Difference between revisions of "Examples of Communication Systems/General Description of DSL"
| (40 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Header | {{Header | ||
|Untermenü=DSL – Digital Subscriber Line | |Untermenü=DSL – Digital Subscriber Line | ||
| − | |Vorherige Seite= | + | |Vorherige Seite=Further Developments of ISDN |
| − | |Nächste Seite= | + | |Nächste Seite=xDSL_Systems |
}} | }} | ||
| − | == # | + | == # OVERVIEW OF THE SECOND MAIN CHAPTER # == |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | ''' | + | $\rm D$igital $\rm S$ubscriber $\rm L$ine – in short $\rm DSL$ – literally means only "digital subscriber line". At the same time, "DSL" was a synonym for "high-speed Internet access in the local loop to the end customer", although "high-speed" must be put into perspective today $(2018)$. |
| + | |||
| + | xDSL has been significantly standardized by the standards committees [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/American_National_Standards_Institute $\rm ANSI$] $($USA$)$ and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ETSI $\rm ETSI$] $($Europe$)$ as well as the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_Telecommunication_Union $\rm ITU$] $($worldwide$)$. Due to different pre-existing technical conditions and preferences of developers and operators, a large variety of nationally different versions of nominally identical xDSL standards resulted. In the following, we will restrict ourselves primarily to the German xDSL versions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This chapter contains in detail: | ||
| + | |||
| + | #An »overview of the historical development and standardization« of xDSL, | ||
| + | #the »differences between ADSL and VDSL« as well as statistics on their penetration, | ||
| + | #a brief description of xDSL from a »communications protocol perspective«, | ||
| + | #the bandwidth allocations for the two »xDSL variants ADSL and VDSL«, | ||
| + | #a detailed description of the »DSL transmission methods QAM, CAP and DMT«, | ||
| + | #the problems of »digital signal transmission over copper twisted pairs« in general, | ||
| + | #the relationship between »SNR, range and transmission rate«, | ||
| + | #the »error correction measures« used to reduce the bit error rate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Network infrastructure for DSL== | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We start as in the [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/General_Description_of_ISDN#Network_infrastructure_for_ISDN|"ISDN chapter"]] with the network infrastructure. DSL was intended to use the existing analog telephone network for cost reasons. | ||
| + | |||
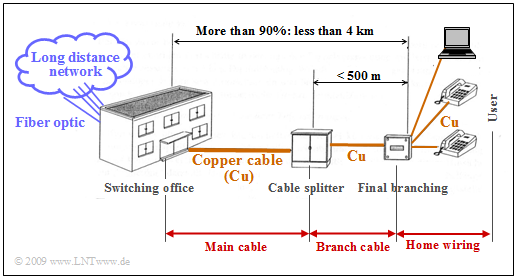
| + | The greatest cost factor of the entire infrastructure is the »'''subscriber line area'''« between a main distribution frame $($e.g. "switching office"$)$ and the subscribers. | ||
| + | [[File:EN_LZI_T_4_3_S2_neu.png| right|frame|Structure of the local loop area]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In Germany, this so-called »'''last mile'''« is shorter than $4$ kilometers on average, and in urban areas $90\%$ of the time it is even shorter than $2.8$ kilometers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Due to the topological conditions, the telephone network is increasingly branching out in a star configuration toward the end customer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In order to avoid having to lay a separate copper cable to the local exchange for each subscriber, splitters have been installed in between and the lines bundled in correspondingly large cables. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The »'''local loop area'''» is therefore usually made up as follows: | ||
| + | |||
| + | # The "main cable" with up to $2000$ pairs between the local exchange (or the switching office) frame and a cable branch, | ||
| + | # the "branch cable" between the cable branch and the final branch, with up to $300$ pairs and a maximum length of 500 meters, which is significantly shorter than a main cable, | ||
| + | # the "house connection cable" between the terminal box and the network termination box at the subscriber with two pairs of wires. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==xDSL types and terms== | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| − | + | {{BlaueBox|TEXT= | |
