Difference between revisions of "Digital Signal Transmission/Error Probability with Intersymbol Interference"
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
{{BlaueBox|TEXT= | {{BlaueBox|TEXT= | ||
| − | $\text{Definition:}$ The '''eye diagram''' (or | + | $\text{Definition:}$ The '''eye diagram''' (or "eye pattern") is the sum of all superimposed sections of the detection signal $d(t)$, whose duration is an integer multiple of the symbol duration $T$. This diagram has a certain resemblance to an eye, which led to its naming.}} |
{{GraueBox|TEXT= | {{GraueBox|TEXT= | ||
$\text{Example 3:}$ We assume a redundancy-free binary bipolar NRZ rectangular signal $s(t)$ and the Gaussian low-pass filter with cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$. | $\text{Example 3:}$ We assume a redundancy-free binary bipolar NRZ rectangular signal $s(t)$ and the Gaussian low-pass filter with cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$. | ||
| − | [[File:P ID1375 Dig T 3 2 S2 version1.png|right|frame|Eye | + | [[File:P ID1375 Dig T 3 2 S2 version1.png|right|frame|On the left: Eye diagram with noise ⇒ signal $d(t)=d_{\rm S}(t) +d_{\rm N}(t)$, <br>on the right: Eye diagram without noise ⇒ signal $d_{\rm S}(t)$|class=fit]] |
| − | + | In the graphic shown are the eye diagrams after the Gaussian low-pass, | |
| − | *left | + | *left inclusive the noise component ⇒ signal $d(t)=d_{\rm S}(t) +d_{\rm N}(t)$, |
*on the right without taking noise into account ⇒ signal $d_{\rm S}(t)$. | *on the right without taking noise into account ⇒ signal $d_{\rm S}(t)$. | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
This representation allows important statements about the quality of a digital transmission system: | This representation allows important statements about the quality of a digital transmission system: | ||
| − | *Only the eye diagram of the signal $d(t)$ can be displayed metrologically on an oscilloscope, which is triggered with the clock signal. From this eye diagram (left graph), for example, the noise rms value $\sigma_d$ can be read – or rather: estimated | + | *Only the eye diagram of the signal $d(t)$ can be displayed metrologically on an oscilloscope, which is triggered with the clock signal. From this eye diagram $($left graph$)$, for example, the noise rms value $\sigma_d$ $($⇒ noise power $\sigma_d^2)$ can be read – or rather: estimated.<br> |
| − | *The eye diagram without noise (right graph) refers to the signal component | + | *The eye diagram without noise (right graph) refers to the signal component $d_{\rm S}(t)$ of the detection signal and can only be determined by means of a computer simulation. For an implemented system, this eye diagram cannot be displayed, since the noise component $d_{\rm N}(t)$ cannot be eliminated.<br> |
| − | *In both diagrams, $2048$ eye lines were drawn in each case. In the right graph, however, only $2^5 = 32$ eye lines are distinguishable because the present | + | *In both diagrams of this example, $2^{11}=2048$ eye lines were drawn in each case. In the right graph, however, only $2^5 = 32$ eye lines are distinguishable because the present detection pulse $g_d(t)$ is limited to the time range $\vert t\vert \le 2T$ <br>$($see [[Digital_Signal_Transmission/Error_Probability_with_Intersymbol_Interference#Gaussian_receiver_filter|graph in Example 1]] with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$, red curve$)$.<br> |
| − | *The inner eye lines determine the '''vertical eye opening''' $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})$. The smaller this is, the greater is the influence of intersymbol interference. For a ( | + | *The inner eye lines determine the '''vertical eye opening''' $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})$. The smaller this is, the greater is the influence of intersymbol interference. For a $($ISI-free$)$ Nyquist system the vertical eye opening is maximum. Normalized to the transmitted amplitude, $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/s_0 = 2$ is then valid. <br> |
| − | *With symmetrical basic pulse, the detection time $T_{\rm D} = 0$ is optimal. With a different value $($for example $T_{\rm D} = T/10) $, | + | *With symmetrical basic detection pulse, the detection time $T_{\rm D} = 0$ is optimal. With a different value $($for example $T_{\rm D} = -T/10) $, $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})$ would be somewhat smaller and thus the error probability would be significantly larger. This case is indicated by the purple–dashed vertical line in the right graph.}} |
== Mean error probability== | == Mean error probability== | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | As with the previous graphs in this chapter, we assume the following: | + | As with the previous graphs in this chapter, we assume the following: |
