Contents
Coding principle and code parameters
A Reed–Solomon Code – hereafter sometimes shortened to RS code is a "linear block code" that is
- an information block $\underline{u}$ with $k$ symbols.
- assings a corresponding codeword $\underline{c}$ with $n > k$
symbols. These codes, still widely used today, were invented as early as the early 1960s by "Irving Stoy Reed" and "Gustave Solomon" .
In the chapter "Objective of Channel Coding" the information block was denoted by $\underline{u}= (u_1,$ ... , $u_k)$ and the codeword by $\underline{x}= (x_1,$ ... , $x_n)$ .
The nomenclature change $\underline{x} \to \underline{c}$ (see graphic) was made to eliminate confusion with the argument of polynomials and to simplify the description of RS codes.
All the properties of linear cyclic block codes mentioned in the section "linear codes and cyclic codes" also apply to a Reed–Solomon–code. In addition:
- Construction and decoding of Reed–Solomon codes are based on the arithmetic of a Galois field ${\rm GF}(q)$, where we restrict ourselves here to binary extension fields with $q=2^m$ elements :
- \[{\rm GF}(2^m) = \big \{\hspace{0.05cm}0\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm} \alpha^{0} ,\hspace{0.05cm}\hspace{0.1cm} \alpha^{1}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm} \alpha^{2}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.1cm}, \alpha^{q-2}\hspace{0.05cm} \big \}\hspace{0.05cm}. \]
- Principally different from the first chapter is that the coefficients $u_0$, $u_1$, ... , $u_{k-1}$ now no longer specify individual bits of information $(0$ or $1)$ but are also elements of ${\rm GF}(2^m)$ . Each of the $n$ symbols represents $m$ bits.
- For Reed–Solomon codes, the parameter $n$ (code length) is always equal to the number of elements of the Galois field excluding the zero word: $n= q-1$.
We use the following nomenclature for this purpose:
- \[{\rm GF}(2^m) \hspace{-0.05cm}\setminus \hspace{-0.05cm} \{0\} = \big \{\hspace{0.05cm} \alpha^{0} ,\hspace{0.05cm}\hspace{0.1cm} \alpha^{1}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm} \alpha^{2}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm}...\hspace{0.1cm}, \alpha^{n-1}\hspace{0.05cm} \big \}\hspace{0.05cm}. \]
- The $k$ coefficients $u_i \in {\rm GF}(2^m)$ of the information block $\underline{u}$, where for the index $ 0 \le i < k$ holds, can also be formally expressed by a polynomial $u(x)$ . The degree of the polynomial is here $k-1$:
- \[u(x) = \sum_{i = 0}^{k-1} u_i \cdot x^{i} = u_0 + u_1 \cdot x + u_2 \cdot x^2 + \hspace{0.1cm}\text{...}\hspace{0.1cm}+ u_{k-1} \cdot x^{k-1} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.4cm} u_i \in {\rm GF}(2^m) \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
- The $n$ symbols of the associated codeword $\underline{c}= (c_0, c_1,$ ... , $c_{n-1})$ result with this polynomial $u(x)$ to be
- \[c_0 = u(\alpha^{0}) \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} c_1 = u(\alpha^{1})\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm}...\hspace{0.1cm},\hspace{0.3cm} c_{n-1}= u(\alpha^{n-1}) \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
- Mostly the code symbols $c_i \in {\rm GF}(2^m)$ are converted back to binary ⇒ ${\rm GF}(2)$ before transmission, where each symbol is then represented by $m$ bits.
We briefly summarize these statements:
$\text{Definition:}$ A $(n, k)$–Reed–Solomon code for the Galois field ${\rm GF}(2^m)$ is defined by.