| + | $\text{Motivation for Digital Subscriber Line}$ | ||
| − | + | $\rm DSL$ $($"Digital Subscriber Line"$)$ arose from the need, '''to provide low cost high rate digital data access to the end user'''. <br>During the design process, it was necessary to take into account: | |
| + | *As explained in the last section, the "last mile" is the largest cost factor in a communications network. | ||
| − | * | + | *Considerations to replace the estimated 130 million kilometers of copper twisted pairs in the local loop network with fiber optic lines $($fiber-to-the-home, $\rm FttH)$ have failed to date due to the enormous costs of the mostly underground laying work. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | *A viable solution was to offer a broadband connection with somewhat lower data rates than in a fiber optic network by using the existing telephone line network and by cleverly combining different transmission techniques and coding methods. | ||
| + | *The telephone service – either analog or digital $\rm (ISDN)$ – should be able to operate simultaneously on the same network.}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Before we turn to the historical DSL development up to the current state, the various types of "$\rm xDSL$" must first be defined and some terms explained. <u>Note:</u> | |
| − | + | #Here, "$\rm x$" is merely a placeholder that designates the various DSL standards. | |
| − | + | #The technical features will be covered in depth in the next chapters. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Part of the xDSL standard:''' | |
| − | + | *$\text{ADSL}$ – "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line: <br>Asymmetric data transmission technology with data rates of $8$ Mbit/s to the subscriber $($"downstream"$)$ and $1$ Mbit/s in the opposite direction $($"upstream"$)$. | |
| − | $\text{ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | *$\text{ADSL2}$ and $\text{ADSL2+}$: <br>Extensions of ADSL with data rates of up to $25$ Mbit/s $($"downstream"$)$ and up to $1$ Mbit/s $($"upstream"$)$. <br>The data rate is dynamically negotiated depending on the channel state. | ||
| − | + | *$\text{Re – ADSL2}$: <br>Another extension of ADSL with about $30\%$ range gain at a data rate of $768$ kbit/s downstream. | |
| + | *$\text{HDSL}$ – "High Data Rate Digital Subscriber Line": <br>Symmetrical data transmission technology – i.e. equal rates in downstream and upstream – with data rates between $1.54$ Mbit/s and $2.04$ Mbit/s. <br><u>Note:</u> The name "HDSL" suggests higher data rates than ADSL; however, this is not the case. | ||
| + | *$\text{SDSL}$ – "Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line": <br>Symmetrical data transmission at rates of up to $3$ Mbit/s. With four-wire wiring $($two copper twisted pairs$)$, a maximum of $4$ Mbit/s can be transmitted. Alternatively, the range can be increased at the expense of bandwidth. | ||
| + | *$\text{VDSL}$ – "Very High Data Rate Digital Subscriber Line": <br>A newer transmission technology based on QAM that operates in the asymmetrical variant with bit rates of $25$ to $50$ Mbit/s downstream and $5$ to $10$ Mbit/s upstream. The symmetrical variant has the same data transmission rates in upstream and downstream. | ||
| − | + | *$\text{VDSL2}$ – "Very High Data Rate Digital Subscriber Line 2": <br>Transmission technology with the currently (2009) highest total data rate of up to $200$ Mbit/s. The process is based on DMT $($"Discrete Multitone Transmission"$)$. | |
| − | + | *$\text{UDSL}$ or $\text{UADSL}$ – "Universal (Asymmetric) Digital Subscriber Line". | |
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Not part of the xDSL standard:''' | |
| − | * | + | #There are also many products circulating under "DSL" that are not part of the xDSL standard. |
| − | * | + | #They are often only intended to make it clear that fast data access is involved. |
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | These include: |
