Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 5.4: Walsh Functions (PCCF, PACF)"
| (17 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite= | + | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Modulation_Methods/Spreading_Sequences_for_CDMA |
}} | }} | ||
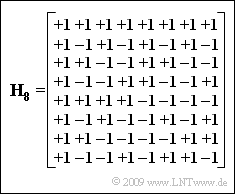
| − | [[File:P_ID1889__Mod_A_5_4.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P_ID1889__Mod_A_5_4.png|right|frame|Hadamard matrix ${\mathbf{H}_{8}}$]] |
| − | + | The so-called "Walsh functions", which can be constructed by means of the Hadamard matrix, are often used for band spreading and band compression. Starting from the matrix | |
:$${\mathbf{H}_{2}} = \left[ \begin{array}{ccc} +1 & +1 \\ +1 & -1 \end{array} \right] $$ | :$${\mathbf{H}_{2}} = \left[ \begin{array}{ccc} +1 & +1 \\ +1 & -1 \end{array} \right] $$ | ||
| − | + | the further Hadamard matrices $ {\mathbf{H}_{4}}$, $ {\mathbf{H}_{8}}$, etc. can be derived by the following recursion: | |
:$$ {\mathbf{H}_{2J}} = \left[ \begin{array}{ccc} \mathbf{H}_J & \mathbf{H}_J \\ \mathbf{H}_J & -\mathbf{H}_J \end{array} \right] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$ {\mathbf{H}_{2J}} = \left[ \begin{array}{ccc} \mathbf{H}_J & \mathbf{H}_J \\ \mathbf{H}_J & -\mathbf{H}_J \end{array} \right] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The diagram shows the matrix $ {\mathbf{H}_{8}}$ for the spreading factor $J = 8$. From this we can derive the spreading sequences | |
:$$ \langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | :$$ \langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
:$$ \langle w_\nu^{(2)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | :$$ \langle w_\nu^{(2)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
:$$...$$ | :$$...$$ | ||
| − | :$$\langle w_\nu^{(7)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{ | + | :$$\langle w_\nu^{(7)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm}$$ |
| − | + | for seven CDMA subscribers. The spreading sequence $ \langle w_\nu^{(0)}\rangle$ corresponding to the first row in the Hadamard matrix is usually not assigned because it does not spread. | |
| − | + | The questions mostly refer to the spreading factor $J = 4$. Thus, correspondingly, a maximum of three CDMA subscribers can be supplied with the spreading sequences $ \langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle$, $ \langle w_\nu^{(2)}\rangle$ and $ \langle w_\nu^{(3)}\rangle$, which result from the second, third and fourth rows of the matrix $ {\mathbf{H}_{4}}$. | |
| − | + | Regarding the correlation functions, the following nomenclature shall apply in this exercise: | |
| − | * | + | * The [[Modulation_Methods/Spreading_Sequences_for_CDMA#Periodic_ACF_and_CCF|periodic cross-correlation function]] $\rm (PCCF)$ between the sequences $ \langle w_\nu^{(i)}\rangle$ and $ \langle w_\nu^{(j)}\rangle$ is denoted by $φ_{ij}(λ)$. Here: |
:$${\it \varphi}_{ij}(\lambda) = {\rm E}\left [ w_{\nu}^{(i)} \cdot w_{\nu+ \lambda}^{(j)} \right ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$${\it \varphi}_{ij}(\lambda) = {\rm E}\left [ w_{\nu}^{(i)} \cdot w_{\nu+ \lambda}^{(j)} \right ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | * If $φ_{ij} \equiv 0$ $($that is: $φ_{ij}(λ) = 0$ for all values of $λ)$, the CDMA subscribers do not interfere with each other, even if they have different propagation times. |
| − | * | + | * If at least $φ_{ij}({\it λ} = 0) = 0$ applies, then no interference occurs, at least in synchronous CDMA operation $($no or equal propagation times of all subscribers$).$ |
| − | * | + | * The [[Modulation_Methods/Spreading_Sequences_for_CDMA#Periodic_ACF_and_CCF|periodic auto-correlation function]] $\rm (PACF)$ of the Walsh function $ \langle w_\nu^{(i)}\rangle$ is denoted by $φ_{ii}(λ)$, and it holds: |