- the $n= 2^{m-1}$ elements of ${\rm GF}(2^m) \hspace{-0.05cm}\setminus \hspace{-0.05cm} \{0\} =\{ \alpha^0, \alpha^1, \, \text{...} \, , \alpha^{n-1}\}$, where $\alpha$ denotes a "primitive element" of ${\rm GF}(2^m)$ denotes,
- an information blockt $\underline{u}$ matched "polynomial" of degree $k-1$ the form
- \[u(x) = \sum_{i = 0}^{k-1} u_i \cdot x^{i} = u_0 + u_1 \cdot x + u_2 \cdot x^2 + \hspace{0.1cm}... \hspace{0.1cm}+ u_{k-1} \cdot x^{k-1} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.4cm} u_i \in {\rm GF}(2^m) \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
Thus, the $(n, k)$–Reed–Solomon code can be described as.
- \[C_{\rm RS} = \Big \{ \underline {c} = \big ( u(\alpha^{0}) \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm} u(\alpha^{1})\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm}...\hspace{0.1cm}, u(\alpha^{n-1})\hspace{0.1cm} \big ) \hspace{0.1cm} \big \vert \hspace{0.2cm} u(x) = \sum_{i = 0}^{k-1} u_i \cdot x^{i}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.2cm} u_i \in {\rm GF}(2^m) \Big \} \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
The previous information will now be illustrated by two simple examples.
$\text{Example 1:}$ We consider the following code parameters:
- \[k = 2 \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.15cm}n = 3 \hspace{0.5cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.5cm} \underline {u} = (u_0, u_1)\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.15cm} \underline {c} = (c_0, c_1, c_2)\hspace{0.05cm},\]
- \[q = n+1 = 4 \hspace{0.45cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.5cm} {\rm GF} (q) = {\rm GF} (2^m) \hspace{0.5cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.5cm} m = 2\hspace{0.05cm}.\]
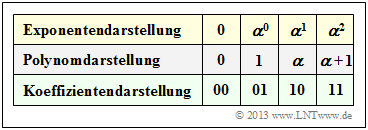
Starting from the conditional equation $p(\alpha) = \alpha^2 + \alpha + 1 = 0$ ⇒ $\alpha^2 = \alpha + 1$ one obtains the assignments between
- the exponential representation,
- the polynomial representation and
- the coefficient representation
of ${\rm GF}(2^2)$ according to the above table. From this it can be seen:
- The coefficient vector is expressed by the polynomial $u(x) = u_0 + u_1 \cdot x$ . The polynomial degree is $k- 1 = 1$.
- For $u_0 = \alpha^1$ and $u_1 = \alpha^2$ we obtain, for example, the polynomial $u(x) = \alpha + \alpha^2 \cdot x$ and thus
- \[c_0 = u (x = \alpha^0) = u (x = 1) = \alpha + \alpha^2 \cdot 1 = \alpha + (\alpha + 1) =1 \hspace{0.05cm},\]
- \[c_1 =u (x = \alpha^1) = \alpha + \alpha^2 \cdot \alpha = \alpha + \alpha^3 = \alpha + \alpha^0 = \alpha + 1 = \alpha^2 \hspace{0.05cm},\]
- \[c_2 =u (x = \alpha^2) = \alpha + \alpha^2 \cdot \alpha^2 = \alpha + \alpha^4 = \alpha + \alpha^1 = 0 \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
This results in the following assignments on symbol or bit level:
- \[\underline {u} =(\alpha^1, \ \alpha^2)\hspace{0.57cm}\leftrightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} \underline {c} = (1, \ \alpha^2, \ 0)\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{1cm}\underline {u}_{\rm bin} =(1,\ 0,\ 1,\ 1)\hspace{0.3cm}\leftrightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} \underline {c}_{\rm bin} = (0,\ 1,\ 1,\ 1,\ 0,\ 0)\hspace{0.05cm}.\]
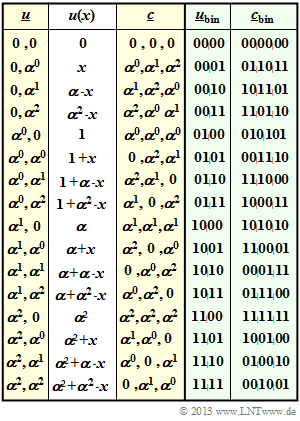
$\text{Example 2:}$ On the right is the code table of the $\text{RSC (3, 2, 2)}_4$ named Reed–Solomon code.
