Difference between revisions of "Signal Representation/Possible Errors when using DFT"
(Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „ {{Header |Untermenü=Zeit- und frequenzdiskrete Signaldarstellung |Vorherige Seite=Diskrete Fouriertransformation (DFT) |Nächste Seite=Spektralanalyse }} =…“) |
|||
| (70 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Header | {{Header | ||
| − | |Untermenü= | + | |Untermenü=Time and Frequency-Discrete Signal Representation |
| − | |Vorherige Seite= | + | |Vorherige Seite=Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) |
| − | |Nächste Seite= | + | |Nächste Seite=Spectrum Analysis |
}} | }} | ||
| − | == | + | ==The mean square error as a quality criteria== |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | In the following, we briefly discuss some error possibilities when applying the DFT, whereby we restrict ourselves to the transformation from the time to the frequency domain. Even in its samples, the spectrum $D(\mu )/f_{\rm A}$ determined via the DFT will generally differ from the actual spectrum $X(\mu \cdot f_{\rm A})$ due to two processes: | ||
| + | *the »sampling«, that is, the reduction of information about $x(t)$ to $N$ numerical values, | ||
| − | + | *the »windowing» that may falsely limit the signal $x(t)$. | |
| − | * | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {{BlaueBox|TEXT= | |
| + | $\text{Definition:}$ | ||
| + | A quality criteria that takes both error types into account is the »'''mean square error'''« $($German: "mittlerer quadratischer Fehler" ⇒ $\rm MQF)$: | ||
| − | $${\rm MQF} = \frac{1}{N}\cdot \sum_{\mu = 0 }^{N-1} | + | :$${\rm MQF} = \frac{1}{N}\cdot \sum_{\mu = 0 }^{N-1} |
| − | \left | + | \left\vert X(\mu \cdot f_{\rm A})-\frac{D(\mu)}{f_{\rm A} }\right \vert^2 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | + | It is always ${\rm MQF} \ne 0$, since with finite $N$ the degradation due to sampling and due to windowing cannot be made zero at the same time.}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | { | + | The magnitude of this evaluation quantity ${\rm MQF}$ depends on the following parameters: |
| − | + | #The properties of the present signal $x(t)$ and of its spectrum $X(f)$, | |
| − | + | #the DFT parameter $N$; the larger $N$ is chosen, the smaller ${\rm MQF}$ becomes, | |
| − | $$ | + | #one of the four further DFT parameters, e.g. $f_{\rm A}$. |
| − | |||
| − | + | For a given $N$ the other DFT parameters are determined via the equations | |
| + | :$$f_{\rm P} = N \cdot f_{\rm A},$$ | ||
| + | :$$T_{\rm P} = 1/f_{\rm A},$$ | ||
| + | :$$T_{\rm A} = T_{\rm P}/N.$$ | ||
| − | + | We refer you already here to the following $($German language$)$ learning video, which clarifies the content of this chapter:<br> [[Fehlermöglichkeiten_bei_Anwendung_der_DFT_(Lernvideo)|»Fehlermöglichkeiten bei Anwendung der DFT«]] ⇒ "Possible errors when using the DFT". | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {{GraueBox|TEXT= | ||
| + | $\text{Example 1:}$ | ||
| + | As an example, we consider a Gaussian pulse with equivalent pulse duration $\Delta t = T$, where $T$ is simultaneously used as a normalization parameter: | ||
| + | [[File:EN_Sig_T_5_1_S1.png|right|frame|Quasi error-free DFT with $N = 16$; ${\rm MQF}$: mean square error <u>Note:</u><br>The given $\text{MQF}$ values apply to a 16 bit processor. For a 32 bit processor $($smaller quantization errors of the computer$)$ $\text{MQF}$ would be even smaller, but never zero.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | :$$x(t) = {\rm e}^{- \pi (t/T)^2} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The Gaussian pulse is very suitable for the application of the DFT due to its fast $($exponential$)$ decay in both time and frequency domain. | |