:$${\it \varphi}_{ii}(\lambda) = {\rm E}\left [ w_{\nu}^{(i)} \cdot w_{\nu+ \lambda}^{(i)} \right ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$${\it \varphi}_{ii}(\lambda) = {\rm E}\left [ w_{\nu}^{(i)} \cdot w_{\nu+ \lambda}^{(i)} \right ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Notes: | ||
| + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Modulation_Methods/Spreizfolgen_für_CDMA|Spreading Sequences for CDMA]]. | ||
| + | *Reference is made in particular to the section [[Modulation_Methods/Spreading_Sequences_for_CDMA#Walsh_functions|Walsh functions]] in the theory part. | ||
| + | * We would also like to draw your attention to the interactive applet [[Applets:Generation_of_Walsh_functions|Generation of Walsh functions]]. | ||
| + | *The abscissa is normalized to the chip duration $T_c$. This means that $λ = 1$ actually describes a shift by the delay time $τ = T_c$. | ||
| − | === | + | |
| + | ===Questions=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | { | + | {What are the spreading sequences for $J = 4$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+ $ \langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle = +\hspace{-0.05cm}1 -\hspace{-0.15cm}1 +\hspace{-0.15cm}1 -\hspace{-0.15cm}1$, | + $ \langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle = +\hspace{-0.05cm}1 -\hspace{-0.15cm}1 +\hspace{-0.15cm}1 -\hspace{-0.15cm}1$, | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
+ $ \langle w_\nu^{(3)}\rangle = +\hspace{-0.05cm}1 -\hspace{-0.15cm}1 -\hspace{-0.15cm}1 +\hspace{-0.15cm}1$. | + $ \langle w_\nu^{(3)}\rangle = +\hspace{-0.05cm}1 -\hspace{-0.15cm}1 -\hspace{-0.15cm}1 +\hspace{-0.15cm}1$. | ||
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true regarding the PCCF values $φ_{ij}(λ = 0)$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + For $J = 4$, $φ_{12}(λ = 0) = 0$. |
| − | + | + | + For $J = 4$, $φ_{13}(λ = 0) = 0$. |
| − | + | + | + For $J = 4$, $φ_{23}(λ = 0) = 0$. |
| − | - | + | - For $J = 8$, $φ_{ij}(λ = 0) ≠ 0$ may well hold $(i ≠ j)$. |
| − | + | + | + In synchronous CDMA, the subscribers do not interfere with each other. |
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true for the PCCF values with $λ ≠ 0$? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + For all values of $λ$, the PCCF is $φ_{12}(λ) = 0$. |
| − | + | + | + For all values of $λ$, the PCCF is $φ_{13}(λ) = 0$. |
| − | - | + | - For all values of $λ$, the PCCF is $φ_{23}(λ) = 0$. |
| − | - | + | - In asynchronous CDMA, the subscribers do not interfere with each other. |
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true for the PACF curves? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + All $φ_{ii}(λ)$ curves are periodic. |
| − | + | + | + $φ_{11}(λ = 0) = +\hspace{-0.05cm}1$ and $φ_{11}(λ = 1) = -\hspace{-0.05cm}1$ hold. |
| − | - | + | - $φ_{22}(λ) = φ_{11}(λ)$ holds. |
| − | + | + | + $φ_{33}(λ) = φ_{22}(λ)$ holds. |
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''1 | + | '''(1)''' <u>All solutions</u> are correct: |
| + | *The matrix $ {\mathbf{H}_{4}}$ is the upper left submatrix of $ {\mathbf{H}_{8}}$. | ||
| + | *The spreading sequences result from the rows 2, 3 and 4 of $ {\mathbf{H}_{4}}$, and agree with the given sequences. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ''' | + | '''(2)''' <u>Solutions 1, 2 and 3</u> are correct: |
| − | $$\ | + | *According to the equations in the data section, the following holds: |
| − | $$\ | + | :$${\it \varphi}_{12}(\lambda = 0) = 1/4 \cdot \left [ (+1) \cdot (+1) + (-1) \cdot (+1) + (+1) \cdot (-1) + (-1) \cdot (-1) \right ] = 0\hspace{0.05cm},$$ |
| − | + | :$${\it \varphi}_{13}(\lambda = 0) = 1/4\cdot \left [ (+1) \cdot (+1) + (-1) \cdot (-1) + (+1) \cdot (-1) + (-1) \cdot (+1) \right ] = 0\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | |
| − | $$\ | + | :$${\it \varphi}_{23}(\lambda = 0) =1/4 \cdot \left [ (+1) \cdot (+1) + (+1) \cdot (-1) + (-1) \cdot (-1) + (-1) \cdot (+1) \right ] = 0\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | + | *Also, for larger values of $J$, for $i ≠ j$ the PCCF value is always $φ_{ij}(λ = 0)= 0$. | |
| − | + | *It follows: In synchronous CDMA, the subscribers do not interfere with each other. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[File:P_ID1890__Mod_A_5_4c.png]] | + | '''(3)''' <u>Solutions 1 and 2</u> are correct: |
| + | *For all values of $λ$, the PCCF is $φ_{12}(λ) = 0$, as shown by the following lines: | ||
| + | :$$\langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$ $$\langle w_\nu^{(2)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm product\hspace{0.1cm} with \hspace{0.1cm}}\langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle: {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$$\langle w_{\nu+1}^{(2)}\rangle = {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm product\hspace{0.1cm} with \hspace{0.1cm}}\langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle: {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$$\langle w_{\nu+2}^{(2)}\rangle = {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm}{\rm product\hspace{0.1cm} with \hspace{0.1cm}}\langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle: {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$$\langle w_{\nu+3}^{(2)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm}{\rm product\hspace{0.1cm} with \hspace{0.1cm}}\langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle: {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$$\langle w_{\nu+4}^{(2)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} = \langle w_\nu^{(2)}\rangle \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
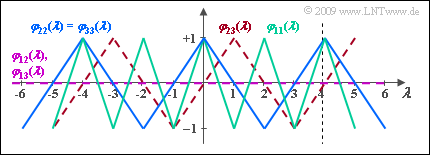
| + | [[File:P_ID1890__Mod_A_5_4c.png|right|frame|Some PCCF and PACF curves]] | ||
| + | *The same is true for the PCCF $φ_{13}(λ)$. | ||
| + | *In contrast, for the PCCF between the sequences $ \langle w_\nu^{(2)}\rangle$ and $ \langle w_\nu^{(3)}\rangle$ we obtain: | ||
| + | :$${\it \varphi}_{23}(\lambda ) = \left\{ \begin{array}{c}0 \\+1\\ -1 \\ \end{array} \right. \begin{array}{*{10}c} {\rm{for}} \\ {\rm{for}} \\ {\rm{for}} \\ \end{array} \begin{array}{*{20}c} \lambda = 0, \pm 2, \pm 4,\pm 6, ... \hspace{0.05cm}, \\ \hspace{0.14cm} \lambda = ... \hspace{0.05cm} , -3, +1, +5, ... \hspace{0.05cm}, \\ \hspace{0.14cm} \lambda = ... \hspace{0.05cm} , -5, -1, +3, ... \hspace{0.05cm}. \\ \end{array}$$ | ||
| + | *This means: If the signal from subscriber $3$ is delayed by one spreading chip with respect to subscriber $2$ or vice versa, the subscribers can no longer be separated and there is a significant increase in the error probability. | ||
| + | *In the diagram, the PCCF curves are drawn in dashed lines (violet and red). | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''(4)''' <u>Statements 1, 2 and 4</u> are correct: | |
| + | * Since the Walsh function no. $1$ is periodic with $T_0 = 2T_c$, the PACF is also periodic with $λ = 2$. | ||
| + | *The second statement is correct, as shown by the following calculation (green curve): | ||
| + | :$${\it \varphi}_{11}(\lambda = 0) = 1/4 \cdot \big [ (+1) \cdot (+1) + (-1) \cdot (-1) + (+1) \cdot (+1) + (-1) \cdot (-1) \big ] = +1\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
| + | :$${\it \varphi}_{11}(\lambda = 1) = 1/4 \cdot \big [ (+1) \cdot (-1) + (+1) \cdot (-1) + (+1) \cdot (-1) + (+1) \cdot (-1) \big ] = -1\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | *Since the two Walsh functions no. $2$ and $3$ differ only by a shift around $T_c$ and a phase in the PACF has no effect in principle, in fact, according to the last statement, $φ_{33}(λ) = φ_{22}(λ)$. These two PACF functions are plotted in blue. | ||