- The label refers to the parameters $n=3$, $k=2$, $d_{\rm min}=2$ and $q = 4$.
- In columns 1 to 3, one can see the relationship $\underline {u} \ → \ u(x) \ → \ \underline {c}$.
- In the last two columns, the coding rule $\underline {u}_{\rm bin} \ ↔ \ \underline {c}_{\rm bin}$ is given.
For clarification again the entry for $(\alpha^0, \ \alpha^2)$:
- \[u(x) = u_0 + u_1 \cdot x = \alpha^0 + \alpha^2 \cdot x. \]
This results in the following code symbols:
- \[c_0 = u (x = \alpha^0) = 1 + \alpha^2 \cdot 1 = 1 + (1+\alpha ) =\alpha \hspace{0.05cm},\]
- \[c_1 = u (x = \alpha^1) = 1 + \alpha^2 \cdot \alpha = 1 + (1+\alpha ) \cdot \alpha = 1 + \alpha + \alpha^2 = 0 \hspace{0.05cm},\]
- \[c_2 =u (x = \alpha^2) = 1 + \alpha^2 \cdot \alpha^2 = 1 + \alpha = \alpha^2 \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
Hints:
- From the element set $\{0, \ \alpha^0 = 1, \ \alpha^1 = \alpha, \ \alpha^2\}$ it should not be concluded that for this code the 3D–representation with axes $\alpha^0 = 1$, $\alpha^1 = \alpha$, $\alpha^2$ applies. See section "primitive polynomials" – example 5.
- On the contrary, from the coefficient representation in $\text{Example 1}$ it is clear that ${\rm GF} (2^2)$ is two-dimensional, where the axes of the two dimensional representation are to be labeled $\alpha^0 = 1$ and $\alpha^1 = \alpha$ .
Generator matrix of Reed-Solomon codes
Since the Reed–Solomon code is a linear block code, the relationship between information word $\underline {u}$ and codeword $\underline {c}$ given by the "Generator Matrix" $\boldsymbol{\rm G}$ :
- \[\underline {c} = \underline {u} \cdot { \boldsymbol{\rm G}} \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
As with any linear $(n, k)$–block code, the generator matrix consists of $k$ rows and $n$ columns. In contrast to the chapter "General Description of Linear Block Codes" however, now the elements of the generator matrix are no longer binary $(0$ or $1)$, but come from the Galois field ${\rm GF}(2^m) \hspace{-0.05cm}\setminus \hspace{-0.05cm} \{0\} $.
$\text{Example 3:}$ We consider as in $\text{Example 2}$ (previous page) the $\text{RSC (3, 2, 2)}_4$ whose generator matrix has the following form:
\[ { \boldsymbol{\rm G} } = \begin{pmatrix} g_{00} & g_{01} & g_{02}\\ g_{10} & g_{11} & g_{12} \end{pmatrix}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} g_{ij} \in {\rm GF}(2^2) \hspace{-0.01cm}\setminus \hspace{-0.01cm} \{0\} = \big \{\hspace{0.05cm} \alpha^{0} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm} \alpha^{1}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm} \alpha^{2} \hspace{0.05cm}\big \}\hspace{0.05cm}. \]
Beside this:
- The first row of $\boldsymbol{\rm G}$ gives the codeword for the information word $\underline {u}_1 = (1, 0)$ respectively for the polynomial function $u_1(x) = 1$. Thus one receives the matrix elements of the first row
- \[g_{00} = u_{1}(\alpha^{0}) = 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} g_{01} = u_{1}(\alpha^{1}) = 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} g_{02} = u_{1}(\alpha^{2}) = 1\hspace{0.05cm}.\]
- The second row is equal to the code word for the information word $\underline {u}_2 = (0, 1)$ ⇒ $u_2(x) = x$. Thus, the matrix elements of the second row are:
- \[g_{10} = u_{2}(\alpha^{0}) = \alpha^{0} = 1\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} g_{11} = u_{2}(\alpha^{1}) = \alpha \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.3cm} g_{12} = u_{2}(\alpha^{2}) = \alpha^{2}\hspace{0.05cm}.\]
- \[\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm} { \boldsymbol{\rm G} } = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1\\ 1 & \alpha & \alpha^2 \end{pmatrix}\hspace{0.05cm}.\]
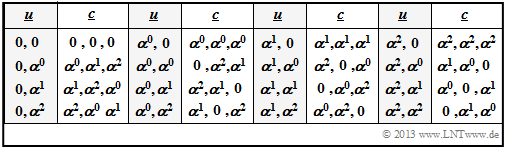
For the information word $\underline {u}= (u_0, \ u_1)$ mit den Symbolen $u_0, \ u_1 ∈ \{0, \ \alpha^0, \ \alpha^1 = \alpha, \ \alpha^2\}$ one obtains, considering the two equations $\alpha^2 = \alpha + 1$ and $\alpha^3 = \alpha^0 = 1$ again the code table of the $\text{RSC (3, 2, 2)}_4$ at symbol level.
