Difference between revisions of "Exercise 2.3Z: xDSL Frequency Band"
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
$K_{\rm down} \ = \ ${ 448 } | $K_{\rm down} \ = \ ${ 448 } | ||
| − | { With how many bits $(b)$ would the | + | { With how many bits $(b)$ would the bins have to be occupied on average ⇒ ${\rm E}\big [ \hspace{0.05cm} b \hspace{0.05cm}\big ]$ so that the bit rate $R_{\rm B} = 25 \ \rm Mbit/s$ is? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$ {\rm E}\big [ \hspace{0.05cm} b \hspace{0.05cm}\big ] \ = \ ${ 13.95 3% } $\ \rm bit$ | $ {\rm E}\big [ \hspace{0.05cm} b \hspace{0.05cm}\big ] \ = \ ${ 13.95 3% } $\ \rm bit$ | ||
Latest revision as of 17:19, 7 March 2023
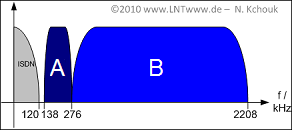
The figure shows the frequency band allocation of a common $\rm xDSL$ system:
- The ISDN band is located at the bottom.
- Two bands follow $\rm A$ and $\rm B$, representing downstream and upstream.
- Nothing is said about the order of the two bands. This is the question for subtask (2).
Further it is standardized with xDSL/DMT that.
- $4000$ frames are transmitted per second,
- a synchronization frame is inserted after every $68$ data frames,
- the symbol duration must be shortened by the factor $16/17$ because of the cyclic prefix,
- each data frame is encoded to a DMT symbol.
This also determines the integration duration $T$ which is evaluated at the receiver for detection, and at the same time also represents the fundamental frequency $f_{0} = 1/T$ of the DMT (Discrete Multitone Transmission) method considered here.
Hint:
- This exercise refers to the chapter "xDSL as Transmission Technology".
- For information on the cyclic prefix, refer to the chapter "Methods to Reduce the Bit Error Rate in DSL".
Questions
Solution
- For ADSL2+, the frequency band ends at $2208 \rm kHz$ as shown in the sketch.
- For ADSL, the frequency band already ends at $1104 \rm kHz$.
- VDSL has a much larger bandwidth, depending on the band plan, with upstream and downstream bands alternating in each case.
(2) Correct is the first proposed solution:
- The upstream was assigned the better (lower) frequencies, since a loss of the fewer upstream channels has a less favorable percentage effect than a loss of a downstream channel.
(3) Without taking into account the synchronization frames (after every $68$ of frames occupied with user data) and the guard interval, the frame duration would result in
- $$T = 1/(4000/{\rm s}) = 250 \ \rm µ s.$$
- With this overhead taken into account, the symbol duration is shorter by a factor of $68/69 \cdot 16/17$:
- $$T = \frac{68}{69} \cdot \frac{16}{17} \cdot 250\, {\rm \mu s} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ \approx 232\, {\rm µ s}} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) The subcarriers lie at DMT at all multiples of $f_0$, where must hold:
- $$f_0 = \frac{1}{T} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 4.3125 \, {\rm kHz}}.$$
- In fact, the time windowing corresponds to the multiplication of the cosine carrier signals by a square wave function of duration $T$.
- In the frequency domain, this results in the convolution with the si function.
- If the system quantities $T$ and $f_0 = 1/T$ were not tuned to each other, a de-orthogonalization of the individual DMT channels and thus intercarrier interference would occur.
(5) Ignoring ISDN/upstream reservation, we get $K_{\rm max} = 2208/4.3125 \underline{= 512}.$
(6) The lower $276/4.3125 = 64$ channels are reserved for ISDN and upstream in the "ADSL2+" system considered here.
- This leaves $K_{\rm down} = 512 - 64\hspace{0.15cm} \underline{= 448}$ usable channels.
(7) For the bitrate holds.
- $$R_{\rm B} = 4000 \, \,\frac {\rm frame}{\rm s} \cdot K \cdot b \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- This results in the (average) bit allocation per bin:
- $${\rm E}\big [ \hspace{0.05cm} b \hspace{0.05cm}\big ] = \frac{R_{\rm B}}{ 4000 \, \, {\rm frame}/{\rm s} \cdot K} = \frac{25 \cdot 10^6 \,\, {\rm bit/s}}{ 4000 \, \, {1}/{\rm s} \cdot 448} \hspace{0.15cm}\underline{= 13.95 \, \, {\rm bit}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$