| + | *$\text{cableDSL}$: Brand name of the German company TELES AG, which offers high-speed Internet access via cable. The name was chosen for marketing reasons only. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *$\text{skyDSL}$: Brand name for Internet access available throughout Europe via satellite with up to $24$ Mbit/s downstream. <br>The upstream here is via POTS $($"Plain old telephone service"$)$ or [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/General_Description_of_ISDN|ISDN ]] $($"Integrated Services Digital Network"$)$. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *$\text{T-DSL via satellite}$: Brand name for a downstream Internet access of Telekom via satellite; uses a conventional modem or an ISDN connection for transmission. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *$\text{WDSL}$ – "Wireless Digital Subscriber Line": Brand name of a German company that uses wireless technology to enable data rates of up to $108$ Mbit/s in DSL-free areas. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *$\text{mvoxSatellit}$: Brand name of an Internet access with "WiMAX-like radio technology", which like WDSL and PortableDSL is only an auxiliary construct for DSL-free areas. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Historical development of xDSL standardizations == |
| + | <br> | ||
| − | + | The need for digital subscriber lines to improve line utilization and increase customer convenience was recognized as early as the 1970s. After the ISDN specification in the early 1980s, the actual development of DSL began. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | *This development was influenced by the findings of many groups located around the world. Accordingly, the standardization proceeded in an unstructured manner. | ||
| − | + | *From the list on the right, it is clear that different committees around the world were in charge of the various standards. | |
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | *In the industry, the technical realizations of the individual xDSL standards often deviated noticeably from the specification. |
| − | + | ||
| + | *Some standards were started as projects even before the specification, since the industry parties were also represented in the standardization committees. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The graph illustrates the relationships between milestones in the theoretical and practical design of transmission systems. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
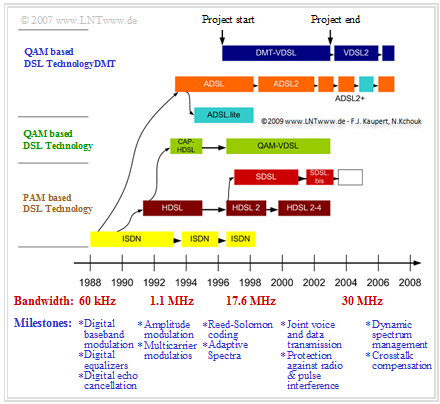
| − | + | [[File:EN_Bei_2_1_s3_v4.png|right|frame|Milestones of the industrial xDSL development]] | |
| + | $\text{Milestones of DSL development in short form:}$ | ||
| − | + | '''1986''' A first concept for $\rm HDSL$ $($"'''H'''igh-bit-rate '''D'''igital '''S'''ubscriber '''L'''ine"$)$ is defined by AT&T, Bell Laboratories and Bellcore. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | '''1989''' First HDSL prototypes appear; ⇒ Bellcore meanwhile works on the conceptual definition of $\rm ADSL$ $($"'''A'''symmetric '''D'''igital '''S'''ubscriber '''L'''ine"$)$. | ||
| − | + | '''1992''' First publication of the $\text{ANSI Technical Report E1T1/92-002R1}$:<br>"High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line"; ⇒ The first ADSL prototypes appear. | |
| − | + | '''1994''' The $\rm VDSL$ concept $($"'''V'''ery-high-speed '''D'''igital '''S'''ubscriber '''L'''ine"$)$ is discussed for the first time. | |
| − | |||
| + | '''1995''' Publication of the $\text{ETSI Technical Report ETR 152:}$ "High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line" and "Transmission Systems on Metallic Local Lines"; <br>⇒ Publication of $\text{ADSL Standard ANSI T1.413}$: $($"Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line Metallic Interface"$)$; ⇒ First field trials with ADSL in the USA . | ||
| − | + | '''1996''' First publication of the $\text{ETSI Technical Report ETR 328}$: "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line" and "Transmission and Multiplexing". | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | '''04/1998''' First publication of $\text{ETSI Technical Specification TS 101 270}$: "Very-high-speed Digital Subscriber Line"; ⇒ Almost simultaneously, first publication of $\text{ANSI Draft Technical Document T1E1.4/98-043R1}$: "Very-high-speed Digital Subscriber Lines". | ||