- Of course, with the generator matrix you get exactly the same code table $\underline {u} ↔ \underline {c}$ as after the calculation via the function $u(x)$.
- The corresponding code table on bit level (see $\text{Example 2}$ on the previous page) results again, if the elements are not given in exponent representation, but in coefficient form:
- \[(0, \hspace{0.1cm}\alpha^{0}, \hspace{0.1cm}\alpha^{1}, \hspace{0.1cm}\alpha^{2}) \hspace{0.3cm}\Leftrightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}(00, \hspace{0.1cm}01, \hspace{0.1cm}10, \hspace{0.1cm}11) \hspace{0.05cm}. \]
Generator matrix and parity-check matrix
We now generalize the result of the last page for a Reed–Solomon code with
- the dimension $k$ (number of symbols per information block),
- the codeword length $n$ (number of symbols per codeword).
"generator matrix" $\boldsymbol{\rm G}$ $(k$ rows, $n$ columns$)$ and "parity-check matrix" $\boldsymbol{\rm H}$ $(n-k$ rows, $n$ columns$)$ must jointly satisfy the following equation:
- \[{ \boldsymbol{\rm G}} \cdot { \boldsymbol{\rm H }}^{\rm T}= { \boldsymbol{\rm 0}}\hspace{0.05cm}.\]
Here, $\boldsymbol{\rm 0}$ denotes a zero matrix $($all elements equal $0)$ with $k$ rows and $n-k$ columns.
$\text{Example 4:}$ We consider the $\text{RSC (7, 3, 5)}_8$ ⇒ code parameter $n= 7$, $k= 3$, based on the Galois field $\rm GF(2^3 = 8)$ with the constraint $\alpha^3 =\alpha + 1$. Note with respect to the code name:
- The third parameter of the nomenclature commonly used for block codes names the free distance $d_{\rm min}= 5$.
- Unlike the binary codes discussed in the chapter "Examples of binary block codes" (single parity-check code, repetition code, Hamming code), the Reed–Solomon codes still have the hint $q$ added to the Galois field $($here: $q = 8)$.