| + | *In contrast, $φ_{22}(λ)$ differs from $φ_{11}(λ)$ by a different periodicity: $φ_{22}(λ) = φ_{33}(λ)$ is twice as wide as $φ_{11}(λ)$. | ||
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
| Line 106: | Line 113: | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Modulation Methods: Exercises|^5.3 Spread Sequences for CDMA^]] |
Latest revision as of 16:31, 13 December 2021
The so-called "Walsh functions", which can be constructed by means of the Hadamard matrix, are often used for band spreading and band compression. Starting from the matrix
- $${\mathbf{H}_{2}} = \left[ \begin{array}{ccc} +1 & +1 \\ +1 & -1 \end{array} \right] $$
the further Hadamard matrices $ {\mathbf{H}_{4}}$, $ {\mathbf{H}_{8}}$, etc. can be derived by the following recursion:
- $$ {\mathbf{H}_{2J}} = \left[ \begin{array}{ccc} \mathbf{H}_J & \mathbf{H}_J \\ \mathbf{H}_J & -\mathbf{H}_J \end{array} \right] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The diagram shows the matrix $ {\mathbf{H}_{8}}$ for the spreading factor $J = 8$. From this we can derive the spreading sequences
- $$ \langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ \langle w_\nu^{(2)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$...$$
- $$\langle w_\nu^{(7)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm}{+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm}$$
for seven CDMA subscribers. The spreading sequence $ \langle w_\nu^{(0)}\rangle$ corresponding to the first row in the Hadamard matrix is usually not assigned because it does not spread.
The questions mostly refer to the spreading factor $J = 4$. Thus, correspondingly, a maximum of three CDMA subscribers can be supplied with the spreading sequences $ \langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle$, $ \langle w_\nu^{(2)}\rangle$ and $ \langle w_\nu^{(3)}\rangle$, which result from the second, third and fourth rows of the matrix $ {\mathbf{H}_{4}}$.
Regarding the correlation functions, the following nomenclature shall apply in this exercise:
- The periodic cross-correlation function $\rm (PCCF)$ between the sequences $ \langle w_\nu^{(i)}\rangle$ and $ \langle w_\nu^{(j)}\rangle$ is denoted by $φ_{ij}(λ)$. Here:
- $${\it \varphi}_{ij}(\lambda) = {\rm E}\left [ w_{\nu}^{(i)} \cdot w_{\nu+ \lambda}^{(j)} \right ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- If $φ_{ij} \equiv 0$ $($that is: $φ_{ij}(λ) = 0$ for all values of $λ)$, the CDMA subscribers do not interfere with each other, even if they have different propagation times.
- If at least $φ_{ij}({\it λ} = 0) = 0$ applies, then no interference occurs, at least in synchronous CDMA operation $($no or equal propagation times of all subscribers$).$
- The periodic auto-correlation function $\rm (PACF)$ of the Walsh function $ \langle w_\nu^{(i)}\rangle$ is denoted by $φ_{ii}(λ)$, and it holds:
- $${\it \varphi}_{ii}(\lambda) = {\rm E}\left [ w_{\nu}^{(i)} \cdot w_{\nu+ \lambda}^{(i)} \right ] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Notes:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter Spreading Sequences for CDMA.
- Reference is made in particular to the section Walsh functions in the theory part.
- We would also like to draw your attention to the interactive applet Generation of Walsh functions.
- The abscissa is normalized to the chip duration $T_c$. This means that $λ = 1$ actually describes a shift by the delay time $τ = T_c$.
Questions
Solution
- The matrix $ {\mathbf{H}_{4}}$ is the upper left submatrix of $ {\mathbf{H}_{8}}$.
- The spreading sequences result from the rows 2, 3 and 4 of $ {\mathbf{H}_{4}}$, and agree with the given sequences.