| − | + | '''10/1998''' First publication of $\text{ITU Recommendation G.991.1}$: "High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line Transceivers"; ⇒ Almost simultaneously publication of $\text{ETSI Technical Specification TS 101 135}$: "High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line – Transmission Systems on Metallic Local Lines". | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''11/1998''' Publication of $\text{ETSI Technical Specification TS 101 388 V1.1.1}$: "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line – European Specific Requirements". | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''1999''' In June, publication of $\text{ITU Recommendations G.992.1}$: "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line – Transceivers" and $\text{G.992.2}$: "Splitterless Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line – Transceivers"; ⇒ On July 22, Deutsche Telekom AG offers ADSL in Germany for the first time $\text{(T-DSL 768)}$. | |
| − | + | '''2001''' In February, publication of $\text{ITU Recommendation G.991.2}$: "Single-pair High-speed Digital Subscriber Line Transceivers"; ⇒ In November, publication of $\text{ITU Recommendation G.993.1}$: "Very-high-speed Digital Subscriber Line transceivers". | |
| − | + | '''2002''' First publications of $\text{ITU Recommendations G.992.3}$: "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line Transceivers 2" $\rm (ADSL2)$ and $\text{G.992.4}$: "Splitterless ADSL2". | |
| − | + | '''2003''' First publication of $\text{ITU Recommendation G.992.5}$: "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line" $\rm (ADSL)$ Transceivers" and "Extended-bandwidth ADSL2" $\rm (ADSL2+)$. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''02/2006''' Publication of $\text{ITU Recommendation G.993.2}$: "Very-high-speed Digital Subscriber Line Transceivers 2" $\rm (VDSL2)$. | |
| − | + | '''10/2006''' Deutsche Telekom AG offers VDSL2 to end customers in selected cities for the first time. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| + | == Development of ADSL and VDSL in Europe == | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | From the above compilation it can be seen that the »'''ADSL standardization'''« was predominantly driven by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/American_National_Standards_Institute $\rm ANSI$] $($"American National Standards Institute"$)$ and that [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ETSI $\rm ETSI$] $($"European Telecommunications Standards Institute"$)$ followed shortly thereafter in each case: | ||
| + | #The first ADSL standard "$\text{ANSI T1.413}$" from 1995 was predominantly optimized for video-on-demand services, which is also made clear by the ratio of the downstream and upstream data rates defined herein: $1.5$ Mbit/s and $16$ kbit/s, $3$ Mbit/s and $16$ kbit/s, and finally $6$ Mbit/s and $64$ kbit/s. | ||
| + | #The frequency range was originally defined in such a way that ADSL could only be used to operate an analog telephone on the access line. ETSI published a technical report "$\text{ETR 328}$" in 1996 with only a few detailed changes and the possibility to transmit $2048$ kbit/s. | ||
| + | #Since the second version of the ANSI standard also allowed only one additional analog telephone, ETSI then defined an ADSL system that differed both in bit rates and in the possibility of using an ISDN basic access on the same twisted pair. | ||
| + | #The ANSI and ETSI standardization efforts of the previous years resulted in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_Telecommunication_Union "ITU"] recommendation "$\text{G.992.1}$" in 1999, which includes both standards and thus allows many options for the implementation. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | However, the many options led to major conceptual differences at the end of the 1990s – worldwide, within Europe and also nationally – depending on the semiconductor manufacturer, among other things. Only a few systems, modems, and measuring devices interoperated with other manufacturers. | |
| − | + | To counteract this proliferation, The "Deutsche Telekom AG" passed the technical guideline "$\text{1TR112}$" at the end of 2001, defining all the necessary interface parameters to ensure the interoperability of different manufacturer modems on the provider and customer side. | |
