Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 2.12: Non-coherent Demodulation"
m |
m (→Solution) |
||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| − | '''(1)''' | + | '''(1)''' Applying the trigonometric transformations given on the exercise page and taking into account the two lowpass filters (the components around twice the carrier frequency are removed), we obtain: |
:$$b_1(t) = q(t) \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \Delta \phi_{\rm T}) \cdot 2 \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) = q(t) \cdot \cos(\Delta \phi_{\rm T})\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | :$$b_1(t) = q(t) \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \Delta \phi_{\rm T}) \cdot 2 \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) = q(t) \cdot \cos(\Delta \phi_{\rm T})\hspace{0.05cm},$$ | ||
:$$ b_2(t) = q(t) \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \Delta \phi_{\rm T}) \cdot (-2) \cdot \sin(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) = q(t) \cdot \sin(\Delta \phi_{\rm T})\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$ b_2(t) = q(t) \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \Delta \phi_{\rm T}) \cdot (-2) \cdot \sin(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) = q(t) \cdot \sin(\Delta \phi_{\rm T})\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * | + | *Thus, <u>the first and fourth answers</u> are correct. |
| − | '''(2)''' | + | '''(2)''' The sum of the squares of the two partial signals gives: |
:$$ b(t) = b_1^2(t) + b_2^2(t)= q^2(t) \cdot \left( \cos^2(\Delta \phi_{\rm T})+ \sin^2(\Delta \phi_{\rm T})\right) = q^2(t)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$ b(t) = b_1^2(t) + b_2^2(t)= q^2(t) \cdot \left( \cos^2(\Delta \phi_{\rm T})+ \sin^2(\Delta \phi_{\rm T})\right) = q^2(t)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | The possible amplitude values are thus: | |
:$$b_{\rm min}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 0},$$ | :$$b_{\rm min}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 0},$$ | ||
:$$ b_{\rm max}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ =9}.$$ | :$$ b_{\rm max}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ =9}.$$ | ||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
| − | '''(3)''' | + | '''(3)''' The <u>second answer</u> is correct: |
:$$v=g(b) = \sqrt{b} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} v(t) = \sqrt{ q^2(t) } = q(t)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$v=g(b) = \sqrt{b} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} v(t) = \sqrt{ q^2(t) } = q(t)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' The result $b(t) = q^2(t)$ – see subtask '''(2)''' – here leads to the result: |
:$$b_{\rm min}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 9},$$ | :$$b_{\rm min}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 9},$$ | ||
:$$b_{\rm max}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ =9}.$$ | :$$b_{\rm max}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ =9}.$$ | ||
| − | + | This shows, that the demodulator considered here only function when for all times $q(t) ≥ 0$ or $q(t) ≤ 0$ holds, and this is known at the receiver. | |
{{ML-Fuß}} | {{ML-Fuß}} | ||
Revision as of 21:52, 22 December 2021
Consider an amplitude modulated signal:
- $$ s(t) = q(t) \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Reaching the receiver based on the channel propagation time, the signal is
- $$ r(t) = q(t) \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \Delta \phi_{\rm T}) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
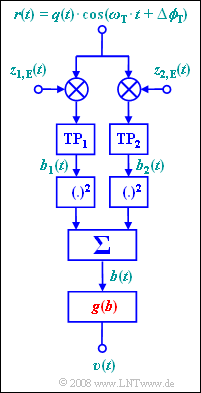
The arrangement shown here allows perfect demodulation – that is, $v(t) = q(t)$ – without knowledge of the phase $Δϕ_T$, but only if the source signal $q(t)$ satisfies certain conditions.
The two receiver-side carrier signals are:
- $$ z_{\rm 1, \hspace{0.08cm}E}(t) = 2 \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ z_{\rm 2, \hspace{0.08cm}E}(t) = -2 \cdot \sin(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
$\rm TP_1$ and $\rm TP_2$ denote two ideal (rectangular) lowpass filters, each with cutoff frequency equal to the carrier frequency $f_{\rm T}$ .
As (digital) source signals we consider:
- the unipolar square wave $q_1(t)$ with dimensionless amplitude values $0$ and $3$,
- the bipolar square wave signal $q_2(t)$ with the dimensionless amplitude values $±3$.
With respect to $s(t)$ , these two signals result in an ASK signal and a BPSK signal, respectively.
The nonlinear function $v = g(b)$ is to be determined in this exercise.
Hints:
- This exercise belongs to the chapter Further AM Variants.
- Particular reference is made to the page Incoherent (non-coherent) Demodulation.
- The following trigonometric transformations are given:
- $$ \cos(\alpha) \cdot \cos(\beta) = 1/2 \cdot \big[ \cos(\alpha - \beta)+ \cos(\alpha + \beta) \big],$$
- $$ \sin(\alpha) \cdot \sin(\beta) = 1/2 \cdot \big[ \cos(\alpha - \beta)- \cos(\alpha + \beta) \big],$$
- $$ \sin(\alpha) \cdot \cos(\beta) = 1/2 \cdot \big[ \sin(\alpha - \beta)+ \sin(\alpha + \beta) \big] \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Questions
Solution
- $$b_1(t) = q(t) \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \Delta \phi_{\rm T}) \cdot 2 \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) = q(t) \cdot \cos(\Delta \phi_{\rm T})\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ b_2(t) = q(t) \cdot \cos(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t + \Delta \phi_{\rm T}) \cdot (-2) \cdot \sin(\omega_{\rm T} \cdot t) = q(t) \cdot \sin(\Delta \phi_{\rm T})\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Thus, the first and fourth answers are correct.
(2) The sum of the squares of the two partial signals gives:
- $$ b(t) = b_1^2(t) + b_2^2(t)= q^2(t) \cdot \left( \cos^2(\Delta \phi_{\rm T})+ \sin^2(\Delta \phi_{\rm T})\right) = q^2(t)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The possible amplitude values are thus:
- $$b_{\rm min}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 0},$$
- $$ b_{\rm max}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ =9}.$$
(3) The second answer is correct:
- $$v=g(b) = \sqrt{b} \hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} v(t) = \sqrt{ q^2(t) } = q(t)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
(4) The result $b(t) = q^2(t)$ – see subtask (2) – here leads to the result:
- $$b_{\rm min}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ = 9},$$
- $$b_{\rm max}\hspace{0.15cm}\underline{ =9}.$$
This shows, that the demodulator considered here only function when for all times $q(t) ≥ 0$ or $q(t) ≤ 0$ holds, and this is known at the receiver.