All elements of the generator matrix and the parity-check matrix,
- \[{ \boldsymbol{\rm G} } = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 1\\ 1 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^5 & \alpha^6\\ 1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^{3} & \alpha^{5} \end{pmatrix}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.4cm} { \boldsymbol{\rm H} } = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^5 & \alpha^6\\ 1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^{3} & \alpha^{5}\\ 1 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{1} & \alpha^{4}\\ 1 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{2} & \alpha^{6} & \alpha^{3} \end{pmatrix}\hspace{0.05cm}, \]
originate from the Galois field ${\rm GF}(2^3) \hspace{-0.01cm}\setminus \hspace{-0.01cm} \{0\} = \big \{\hspace{0.05cm} \alpha^{0} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm}\alpha^{1}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm} \alpha^{2} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm} \alpha^{3} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm}\alpha^{4}\hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm} \alpha^{5} \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.1cm} \alpha^{6} \hspace{0.05cm}\big \}$. For the matrix product holds:
- \[{ \boldsymbol{\rm G} } \cdot { \boldsymbol{\rm H } }^{\rm T}= \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 1\\ 1 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^5 & \alpha^6\\ 1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^{3} & \alpha^{5} \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 \\ \alpha^1 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^3 & \alpha^4\\ \alpha^2 & \alpha^4 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^1\\ \alpha^3 & \alpha^6 & \alpha^2 & \alpha^{5}\\ \alpha^4 & \alpha^1 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{2}\\ \alpha^5 & \alpha^{3} & \alpha^{1} & \alpha^{6}\\ \alpha^6 & \alpha^{5} & \alpha^{4} & \alpha^{3} \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \end{pmatrix} \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
This will be demonstrated here for two elements only:
- First row, first column:
- \[1 \hspace{0.1cm} \cdot \hspace{0.1cm} \big [1 + \alpha^1 + \alpha^2 + \alpha^3 + \alpha^4 + \alpha^5 + \alpha^6 \big ] = 1 + \alpha + \alpha^2 + (\alpha + 1) + (\alpha^2 + \alpha)+ (\alpha^2 + \alpha +1)+ (\alpha^2 + 1) = 0 \hspace{0.05cm}; \]
- Last row, last column:
- \[1 \hspace{0.1cm} \cdot \hspace{0.1cm} 1 + \alpha^2 \cdot \alpha^4 + \alpha^4 \cdot \alpha^1 + \alpha^6 \cdot \alpha^5+ \alpha^1 \cdot \alpha^2+ \alpha^3 \cdot \alpha^6+ \alpha^5 \cdot \alpha^3= 1 + \alpha^6 + \alpha^5 + \alpha^{11} + \alpha^{3}+ \alpha^{9}+ \alpha^{8} =\]
- \[ \hspace{1.5cm} = \hspace{0.15cm} 1 + \alpha^6 + \alpha^5 + \alpha^{4} + \alpha^{3}+ \alpha^{2}+ \alpha^{1} =0 \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
Singleton bound and minimum distance
An important parameter of any block code is the "minimum distance" between any two code words $\underline {c}_i$ and $\underline {c}_j$.
- The Reed–Solomon–codes belong to the class of linear and cyclic codes. For these, one can start from the zero word $\underline {c}_0 = (0, 0, \hspace{0.05cm} \text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}, 0)$ as the reference.
- From the number of zeros in the other codewords $\underline {c}_j ≠ \underline {c}_0$ the "distance spectrum" $\{ \hspace{0.05cm}W_j\hspace{0.05cm}\}$ can be specified.
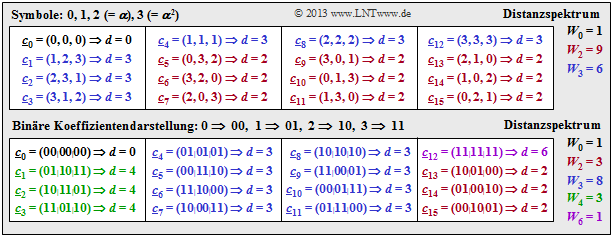
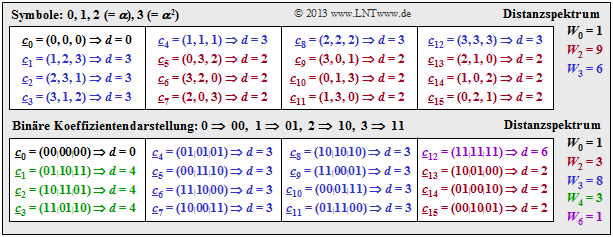
$\text{Example 5:}$ The table illustrates the determination of the distance spectrum for the $\text{RSC (3, 2, 2)}_4$.
- Compared to the previous graphs, the symbol set is simplified by $\{0,\ 1,\ 2,\ 3\}$ instead of $\{0,\ \alpha^0,\ \alpha^1,\ \alpha^2\}$ .