| − | + | *Due to Telekom's market power, this became the quasi-standard for Germany. | |
| − | |||
| + | *Furthermore, only those ADSL variants were used in Germany that allowed simultaneous operation of ISDN at any time. Thus, when switching from POTS to ISDN, it was not necessary to change the ADSL version as well. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | The »'''VDSL standardization'''« relevant for Europe was decisively shaped by ETSI and often happened in parallel to the American activities. Overall, VDSL standardization proceeded in a more orderly fashion than ADSL. The 3-step plan adopted by ETSI provided for: | |
| + | *Stage 1: Functional and electrical requirements for VDSL systems, | ||
| − | + | *Stage 2: Transmission coding and access method requirements, | |
| − | + | *Stage 3: Interoperability requirements. | |
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | These efforts culminated in April 1998 in the publication of the ETSI Technical Specification "$\text{TS 101 270-1}$", which defines as modulation methods both [[Modulation_Methods/Further_OFDM_Applications#A_brief_description_of_DSL_-_Digital_Subscriber_Line|$\rm DMT$]] $($"Discrete Multitone Transmission"$)$ and [[Modulation_Methods/Quadrature_Amplitude_Modulation|$\rm QAM$]] $($"Quadrature Amplitude Modulation"$)$. The semiconductor manufacturers could not agree on a worldwide line code standard for a long time and there was even talk of the "VDSL Line Code War". |
| − | + | In 2003, at the so-called "VDSL Olympics", the decision was made in favor of DMT and against QAM or the slightly modified variant [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/xDSL_as_Transmission_Technology#Carrierless_Amplitude_Phase_Modulation|$\rm CAP$]] $($"Carrierless Amplitude Phase Modulation"$)$, namely | |
| + | *because of the robustness of DMT against narrowband interference sources, | ||
| − | + | *although QAM/ CAP would allow a faster call setup. | |
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | ==Exercises for the chapter == |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[Exercise_2.1:_General_Description_of_xDSL|Exercise 2.1: General Description of xDSL]] | ||
{{Display}} | {{Display}} | ||
Latest revision as of 22:01, 21 March 2023
Contents
# OVERVIEW OF THE SECOND MAIN CHAPTER #
$\rm D$igital $\rm S$ubscriber $\rm L$ine – in short $\rm DSL$ – literally means only "digital subscriber line". At the same time, "DSL" was a synonym for "high-speed Internet access in the local loop to the end customer", although "high-speed" must be put into perspective today $(2018)$.
xDSL has been significantly standardized by the standards committees $\rm ANSI$ $($USA$)$ and $\rm ETSI$ $($Europe$)$ as well as the $\rm ITU$ $($worldwide$)$. Due to different pre-existing technical conditions and preferences of developers and operators, a large variety of nationally different versions of nominally identical xDSL standards resulted. In the following, we will restrict ourselves primarily to the German xDSL versions.
This chapter contains in detail:
- An »overview of the historical development and standardization« of xDSL,
- the »differences between ADSL and VDSL« as well as statistics on their penetration,
- a brief description of xDSL from a »communications protocol perspective«,
- the bandwidth allocations for the two »xDSL variants ADSL and VDSL«,
- a detailed description of the »DSL transmission methods QAM, CAP and DMT«,
- the problems of »digital signal transmission over copper twisted pairs« in general,
- the relationship between »SNR, range and transmission rate«,
- the »error correction measures« used to reduce the bit error rate.
Network infrastructure for DSL
We start as in the "ISDN chapter" with the network infrastructure. DSL was intended to use the existing analog telephone network for cost reasons.
The greatest cost factor of the entire infrastructure is the »subscriber line area« between a main distribution frame $($e.g. "switching office"$)$ and the subscribers.
- In Germany, this so-called »last mile« is shorter than $4$ kilometers on average, and in urban areas $90\%$ of the time it is even shorter than $2.8$ kilometers.