| + | The graph below shows the DFT result | ||
| + | *for $N = 16$ and | ||
| + | *$T_{\rm A}/T = 0.25$ ⇒ $f_{\rm A} \cdot T = 0.25$ ⇒ $T_{\rm P}/T = 4$. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | The following should be noted about this plot: | |
| − | + | #The considered samples of $x(t)$ are in the range $\vert t/T \vert≤ 2$. Since $x(\pm 2T)$ is very small, periodization in time domain with $T_{\rm P}/T = N \cdot T_{\rm A}/T = 4$ does not lead to serious errors. | |
| − | + | #With $f_{\rm A} \cdot T = 0.25$ and $N = 16$ the $($normalized$)$ DFT parameter is $f_{\rm P} \cdot T = 4$. The discrete spectral lines thus lie in the range $-2/T ≤ f < +2/T$. | |
| − | + | #The mean squared error is relatively small $\text{(MQF} \approx 10^{-12})$, which is due to the favourable choice of $f_{\rm A} \cdot T = 0.25$ $($for the given $N = 16)$ . | |
| − | + | #The DFT accuracy can be improved by increasing $N$ : | |
| − | + | #For $N = 1024$ the minimum value $\text{MQF} \approx 8 \cdot 10^{-17}$ is obtained, if $f_{\rm A} \cdot T = 0.125$ is chosen. | |
| − | + | #The following then applies to the other DFT parameters: | |
| + | :: $$f_{\rm P} \cdot T = 128, \hspace{0.5cm}T_{\rm A}/T = 1/128, \hspace{0.5cm} T_{\rm P}/T = N \cdot T_{\rm A}/T= 8.$$ }} | ||
| − | + | ==DFT falsification due to windowing – Truncation error== | |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | A typical error when using the DFT is due to »windowing«. This falsification, known as »'''truncation error'''« can be explained as follows: | ||
| + | #The windowing implicit in the DFT algorithm corresponds to the multiplication of the signal $x(t)$ by a rectangular function of height $1$ and duration $T_{\rm P} = N \cdot T_{\rm A}$. | ||
| + | #If the signal $x(t)$ is not limited to the range $T_{\rm P}$ the DFT result does not coincide with the actual spectrum $X(f)$ but is obtained from it by convolution with the spectral function $T_{\rm P} \cdot \text{sinc}(f\cdot T_{\rm P})$. | ||
| + | #In the limiting case $T_{\rm P} \to \infty$, which for a given distance $T_{\rm A}$ of the samples would also mean an infinitely large number $N$ of interpolation points, $T_{\rm P} \cdot \text{sinc}(f\cdot T_{\rm P})$ degenerates to a Dirac delta function and the original spectrum $X(f)$ would remain. | ||
| + | #The DFT of an unlimited signal in time – for example a periodic signal – will always cause a truncation error which can only be kept within limits by special measures. This is discussed in more detail in the chapter [[Signal_Representation/Spectrum_Analysis|»Spectrum Analysis«]]. | ||
| + | #For time-limited signals ⇒ »pulses«, the truncation error can be avoided by choosing $T_{\rm P}$ sufficiently large. By further enlarging the window into areas with $x(t) \equiv 0$ no additional information gain results ⇒ $\text{MQF}$ does not become smaller. | ||
| + | #By this addition of zeros called »'''zero-padding'''« the $X(f)$ samples now occur at a smaller distance $f_{\rm A} = 1/T_{\rm A}$. By doubling $T_{\rm P}$ one achieves an interpolation of the frequency samples exactly in the middle between two previous grid points. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | The following example shows a »truncation error« due to unfavourably chosen DFT parameters. Again, we refer to the learning video $($in German language$)$ <br> [[Fehlermöglichkeiten_bei_Anwendung_der_DFT_(Lernvideo)|»Fehlermöglichkeiten bei Anwendung der DFT«]] ⇒ "Possible errors when using the DFT". |
| − | + | {{GraueBox|TEXT= | |
| − | * | + | $\text{Example 2:}$ |