| − | *NRZ rectangles with amplitude $s_0$, AWGN noise with $N_0$, where | + | [[File:P ID1377 Dig T 3 2 S3 version1.png|right|frame|Eye diagram and discrete PDF of the signal component $d_{\rm S}(t)$ from $d(t)$|class=fit]] |
| + | *NRZ rectangles with amplitude $s_0$, AWGN noise with power-spectral density $N_0$, where | ||
:$$10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm} \frac{s_0^2 \cdot T}{N_0}\approx | :$$10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm} \frac{s_0^2 \cdot T}{N_0}\approx | ||
| − | 13\,{\rm dB}\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} | + | 13\,{\rm dB}\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} |
\frac{N_0}{s_0^2 \cdot T} = 0.05\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \frac{N_0}{s_0^2 \cdot T} = 0.05\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
*Gaussian receiver filter with cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$: | *Gaussian receiver filter with cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$: | ||
:$$\sigma_d^2 = \frac{(N_0 /T)\cdot (f_{\rm G}\cdot T)}{\sqrt{2}}= \frac{0.05 \cdot | :$$\sigma_d^2 = \frac{(N_0 /T)\cdot (f_{\rm G}\cdot T)}{\sqrt{2}}= \frac{0.05 \cdot | ||
| − | s_0^2\cdot0.4}{\sqrt{2}} | + | s_0^2\cdot0.4}{\sqrt{2}}$$ |
| + | :$$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \sigma_d = \sqrt{0.0141}\cdot s_0 | ||
\approx 0.119 \cdot s_0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \approx 0.119 \cdot s_0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | * Let $g_d(\nu \cdot T) \approx 0$ be valid for $|\nu| \ge 2$. The other basic | + | * Let $g_d(\nu \cdot T) \approx 0$ be valid for $|\nu| \ge 2$. The other basic detection pulse values are given as follows: |
| − | :$$g_0 = g_d(t=0) \approx 0.68 \cdot s_0, | + | :$$g_0 = g_d(t=0) \approx 0.68 \cdot s_0,$$ |
| + | :$$g_1 = g_d(t=T) \approx 0.16 \cdot s_0,$$ | ||
| + | :$$g_{-1} = g_d(t=-T) \approx | ||
0.16 \cdot s_0\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | 0.16 \cdot s_0\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | + | Let us now analyze the possible values for the signal component $d_{\rm S}(t)$ at the detection times: | |
| + | *Of the total $32$ eye lines, four lines intersect the ordinate $(t = 0)$ at $g_0 + 2 \cdot g_1 = s_0$. These lines belong to the amplitude coefficients "$\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.1cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} {\it +\hspace{-0.05cm}1},\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$". Here, the "middle" coefficient $a_{\nu = 0}$ is highlighted in italics.<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The four eye lines, each representing the coefficients "$\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.1cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} {\it +\hspace{-0.05cm}1},\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.05cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$" result in the signal value $d_{\rm S}(T_{\rm D} = 0) =g_0 - 2 \cdot g_1 = 0.36 \cdot s_0$.<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In contrast, the signal value $d_{\rm S}(T_{\rm D} = 0) =g_0 = 0.68 \cdot s_0$ occurs twice as often. This goes back either to the coefficients "$\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.1cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} {\it +\hspace{-0.05cm}1},\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$" or to "$\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.1cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} {\it +\hspace{-0.05cm}1},\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$". <br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*For the $16$ eye lines which intersect the ordinate $T_{\rm D} = 0$ below the decision threshold $E = 0$, exactly mirror-image relations result.<br><br> | *For the $16$ eye lines which intersect the ordinate $T_{\rm D} = 0$ below the decision threshold $E = 0$, exactly mirror-image relations result.<br><br> | ||
| − | The possible values $d_{\rm S}(T_{\rm D})$ and their occurrence probabilities can be found in the above graph on the left side in the [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Probability_Density_Function#PDF_definition_for_discrete_random_variables| | + | The possible values $d_{\rm S}(T_{\rm D})$ and their occurrence probabilities can be found in the above graph on the left side in the (discrete) [[Theory_of_Stochastic_Signals/Probability_Density_Function#PDF_definition_for_discrete_random_variables|probability density function]] $\rm (PDF)$ of the noise-free detection signal samples: |
:$$f_{d{\rm S}}(d_{\rm S}) = {1}/{8} \cdot \delta (d_{\rm S} | :$$f_{d{\rm S}}(d_{\rm S}) = {1}/{8} \cdot \delta (d_{\rm S} | ||