- Due to the topological conditions, the telephone network is increasingly branching out in a star configuration toward the end customer.
- In order to avoid having to lay a separate copper cable to the local exchange for each subscriber, splitters have been installed in between and the lines bundled in correspondingly large cables.
The »local loop area» is therefore usually made up as follows:
- The "main cable" with up to $2000$ pairs between the local exchange (or the switching office) frame and a cable branch,
- the "branch cable" between the cable branch and the final branch, with up to $300$ pairs and a maximum length of 500 meters, which is significantly shorter than a main cable,
- the "house connection cable" between the terminal box and the network termination box at the subscriber with two pairs of wires.
xDSL types and terms
$\text{Motivation for Digital Subscriber Line}$
$\rm DSL$ $($"Digital Subscriber Line"$)$ arose from the need, to provide low cost high rate digital data access to the end user.
During the design process, it was necessary to take into account:
- As explained in the last section, the "last mile" is the largest cost factor in a communications network.
- Considerations to replace the estimated 130 million kilometers of copper twisted pairs in the local loop network with fiber optic lines $($fiber-to-the-home, $\rm FttH)$ have failed to date due to the enormous costs of the mostly underground laying work.
- A viable solution was to offer a broadband connection with somewhat lower data rates than in a fiber optic network by using the existing telephone line network and by cleverly combining different transmission techniques and coding methods.
- The telephone service – either analog or digital $\rm (ISDN)$ – should be able to operate simultaneously on the same network.
Before we turn to the historical DSL development up to the current state, the various types of "$\rm xDSL$" must first be defined and some terms explained. Note:
- Here, "$\rm x$" is merely a placeholder that designates the various DSL standards.
- The technical features will be covered in depth in the next chapters.
Part of the xDSL standard:
- $\text{ADSL}$ – "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line:
Asymmetric data transmission technology with data rates of $8$ Mbit/s to the subscriber $($"downstream"$)$ and $1$ Mbit/s in the opposite direction $($"upstream"$)$.
- $\text{ADSL2}$ and $\text{ADSL2+}$:
Extensions of ADSL with data rates of up to $25$ Mbit/s $($"downstream"$)$ and up to $1$ Mbit/s $($"upstream"$)$.
The data rate is dynamically negotiated depending on the channel state.
- $\text{Re – ADSL2}$:
Another extension of ADSL with about $30\%$ range gain at a data rate of $768$ kbit/s downstream.
- $\text{HDSL}$ – "High Data Rate Digital Subscriber Line":
Symmetrical data transmission technology – i.e. equal rates in downstream and upstream – with data rates between $1.54$ Mbit/s and $2.04$ Mbit/s.
Note: The name "HDSL" suggests higher data rates than ADSL; however, this is not the case.
- $\text{SDSL}$ – "Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line":
Symmetrical data transmission at rates of up to $3$ Mbit/s. With four-wire wiring $($two copper twisted pairs$)$, a maximum of $4$ Mbit/s can be transmitted. Alternatively, the range can be increased at the expense of bandwidth.
- $\text{VDSL}$ – "Very High Data Rate Digital Subscriber Line":
A newer transmission technology based on QAM that operates in the asymmetrical variant with bit rates of $25$ to $50$ Mbit/s downstream and $5$ to $10$ Mbit/s upstream. The symmetrical variant has the same data transmission rates in upstream and downstream.
- $\text{VDSL2}$ – "Very High Data Rate Digital Subscriber Line 2":
Transmission technology with the currently (2009) highest total data rate of up to $200$ Mbit/s. The process is based on DMT $($"Discrete Multitone Transmission"$)$.
- $\text{UDSL}$ or $\text{UADSL}$ – "Universal (Asymmetric) Digital Subscriber Line".
Not part of the xDSL standard:
- There are also many products circulating under "DSL" that are not part of the xDSL standard.
- They are often only intended to make it clear that fast data access is involved.
