B} = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm e}^{- 8.4} \approx \underline{1.12 \cdot 10^{-4}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$${E_{\rm B}} /{N_{\rm 0}}= 10^{1.26} \approx 16.8 \hspace{0.25cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.25cm} ({E_{\rm B}} /{N_{\rm 0}})/2 \approx 8.4 \hspace{0.25cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.25cm} p_{\rm B} = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm e}^{- 8.4} \approx \underline{1.12 \cdot 10^{-4}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | This means that for the same $E_{\rm B}/N_0$, the error probability of incoherent demodulation is increased by a factor of $11$ compared to that of coherent demodulation (see answer to question '''1''') . | |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| Line 79: | Line 88: | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Modulation Methods: Exercises|^4.4 Non-linear Digital Modulation^]] |
Latest revision as of 11:52, 12 April 2022
The graph shows the bit error probability for binary FSK modulation $\rm (BFSK)$ in
- coherent demodulation , as well as in
- non-coherent demodulation
in comparison with binary phase modulation $\rm (BPSK)$.
Orthogonality is always assumed. For coherent demodulation, the modulation index can be a multiple of $h = 0.5$ , so that the middle plot can also apply to Minimum Shift Keying $\rm (MSK)$ . In contrast, for non-coherent demodulation of BFSK, the modulation index must be a multiple of $h = 1$ .
This system comparison is once again based on the AWGN channel , characterized by the relationship $E_{\rm B}/N_0$. The equations for the bit error probabilities are as follows
- for Binary Phase Shift Keying $\rm (BPSK)$:
- $$p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{{2 \cdot E_{\rm B}}/{N_0 }} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ) = {1}/{2}\cdot {\rm erfc}\left ( \sqrt{{E_{\rm B}}/{N_0 }} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ),$$
- for Binary Frequency Shift Keying $\rm (BFSK)$ with coherent demodulation:
- $$p_{\rm B} = {\rm Q}\left ( \sqrt{{E_{\rm B}}/{N_0 }} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ) = {1}/{2}\cdot {\rm erfc}\left ( \sqrt{{E_{\rm B}}/(2 N_0 )} \hspace{0.1cm}\right ),$$
- for Binary Frequency Shift Keying $\rm (BFSK)$ with incoherent demodulation:
- $$p_{\rm B} = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm e}^{- E_{\rm B}/{(2N_0) }}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
It was shown in Exercise 4.8 , that for BPSK, the log ratio $10 · \lg \ E_{\rm B}/N_0$ must be at least $9.6 \ \rm dB$ so that the bit error probability does not exceed $p_{\rm B} = 10^{–5}$ .
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Nonlinear_Digital_Modulation.
- However, reference is also made to the page Linear Digital Modulation.
- Use the approximation $\lg(2) ≈ 0.3$.
Questions
Solution
- In other words: the coherent BFSK curve is $10 · \lg (2) ≈ 3 \ \rm dB$ to the right of the the BPSK curve.
- Thus, to guarantee $p_{\rm B} \le 10^{–5}$ it must hold that:
- $$10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.05cm}{E_{\rm B}} /{N_{\rm 0}}= 9.6\,\,{\rm dB} + 3\,\,{\rm dB} = \underline{12.6\,\,{\rm dB}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(2) Answer 2 is correct:
- The equation given does not just hold for MSK $($this is a FSK with $h = 0.5)$, but also for every form of orthogonal FSK.
- This is the case whenever the modulation index $h$ is an integer multiple of $0.5$ , such as when $h = 1$.
- When $h = 0.7$ , there is no orthogonal FSK.
(3) From the inverse function of the equation given we get:
- $$\frac{E_{\rm B}} {2 \cdot N_{\rm 0}}= {\rm ln}\hspace{0.05cm}\frac{1}{2 p_{\rm B}}= {\rm ln}(50000)\approx 10.82 \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}{E_{\rm B}} /{N_{\rm 0}}= 21.64 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.05cm}{E_{\rm B}}/ {N_{\rm 0}}\approx \underline{13.4\,\,{\rm dB}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) From $10 · \lg \ E_{\rm B}/N_0 = 12.6 \ \rm dB$ it follows that:
- $${E_{\rm B}} /{N_{\rm 0}}= 10^{1.26} \approx 16.8 \hspace{0.25cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.25cm} ({E_{\rm B}} /{N_{\rm 0}})/2 \approx 8.4 \hspace{0.25cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.25cm} p_{\rm B} = {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm e}^{- 8.4} \approx \underline{1.12 \cdot 10^{-4}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
This means that for the same $E_{\rm B}/N_0$, the error probability of incoherent demodulation is increased by a factor of $11$ compared to that of coherent demodulation (see answer to question 1) .