| − | + | The graph shows the DFT result for the same $x(t)$ and $X(f)$ as well as the same $N = 16$ as in [[Signal_Representation/Possible_Errors_when_using_DFT#The_mean_square_error_as_a_quality_criteria|$\text{Example 1}$]], but now with finer sampling in the time domain by a factor of $2$ ⇒ $T_{\rm A}/T = 0.125$ | |
| − | + | [[File:EN_Sig_T_5_1_S2.png|right|frame|Truncation error for a DFT with $N = 16$; ${\rm MQF}$: Mean square error]] | |
| + | |||
| + | The comparison with [[Signal_Representation/Possible_Errors_when_using_DFT#The_mean_square_error_as_a_quality_criteria|$\text{Example 1}$]] shows: | ||
| + | *The spacing of the frequency samples increases from $f_{\rm A} \cdot T = 0.25$ to $f_{\rm A} \cdot T = 0.5$ . | ||
| + | *At the same time, $T_{\rm P}/T$ decreases from $4$ to $2$. | ||
| − | + | *With this, only the signal components in the range $\vert t \vert < T$ are now captured by the DFT. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ⇒ With these parameters, a »truncation error« or »termination error« arises, by which the mean square error is significantly increased from $\rm MQF= 10^{-12}$ to $\rm MQF= 4 \cdot 10^{-5}$. | |
| − | + | }} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==DFT falsification due to sampling – Aliasing error== | |
| + | <br> | ||
| − | + | An unsuitable sampling of the time function $x(t)$ can also significantly falsify the DFT result. This so-called »'''aliasing error'''« can be explained as follows: | |
| − | + | *Sampling $x(t)$ at a distance $T_{\rm A}$ causes a periodic continuation of the spectrum at multiples of the periodization frequency $f_{\rm P} = 1/T_{\rm A}$. | |
| − | + | *If $X(f)$ has spectral components at $|f| > f_{\rm P}/2$, the sampling theorem is not fulfilled and overlaps of the shifted frequency components to be added occur. | |
| − | + | *Only with a band-limited signal the aliasing error can be avoided by suitable DFT parameters. In contrast, this error is unavoidable with time-limited signals ⇒ »pulses«, since time-limited signals cannot be band-limited at the same time. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | *The aliasing error is reduced by finer sampling $($smaller $T_{\rm A} = 1/f_{\rm P})$. This can only be achieved with a constant $T_{\rm A}$ – in order not to let the truncation error increase – by a larger $N$ and thus a greater computational effort. | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | The following $\text{Example 3}$ shows such an aliasing error due to wrongly chosen DFT parameters: |
| − | + | *Compared to the comparison system according to [[Signal_Representation/Possible_Errors_when_using_DFT#The_mean_square_error_as_a_quality_criteria|$\text{Example 1}$]]: $T_{\rm A}$ is too large and $f_{\rm A}$ is too small dimensioned. | |
| − | * | + | |
| + | *The number of interpolation points is in both cases: $N = 16$. | ||
| − | + | {{GraueBox|TEXT= | |
| − | + | $\text{Example 3:}$ | |
| − | * | + | Let the DFT parameters be $N = 16$ and $f_{\rm A} \cdot T= 0.125$. Thus, we get for the other three DFT parameters: |
| + | [[File:EN_Sig_T_5_1_S3._neu.png|right|frame|Aliasing error of a DFT with $N = 16$; ${\rm MQF}$: mean square error]] | ||
| + | * $T_{\rm P}/T = 8 \hspace{0.8cm} \text{(Example 1:} \ \ T_{\rm P}/T = 4)$, | ||
| + | * $f_{\rm P} \cdot T = 2 \hspace{0.75cm} \text{(Example 1:} \ \ f_{\rm P} \cdot T = 4)$, | ||
| + | * $T_{\rm A}/T = 0.5\hspace{0.45cm} \text{(Example 1:} \ \ T_{\rm A}/T = 0.25)$. | ||
| − | {{ | + | This results in the following consequences: |
| + | #The truncation error continues to play no role because of $T_{\rm P} /T = 8$ $($already $T_{\rm P} /T = 4$ was sufficient$)$. | ||