(2) Solutions 1, 2 and 3 are correct:
- According to the equations in the data section, the following holds:
- $${\it \varphi}_{12}(\lambda = 0) = 1/4 \cdot \left [ (+1) \cdot (+1) + (-1) \cdot (+1) + (+1) \cdot (-1) + (-1) \cdot (-1) \right ] = 0\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $${\it \varphi}_{13}(\lambda = 0) = 1/4\cdot \left [ (+1) \cdot (+1) + (-1) \cdot (-1) + (+1) \cdot (-1) + (-1) \cdot (+1) \right ] = 0\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $${\it \varphi}_{23}(\lambda = 0) =1/4 \cdot \left [ (+1) \cdot (+1) + (+1) \cdot (-1) + (-1) \cdot (-1) + (-1) \cdot (+1) \right ] = 0\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Also, for larger values of $J$, for $i ≠ j$ the PCCF value is always $φ_{ij}(λ = 0)= 0$.
- It follows: In synchronous CDMA, the subscribers do not interfere with each other.
(3) Solutions 1 and 2 are correct:
- For all values of $λ$, the PCCF is $φ_{12}(λ) = 0$, as shown by the following lines:
- $$\langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$ $$\langle w_\nu^{(2)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm product\hspace{0.1cm} with \hspace{0.1cm}}\langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle: {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$\langle w_{\nu+1}^{(2)}\rangle = {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.3cm}{\rm product\hspace{0.1cm} with \hspace{0.1cm}}\langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle: {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$\langle w_{\nu+2}^{(2)}\rangle = {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm}{\rm product\hspace{0.1cm} with \hspace{0.1cm}}\langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle: {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$\langle w_{\nu+3}^{(2)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm}{\rm product\hspace{0.1cm} with \hspace{0.1cm}}\langle w_\nu^{(1)}\rangle: {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$\langle w_{\nu+4}^{(2)}\rangle = {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {+\hspace{-0.05cm}1} \hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1}\hspace{0.15cm} {-\hspace{-0.05cm}1} = \langle w_\nu^{(2)}\rangle \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The same is true for the PCCF $φ_{13}(λ)$.
- In contrast, for the PCCF between the sequences $ \langle w_\nu^{(2)}\rangle$ and $ \langle w_\nu^{(3)}\rangle$ we obtain:
- $${\it \varphi}_{23}(\lambda ) = \left\{ \begin{array}{c}0 \\+1\\ -1 \\ \end{array} \right. \begin{array}{*{10}c} {\rm{for}} \\ {\rm{for}} \\ {\rm{for}} \\ \end{array} \begin{array}{*{20}c} \lambda = 0, \pm 2, \pm 4,\pm 6, ... \hspace{0.05cm}, \\ \hspace{0.14cm} \lambda = ... \hspace{0.05cm} , -3, +1, +5, ... \hspace{0.05cm}, \\ \hspace{0.14cm} \lambda = ... \hspace{0.05cm} , -5, -1, +3, ... \hspace{0.05cm}. \\ \end{array}$$
- This means: If the signal from subscriber $3$ is delayed by one spreading chip with respect to subscriber $2$ or vice versa, the subscribers can no longer be separated and there is a significant increase in the error probability.
- In the diagram, the PCCF curves are drawn in dashed lines (violet and red).
(4) Statements 1, 2 and 4 are correct:
- Since the Walsh function no. $1$ is periodic with $T_0 = 2T_c$, the PACF is also periodic with $λ = 2$.
- The second statement is correct, as shown by the following calculation (green curve):
- $${\it \varphi}_{11}(\lambda = 0) = 1/4 \cdot \big [ (+1) \cdot (+1) + (-1) \cdot (-1) + (+1) \cdot (+1) + (-1) \cdot (-1) \big ] = +1\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $${\it \varphi}_{11}(\lambda = 1) = 1/4 \cdot \big [ (+1) \cdot (-1) + (+1) \cdot (-1) + (+1) \cdot (-1) + (+1) \cdot (-1) \big ] = -1\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Since the two Walsh functions no. $2$ and $3$ differ only by a shift around $T_c$ and a phase in the PACF has no effect in principle, in fact, according to the last statement, $φ_{33}(λ) = φ_{22}(λ)$. These two PACF functions are plotted in blue.
- In contrast, $φ_{22}(λ)$ differs from $φ_{11}(λ)$ by a different periodicity: $φ_{22}(λ) = φ_{33}(λ)$ is twice as wide as $φ_{11}(λ)$.