- The distance $d$ between $\underline {c}_j$ and the null word $\underline {c}_0$ is identical to "Hamming weight" $w_{\rm H}(\underline {c}_j)$.
From the upper table can be read, among others:
- Nine codewords differ from the zero word in two symbols and six codewords differ in three symbols: $W_2 = 9$, $W_3 = 6$.
- There is not a single codeword with only one zero. That means: The minimum distance here is $d_{\rm min} = 2$.
From the table below one can see that also for the binary representation $d_{\rm min} = 2$ holds.
This empirical result will now be generalized:
$\text{Without proof:}$
- The minimum distance of each $(n, k)$–Reed–Solomon codes is $d_{\rm min} =n-k+1$ ⇒ symbol errors can be detected $e = d_{\rm min} -1 =n-k$ .
- For error correcting codes one usually chooses $d_{\rm min} $ odd ⇒ $n-k$ even. For RS–codes then up to $t =(n-k)/2$ symbol errors can be corrected.
- The "Singleton bound" says tat $d_{\rm min} \le n-k+1$ holds for all linear codes. RS codes reach this bound with equality; they are so-called "MDS codes" (Maximum Distance Separable ).
- The "distance spectrum" is composed of $W_0 = 1$ and other weight factors $W_i$ with $d ≤ i ≤ n$, where in the following equation $d_{\rm min}$ is abbreviated as $d$ :
- \[W_i = {n \choose i} \cdot \sum_{j = 0}^{i-d}\hspace{0.15cm}(-1)^j \cdot {i \choose j} \cdot \bigg [\hspace{0.03cm}q^{i\hspace{0.03cm}-\hspace{0.03cm}j\hspace{0.03cm}-\hspace{0.03cm}d\hspace{0.03cm}+\hspace{0.03cm}1}-1 \hspace{0.03cm} \bigg ]\hspace{0.05cm}.\]
Code name and code rate
The usual designation for the Reed–Solomon codes is ${\rm RSC} \ \ (n,\ k, \ d_{\rm min})_q$ with.
- the length $n$ of the code (symbol number of a codeword),
- of the dimension $k$ of the code (symbol number of an information word),
- of the minimum distance $d_{\rm min} = n-k+1$, maximum corresponding to the Singleton bound, and
- the size $q = 2^m$ of the Galois field ${\rm GF}(q)$.
All elements $u_i$ of the information word $\underline{u}= (u_0, \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}, u_i, \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}, u_{k-1})$ and all elements ci of the codeword $\underline{c}= (c_0, \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}, c_i, \hspace{0.05cm}\text{...} \hspace{0.05cm}, c_{n-1})$ are non-binary symbols and come from the Galois field ${\rm GF}(q)$.
For the realization these symbols are always also represented in binary and one arrives at the equivalent binary Reed–Solomon code ${\rm RSC} \ \ (n_{\rm bin},\ k_{\rm bin}, \ d_{\rm min})_2$ with.
- $n_{\rm bin} = n \cdot m$ bits of a codeword,
- $k_{\rm bin} = k \cdot m$ bit of an information word.
The code rate is not changed by this action:
- \[R_{\rm bin} = \frac{k_{\rm bin}}{n_{\rm bin}} = \frac{k \cdot m}{n \cdot m} = \frac{k}{n} = R \hspace{0.05cm}.\]
Similarly, the transition from ${\rm GF}(q)$ to ${\rm GF}(2)$ does not change the minimum distance $d_{\rm min}$.
$\text{Example 6:}$ As in $\text{Example 5}$ (previous page), we again consider the $\text{RSC (3, 2, 2)}_4$ and give its distance spectrum $\{ \hspace{0.05cm}W_j\hspace{0.05cm}\}$ again (upper table). The lower table applies to the equivalent binary Reed–Solomon code $\text{RSC (6, 4, 2)}_2$.
- Both codes have the same code rate $R = k/n =2/3$ and also the same minimum distance $d_{\rm min} = 2$.