| + | #However, aliasing now arises, because the DFT is derived from many Gaussian functions at distance $f_{\rm P} \cdot T = 2$ $($thin dashed curves in the graph$)$. | ||
| + | #The DFT coefficients are falsified differently: The mean DFT coefficient $($for $f = 0)$ is almost correct, while the errors of the DFT coefficients increase significantly towards the edges. | ||
| + | #Here, the DFT coefficient for $f \cdot T = -1$ is twice as large as it should be, since the Gaussian function with the center at $f \cdot T = -2$ gives the same contribution as the Gaussian function around $f \cdot T = 0$ (see yellow background). | ||
| − | + | Thus, here with $\text{MQF} \approx 2 \cdot 10^{-4}$ an error value four times larger than that caused by the truncation error in [[Signal_Representation/Possible_Errors_when_using_DFT#DFT_falsification_due_to_windowing_.E2.80.93_Truncation_error|$\text{Example 2}$]]. | |
| + | Again, we refer to the $($German language$)$ learning video:<br> [[Fehlermöglichkeiten_bei_Anwendung_der_DFT_(Lernvideo)|»Fehlermöglichkeiten bei Anwendung der DFT«]] ⇒ "Possible errors when using the DFT". }} | ||
| + | ==Exercises for the chapter== | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[Aufgaben:Exercise 5.3: Mean Square Error|Exercise 5.3: Mean Square Error]] | ||
| + | [[Aufgaben:Exercise 5.3Z: Zero-Padding|Exercise 5.3Z: Zero-Padding]] | ||
{{Display}} | {{Display}} | ||
Latest revision as of 17:16, 24 June 2023
Contents
The mean square error as a quality criteria
In the following, we briefly discuss some error possibilities when applying the DFT, whereby we restrict ourselves to the transformation from the time to the frequency domain. Even in its samples, the spectrum $D(\mu )/f_{\rm A}$ determined via the DFT will generally differ from the actual spectrum $X(\mu \cdot f_{\rm A})$ due to two processes:
- the »sampling«, that is, the reduction of information about $x(t)$ to $N$ numerical values,
- the »windowing» that may falsely limit the signal $x(t)$.
$\text{Definition:}$ A quality criteria that takes both error types into account is the »mean square error« $($German: "mittlerer quadratischer Fehler" ⇒ $\rm MQF)$:
- $${\rm MQF} = \frac{1}{N}\cdot \sum_{\mu = 0 }^{N-1} \left\vert X(\mu \cdot f_{\rm A})-\frac{D(\mu)}{f_{\rm A} }\right \vert^2 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
It is always ${\rm MQF} \ne 0$, since with finite $N$ the degradation due to sampling and due to windowing cannot be made zero at the same time.
The magnitude of this evaluation quantity ${\rm MQF}$ depends on the following parameters:
- The properties of the present signal $x(t)$ and of its spectrum $X(f)$,
- the DFT parameter $N$; the larger $N$ is chosen, the smaller ${\rm MQF}$ becomes,
- one of the four further DFT parameters, e.g. $f_{\rm A}$.
For a given $N$ the other DFT parameters are determined via the equations
- $$f_{\rm P} = N \cdot f_{\rm A},$$
- $$T_{\rm P} = 1/f_{\rm A},$$
- $$T_{\rm A} = T_{\rm P}/N.$$
We refer you already here to the following $($German language$)$ learning video, which clarifies the content of this chapter:
»Fehlermöglichkeiten bei Anwendung der DFT« ⇒ "Possible errors when using the DFT".
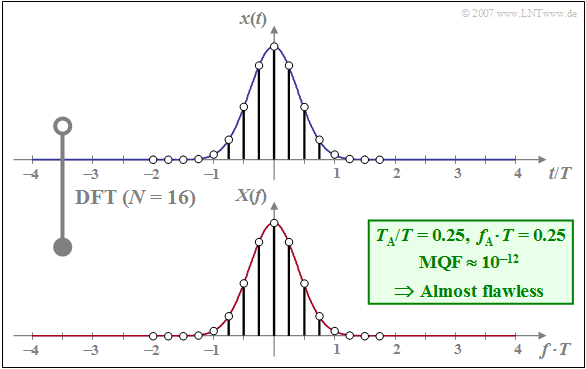
$\text{Example 1:}$ As an example, we consider a Gaussian pulse with equivalent pulse duration $\Delta t = T$, where $T$ is simultaneously used as a normalization parameter:
- $$x(t) = {\rm e}^{- \pi (t/T)^2} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The Gaussian pulse is very suitable for the application of the DFT due to its fast $($exponential$)$ decay in both time and frequency domain.
The graph below shows the DFT result
- for $N = 16$ and
- $T_{\rm A}/T = 0.25$ ⇒ $f_{\rm A} \cdot T = 0.25$ ⇒ $T_{\rm P}/T = 4$.