- s_0)+ {1}/{4} \cdot \delta (d_{\rm S} - 0.68 \cdot s_0)+ | - s_0)+ {1}/{4} \cdot \delta (d_{\rm S} - 0.68 \cdot s_0)+ | ||
| Line 153: | Line 157: | ||
\delta (d_{\rm S} + 0.36 \cdot s_0)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \delta (d_{\rm S} + 0.36 \cdot s_0)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | Thus, the (average) symbol error probability of the | + | Thus, the (average) symbol error probability of the of the ISI-afflicted system can be given. Taking advantage of the symmetry, one obtains with $\sigma_d/s_0 = 0.119$: |
:$$p_{\rm S} = {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \frac{s_0}{ \sigma_d} | :$$p_{\rm S} = {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \frac{s_0}{ \sigma_d} | ||
\right)+ {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \frac{0.68 \cdot s_0}{ \sigma_d} | \right)+ {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \frac{0.68 \cdot s_0}{ \sigma_d} | ||
| Line 165: | Line 169: | ||
{{BlaueBox|TEXT= | {{BlaueBox|TEXT= | ||
| − | $\text{ | + | $\text{On the basis of this numerical example one recognizes:}$ |
| − | + | #In the presence of intersymbol interference, the (average) symbol error probability $p_{\rm S}$ is essentially determined by the inner eye lines.<br> | |
| − | + | #The computational cost of determining $p_{\rm S}$ can become very large, especially if the ISI comes from very many basic detection pulse values $g_\nu$. }} | |
| − | |||
{{GraueBox|TEXT= | {{GraueBox|TEXT= | ||
$\text{Example 4:}$ | $\text{Example 4:}$ | ||
| − | *If the | + | *If the pulse values $g_{-5}, \text{...} \ , g_{+5}$ are different from zero and $E \ne 0$, an averaging over $2^{11} = 2048$ eye lines is necessary to determine the error probability $p_{\rm S}$. |
| − | *If, on the other hand, only the | + | |
| − | * If, in addition, the symmetry $g_{-1} = g_{+1}$ applies as with the above numerical values, then the symmetry with respect to $T_{\rm D}$ can also be exploited and averaging over three terms is sufficient. }} <br> | + | *If, on the other hand, only the pulse values $g_{-1}, \ g_0, \ g_{+1}$ are different from zero and, in addition, the symmetry with respect to the threshold $E = 0$ is taken into account, the effort is reduced to averaging over four terms. |
| + | |||
| + | * If, in addition, the symmetry $g_{-1} = g_{+1}$ applies as with the above numerical values, then the symmetry with respect to $T_{\rm D}$ can also be exploited and averaging over three terms is sufficient. }} <br> | ||
== Worst-case error probability== | == Worst-case error probability== | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | In the past, a variety of approximations for the average error probability have been given, among others: | + | In the past, a variety of approximations for the average error probability have been given, among others: '''Bitte dieses Kapitel sehr kritisch checken''' |
{{BlaueBox|TEXT= | {{BlaueBox|TEXT= | ||
$\text{Definition:}$ As a very simple approximation for the actual error probability $p_{\rm S}$, | $\text{Definition:}$ As a very simple approximation for the actual error probability $p_{\rm S}$, | ||
| − | the '''worst-case error probability''' | + | the '''worst-case error probability''' (German: "ungünstigste Fehlerwahrscheinlichkeit" ⇒ subscript: "U") is often used: |
| − | [[File:P ID1379 Dig T 3 2 S4 version1.png|right|frame| | + | [[File:P ID1379 Dig T 3 2 S4 version1.png|right|frame|"Mean symbol error probability" $p_{\rm S}$ vs. "worst-case symbol error probability" $p_{\rm U}$|class=fit]] |
:$$p_{\rm U} = {\rm Q} \left( \frac{\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/2}{ \sigma_d} | :$$p_{\rm U} = {\rm Q} \left( \frac{\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/2}{ \sigma_d} | ||
| − | \right) \hspace{0.05cm}$$ | + | \right) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ |
| − | For their calculation, the worst-case symbol sequences are always assumed. This means: | + | For their calculation, the "worst-case symbol sequences" are always assumed. This means: |
| − | *The actual PDF of the | + | *The actual probability density function $\rm (PDF)$ of the samples $d_{\rm S}(T_{\rm D})$ (left graph: six red Dirac delta functions) is replaced by a simplified PDF with only the inner Dirac delta functions (right graph: two green Diracs).<br> |
| − | *For the half vertical eye opening, with the basic pulse values $g_\nu = g_d( T_{\rm D}+ \nu \cdot T)$ generally holds: | + | *For the half vertical eye opening, with the basic detection pulse values $g_\nu = g_d( T_{\rm D}+ \nu \cdot T)$ generally holds: |