These include:
- $\text{cableDSL}$: Brand name of the German company TELES AG, which offers high-speed Internet access via cable. The name was chosen for marketing reasons only.
- $\text{skyDSL}$: Brand name for Internet access available throughout Europe via satellite with up to $24$ Mbit/s downstream.
The upstream here is via POTS $($"Plain old telephone service"$)$ or ISDN $($"Integrated Services Digital Network"$)$.
- $\text{T-DSL via satellite}$: Brand name for a downstream Internet access of Telekom via satellite; uses a conventional modem or an ISDN connection for transmission.
- $\text{WDSL}$ – "Wireless Digital Subscriber Line": Brand name of a German company that uses wireless technology to enable data rates of up to $108$ Mbit/s in DSL-free areas.
- $\text{mvoxSatellit}$: Brand name of an Internet access with "WiMAX-like radio technology", which like WDSL and PortableDSL is only an auxiliary construct for DSL-free areas.
Historical development of xDSL standardizations
The need for digital subscriber lines to improve line utilization and increase customer convenience was recognized as early as the 1970s. After the ISDN specification in the early 1980s, the actual development of DSL began.
- This development was influenced by the findings of many groups located around the world. Accordingly, the standardization proceeded in an unstructured manner.
- From the list on the right, it is clear that different committees around the world were in charge of the various standards.
- In the industry, the technical realizations of the individual xDSL standards often deviated noticeably from the specification.
- Some standards were started as projects even before the specification, since the industry parties were also represented in the standardization committees.
The graph illustrates the relationships between milestones in the theoretical and practical design of transmission systems.
$\text{Milestones of DSL development in short form:}$
1986 A first concept for $\rm HDSL$ $($"High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line"$)$ is defined by AT&T, Bell Laboratories and Bellcore.
1989 First HDSL prototypes appear; ⇒ Bellcore meanwhile works on the conceptual definition of $\rm ADSL$ $($"Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line"$)$.
1992 First publication of the $\text{ANSI Technical Report E1T1/92-002R1}$:
"High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line"; ⇒ The first ADSL prototypes appear.
1994 The $\rm VDSL$ concept $($"Very-high-speed Digital Subscriber Line"$)$ is discussed for the first time.
1995 Publication of the $\text{ETSI Technical Report ETR 152:}$ "High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line" and "Transmission Systems on Metallic Local Lines";
⇒ Publication of $\text{ADSL Standard ANSI T1.413}$: $($"Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line Metallic Interface"$)$; ⇒ First field trials with ADSL in the USA .
1996 First publication of the $\text{ETSI Technical Report ETR 328}$: "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line" and "Transmission and Multiplexing".
04/1998 First publication of $\text{ETSI Technical Specification TS 101 270}$: "Very-high-speed Digital Subscriber Line"; ⇒ Almost simultaneously, first publication of $\text{ANSI Draft Technical Document T1E1.4/98-043R1}$: "Very-high-speed Digital Subscriber Lines".
10/1998 First publication of $\text{ITU Recommendation G.991.1}$: "High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line Transceivers"; ⇒ Almost simultaneously publication of $\text{ETSI Technical Specification TS 101 135}$: "High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line – Transmission Systems on Metallic Local Lines".
11/1998 Publication of $\text{ETSI Technical Specification TS 101 388 V1.1.1}$: "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line – European Specific Requirements".
1999 In June, publication of $\text{ITU Recommendations G.992.1}$: "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line – Transceivers" and $\text{G.992.2}$: "Splitterless Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line – Transceivers"; ⇒ On July 22, Deutsche Telekom AG offers ADSL in Germany for the first time $\text{(T-DSL 768)}$.
2001 In February, publication of $\text{ITU Recommendation G.991.2}$: "Single-pair High-speed Digital Subscriber Line Transceivers"; ⇒ In November, publication of $\text{ITU Recommendation G.993.1}$: "Very-high-speed Digital Subscriber Line transceivers".