The following should be noted about this plot:
- The considered samples of $x(t)$ are in the range $\vert t/T \vert≤ 2$. Since $x(\pm 2T)$ is very small, periodization in time domain with $T_{\rm P}/T = N \cdot T_{\rm A}/T = 4$ does not lead to serious errors.
- With $f_{\rm A} \cdot T = 0.25$ and $N = 16$ the $($normalized$)$ DFT parameter is $f_{\rm P} \cdot T = 4$. The discrete spectral lines thus lie in the range $-2/T ≤ f < +2/T$.
- The mean squared error is relatively small $\text{(MQF} \approx 10^{-12})$, which is due to the favourable choice of $f_{\rm A} \cdot T = 0.25$ $($for the given $N = 16)$ .
- The DFT accuracy can be improved by increasing $N$ :
- For $N = 1024$ the minimum value $\text{MQF} \approx 8 \cdot 10^{-17}$ is obtained, if $f_{\rm A} \cdot T = 0.125$ is chosen.
- The following then applies to the other DFT parameters:
- $$f_{\rm P} \cdot T = 128, \hspace{0.5cm}T_{\rm A}/T = 1/128, \hspace{0.5cm} T_{\rm P}/T = N \cdot T_{\rm A}/T= 8.$$
DFT falsification due to windowing – Truncation error
A typical error when using the DFT is due to »windowing«. This falsification, known as »truncation error« can be explained as follows:
- The windowing implicit in the DFT algorithm corresponds to the multiplication of the signal $x(t)$ by a rectangular function of height $1$ and duration $T_{\rm P} = N \cdot T_{\rm A}$.
- If the signal $x(t)$ is not limited to the range $T_{\rm P}$ the DFT result does not coincide with the actual spectrum $X(f)$ but is obtained from it by convolution with the spectral function $T_{\rm P} \cdot \text{sinc}(f\cdot T_{\rm P})$.
- In the limiting case $T_{\rm P} \to \infty$, which for a given distance $T_{\rm A}$ of the samples would also mean an infinitely large number $N$ of interpolation points, $T_{\rm P} \cdot \text{sinc}(f\cdot T_{\rm P})$ degenerates to a Dirac delta function and the original spectrum $X(f)$ would remain.
- The DFT of an unlimited signal in time – for example a periodic signal – will always cause a truncation error which can only be kept within limits by special measures. This is discussed in more detail in the chapter »Spectrum Analysis«.
- For time-limited signals ⇒ »pulses«, the truncation error can be avoided by choosing $T_{\rm P}$ sufficiently large. By further enlarging the window into areas with $x(t) \equiv 0$ no additional information gain results ⇒ $\text{MQF}$ does not become smaller.
- By this addition of zeros called »zero-padding« the $X(f)$ samples now occur at a smaller distance $f_{\rm A} = 1/T_{\rm A}$. By doubling $T_{\rm P}$ one achieves an interpolation of the frequency samples exactly in the middle between two previous grid points.
The following example shows a »truncation error« due to unfavourably chosen DFT parameters. Again, we refer to the learning video $($in German language$)$
»Fehlermöglichkeiten bei Anwendung der DFT« ⇒ "Possible errors when using the DFT".
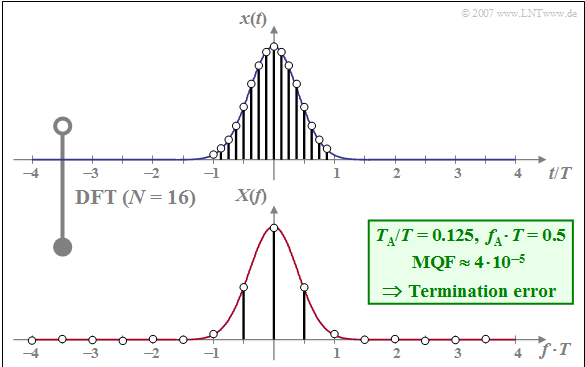
$\text{Example 2:}$ The graph shows the DFT result for the same $x(t)$ and $X(f)$ as well as the same $N = 16$ as in $\text{Example 1}$, but now with finer sampling in the time domain by a factor of $2$ ⇒ $T_{\rm A}/T = 0.125$
The comparison with $\text{Example 1}$ shows:
- The spacing of the frequency samples increases from $f_{\rm A} \cdot T = 0.25$ to $f_{\rm A} \cdot T = 0.5$ .