- But the two codes differ in terms of the distance spectrum $\{ \hspace{0.05cm}W_j\hspace{0.05cm}\}$ and the "weight enumerator function" $W(X)$:
- $$\text{RSC (3, 2, 2)}_4\text{:} \hspace{0.3cm} W_0 = 1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}W_2 = 9\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}W_3 = 6\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}W(X) = 1 + 9 \cdot X^2 + 6 \cdot X^3\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- $$\text{RSC (6, 4, 2)}_2\text{:} \hspace{0.3cm} W_0 = 1\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}W_2 = 3\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}W_3 = 8 \hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}W_4 = 3\hspace{0.05cm}, \hspace{0.2cm}W_6 = 1 \hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow\hspace{0.3cm}W(X) = 1 + 3 \cdot X^2 + 8 \cdot X^3 + 4 \cdot X^4 + X^6 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Meaning of the Reed-Solomon codes
Using the $\text{RSC (3, 2, 2)}_4$ often considered here as an example, we were able to learn many properties of Reed–Solomon codes in a manageable way. However, this code is not relevant in practice, since due to $d_{\rm min} = 2$ not a single error can be corrected, and not even a single error can be detected. Already the next larger code $\text{RSC (7, 3, 5)}_8$, which can correct up to $t = 2$ errors, already has a code table with $8^3 = 512$ entries and is unsuitable for demonstration purposes.
In practice, very large RS codes are usually used, for example the $\text{RSC (255, 223, 33)}_{256}$ with the following properties:
- The code is based on the Galois field $\rm GF(2^8)$. Each symbol thus corresponds to one byte. The code rate is relatively large with $R = 0.8745$ .
- Despite this large code rate (i.e., low redundancy), this code can detect up to $e = 32$ errors within a block of $255$ symbols and $t = 16$ correct errors.
- The code table, however, would $2^{8 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot \hspace{0.05cm} 223}= 2^{ \hspace{0.05cm} 1784} ≈ 10^{537}$ entries, and is therefore unlikely to be actually created by anyone.
The great advantage of Reed–Solomon codes (and a whole series of further codes derived from them) is on the one hand that they can be constructed analytically closed, on the other hand their large flexibility regarding the code parameters. Usually one proceeds as follows:
- One specifies the correction capability in the form of the parameter $t$ . From this, the minimum distance $d_{\rm min} = 2t + 1$ and the difference $n-k = 2t$ corresponding to the Singleton bound. There is no better value.
- Another design parameter is the code rate $R=k/n$, where the codeword length $n = 2^m -1$ is not completely arbitrary. By extension, shortening and puncturing– see "Exercise 1.9Z" – the variety of possible codes can be further increased.
- For Reed–Solomon codes, the weight distribution is known exactly and adaptation to the error structure of the channel is possible. These codes are particularly well suited for bundle error channels, which are often present in mobile radio systems due to temporary shadowing.
- In the case of statistically independent errors, "BCH codes" (from $\rm B$ose–$\rm C$haudhuri–$\rm H$ocquenghem) are more suitable. These are closely related to RS codes, but they do not always satisfy the Singleton criterion. A detailed description can be found in [Fri96][1].
- Decoding according to the "BDD Principle" (Bounded Distance Decoding ) can be done computationally very easily, for example with the "Berlekamp–Massey Algorithm". Moreover, the decoder can also process "Soft Decision Information" without much additional effort.
Exercises for the chapter
Exercise 2.07: Reed-Solomon Code (7, 3, 5) to Base 8
Exercise 2.07Z: Reed-Solomon Code (15, 5, 11) to Base 16
Exercise 2.08: Generator Polynomials for Reed-Solomon
Exercise 2.08Z: Addition and Multiplication in GF(2 power 3)
Exercise 2.09: Reed–Solomon Parameters
Exercise 2.10: Reed-Solomon Fault Detection
Exercise 2.10Z: Code Rate and Minimum Distance
Sources
- ↑ Friedrichs, B.: Kanalcodierung - Grundlagen und Anwendungen in modernen Kommunikations- systemen. Berlin - Heidelberg: Springer, 1996.