2002 First publications of $\text{ITU Recommendations G.992.3}$: "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line Transceivers 2" $\rm (ADSL2)$ and $\text{G.992.4}$: "Splitterless ADSL2".
2003 First publication of $\text{ITU Recommendation G.992.5}$: "Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line" $\rm (ADSL)$ Transceivers" and "Extended-bandwidth ADSL2" $\rm (ADSL2+)$.
02/2006 Publication of $\text{ITU Recommendation G.993.2}$: "Very-high-speed Digital Subscriber Line Transceivers 2" $\rm (VDSL2)$.
10/2006 Deutsche Telekom AG offers VDSL2 to end customers in selected cities for the first time.
Development of ADSL and VDSL in Europe
From the above compilation it can be seen that the »ADSL standardization« was predominantly driven by $\rm ANSI$ $($"American National Standards Institute"$)$ and that $\rm ETSI$ $($"European Telecommunications Standards Institute"$)$ followed shortly thereafter in each case:
- The first ADSL standard "$\text{ANSI T1.413}$" from 1995 was predominantly optimized for video-on-demand services, which is also made clear by the ratio of the downstream and upstream data rates defined herein: $1.5$ Mbit/s and $16$ kbit/s, $3$ Mbit/s and $16$ kbit/s, and finally $6$ Mbit/s and $64$ kbit/s.
- The frequency range was originally defined in such a way that ADSL could only be used to operate an analog telephone on the access line. ETSI published a technical report "$\text{ETR 328}$" in 1996 with only a few detailed changes and the possibility to transmit $2048$ kbit/s.
- Since the second version of the ANSI standard also allowed only one additional analog telephone, ETSI then defined an ADSL system that differed both in bit rates and in the possibility of using an ISDN basic access on the same twisted pair.
- The ANSI and ETSI standardization efforts of the previous years resulted in the "ITU" recommendation "$\text{G.992.1}$" in 1999, which includes both standards and thus allows many options for the implementation.
However, the many options led to major conceptual differences at the end of the 1990s – worldwide, within Europe and also nationally – depending on the semiconductor manufacturer, among other things. Only a few systems, modems, and measuring devices interoperated with other manufacturers.
To counteract this proliferation, The "Deutsche Telekom AG" passed the technical guideline "$\text{1TR112}$" at the end of 2001, defining all the necessary interface parameters to ensure the interoperability of different manufacturer modems on the provider and customer side.
- Due to Telekom's market power, this became the quasi-standard for Germany.
- Furthermore, only those ADSL variants were used in Germany that allowed simultaneous operation of ISDN at any time. Thus, when switching from POTS to ISDN, it was not necessary to change the ADSL version as well.
The »VDSL standardization« relevant for Europe was decisively shaped by ETSI and often happened in parallel to the American activities. Overall, VDSL standardization proceeded in a more orderly fashion than ADSL. The 3-step plan adopted by ETSI provided for:
- Stage 1: Functional and electrical requirements for VDSL systems,
- Stage 2: Transmission coding and access method requirements,
- Stage 3: Interoperability requirements.
These efforts culminated in April 1998 in the publication of the ETSI Technical Specification "$\text{TS 101 270-1}$", which defines as modulation methods both $\rm DMT$ $($"Discrete Multitone Transmission"$)$ and $\rm QAM$ $($"Quadrature Amplitude Modulation"$)$. The semiconductor manufacturers could not agree on a worldwide line code standard for a long time and there was even talk of the "VDSL Line Code War".
In 2003, at the so-called "VDSL Olympics", the decision was made in favor of DMT and against QAM or the slightly modified variant $\rm CAP$ $($"Carrierless Amplitude Phase Modulation"$)$, namely
- because of the robustness of DMT against narrowband interference sources,
- although QAM/ CAP would allow a faster call setup.
Exercises for the chapter
Exercise 2.1: General Description of xDSL