- At the same time, $T_{\rm P}/T$ decreases from $4$ to $2$.
- With this, only the signal components in the range $\vert t \vert < T$ are now captured by the DFT.
⇒ With these parameters, a »truncation error« or »termination error« arises, by which the mean square error is significantly increased from $\rm MQF= 10^{-12}$ to $\rm MQF= 4 \cdot 10^{-5}$.
DFT falsification due to sampling – Aliasing error
An unsuitable sampling of the time function $x(t)$ can also significantly falsify the DFT result. This so-called »aliasing error« can be explained as follows:
- Sampling $x(t)$ at a distance $T_{\rm A}$ causes a periodic continuation of the spectrum at multiples of the periodization frequency $f_{\rm P} = 1/T_{\rm A}$.
- If $X(f)$ has spectral components at $|f| > f_{\rm P}/2$, the sampling theorem is not fulfilled and overlaps of the shifted frequency components to be added occur.
- Only with a band-limited signal the aliasing error can be avoided by suitable DFT parameters. In contrast, this error is unavoidable with time-limited signals ⇒ »pulses«, since time-limited signals cannot be band-limited at the same time.
- The aliasing error is reduced by finer sampling $($smaller $T_{\rm A} = 1/f_{\rm P})$. This can only be achieved with a constant $T_{\rm A}$ – in order not to let the truncation error increase – by a larger $N$ and thus a greater computational effort.
The following $\text{Example 3}$ shows such an aliasing error due to wrongly chosen DFT parameters:
- Compared to the comparison system according to $\text{Example 1}$: $T_{\rm A}$ is too large and $f_{\rm A}$ is too small dimensioned.
- The number of interpolation points is in both cases: $N = 16$.
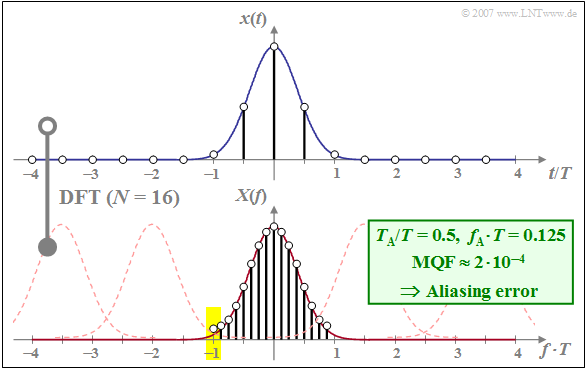
$\text{Example 3:}$ Let the DFT parameters be $N = 16$ and $f_{\rm A} \cdot T= 0.125$. Thus, we get for the other three DFT parameters:
- $T_{\rm P}/T = 8 \hspace{0.8cm} \text{(Example 1:} \ \ T_{\rm P}/T = 4)$,
- $f_{\rm P} \cdot T = 2 \hspace{0.75cm} \text{(Example 1:} \ \ f_{\rm P} \cdot T = 4)$,
- $T_{\rm A}/T = 0.5\hspace{0.45cm} \text{(Example 1:} \ \ T_{\rm A}/T = 0.25)$.
This results in the following consequences:
- The truncation error continues to play no role because of $T_{\rm P} /T = 8$ $($already $T_{\rm P} /T = 4$ was sufficient$)$.
- However, aliasing now arises, because the DFT is derived from many Gaussian functions at distance $f_{\rm P} \cdot T = 2$ $($thin dashed curves in the graph$)$.
- The DFT coefficients are falsified differently: The mean DFT coefficient $($for $f = 0)$ is almost correct, while the errors of the DFT coefficients increase significantly towards the edges.
- Here, the DFT coefficient for $f \cdot T = -1$ is twice as large as it should be, since the Gaussian function with the center at $f \cdot T = -2$ gives the same contribution as the Gaussian function around $f \cdot T = 0$ (see yellow background).
Thus, here with $\text{MQF} \approx 2 \cdot 10^{-4}$ an error value four times larger than that caused by the truncation error in $\text{Example 2}$.
Again, we refer to the $($German language$)$ learning video:
»Fehlermöglichkeiten bei Anwendung der DFT« ⇒ "Possible errors when using the DFT".
Exercises for the chapter
Exercise 5.3: Mean Square Error