:$$\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/{ 2}= g_0 - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{n} \vert g_{\nu} \vert- \sum_{\nu = 1}^{v} \vert g_{-\nu} \vert \hspace{0.05cm}.$$}} | :$$\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/{ 2}= g_0 - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{n} \vert g_{\nu} \vert- \sum_{\nu = 1}^{v} \vert g_{-\nu} \vert \hspace{0.05cm}.$$}} | ||
This equation can be interpreted as follows: | This equation can be interpreted as follows: | ||
| − | *$g_0 = g_d( T_{\rm D})$ is the so-called | + | *$g_0 = g_d( T_{\rm D})$ is the so-called "main value" of the basic detection pulse. For Nyquist systems $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/{ 2}= g_0$ is always valid. In the following (mostly) $T_{\rm D}= 0$ is set.<br> |
| − | *The first sum describes the | + | |
| − | *The second sum considers the influence of the $v$ | + | *The first sum describes the ISI influence of the $n$ "trailers" $($German: "Nachläufer" ⇒ variable $n)$ of preceding pulses. Tacitly assumed is $g_\nu = 0$ for $\nu \gt n$.<br> |
| − | *If all | + | |
| − | *If some basic pulse values are negative, this is taken into account in the above equation by the magnitude formation. This results in other "worst–case" sequences than those just mentioned.<br> | + | *The second sum considers the influence of the $v$ "precursors" $($German: "Vorläufer" ⇒ variable $v)$ of following pulses under the condition $g_{-\nu} = 0$ for $\nu \gt v$.<br> |
| + | |||
| + | *If all precursors and trailers are positive, the two worst-case symbol sequences are "$\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.1cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.05cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} {\it +\hspace{-0.05cm}1},\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.05cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$" and "$\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.1cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} {\it -\hspace{-0.05cm}1},\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$" (coefficient $a_{\nu = 0}$ is in italics in each case). These specifications apply, for example, to the Gaussian receiver filter considered here.<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *If some basic detection pulse values $g_{\nu\ne 0}$ are negative, this is taken into account in the above equation by the magnitude formation. This results in other "worst–case" sequences than those just mentioned.<br> | ||
{{GraueBox|TEXT= | {{GraueBox|TEXT= | ||
| − | $\text{Example 5:}$ The graph shows the error probabilities of the AWGN channel as a function of the (logarithmized) quotient $E_{\rm B}/N_0$, namely | + | $\text{Example 5:}$ The graph shows the error probabilities of the AWGN channel as a function of the (logarithmized) quotient $E_{\rm B}/N_0$, namely |
*the average error probability $p_{\rm S}$ with a Gaussian receive filter (blue circles),<br> | *the average error probability $p_{\rm S}$ with a Gaussian receive filter (blue circles),<br> | ||
*the worst-case error probability $p_{\rm U}$ with Gaussian receiver filter (blue rectangles),<br> | *the worst-case error probability $p_{\rm U}$ with Gaussian receiver filter (blue rectangles),<br> | ||
| Line 212: | Line 221: | ||
Here, the energy per bit is equal to $E_{\rm B} = s_0^2 \cdot T$ (NRZ rectangular transmitted pulses).<br> | Here, the energy per bit is equal to $E_{\rm B} = s_0^2 \cdot T$ (NRZ rectangular transmitted pulses).<br> | ||
| − | [[File:P ID1385 Dig T 3 2 S4b version2.png| | + | [[File:P ID1385 Dig T 3 2 S4b version2.png|right|frame|Mean and worst-case error probability vs. $E_{\rm B}/N-0$|class=fit]]<br> |
The left graph is for the (normalized) cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$, the right one for a broader band receiver filter with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.8$. The results can be interpreted as follows: | The left graph is for the (normalized) cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$, the right one for a broader band receiver filter with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.8$. The results can be interpreted as follows: | ||
Revision as of 15:30, 1 June 2022
Contents
Gaussian receiver filter
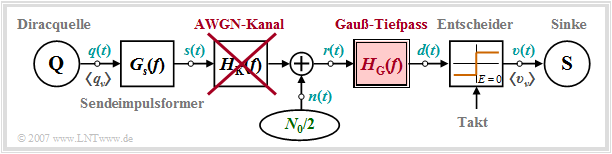
We start from the block diagram sketched below. The following configuration is assumed for quantitative consideration of "intersymbol interference":
- Rectangular NRZ basic transmission pulse $g_s(t)$ with height $s_0$ and duration $T$,
- Gaussian-shaped receiver filter $H_{\rm G}(f)$ with cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G}$:
- $$H_{\rm E}(f) = H_{\rm G}(f) = {\rm exp}\left [- \frac{\pi \cdot f^2}{(2f_{\rm G})^2} \right ] \hspace{0.2cm} \bullet\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\circ \hspace{0.2cm}h_{\rm E}(t) = h_{\rm G}(t) = {\rm exp}\left [- \pi \cdot (2 f_{\rm G} t)^2\right ] \hspace{0.05cm},\hspace{0.5cm}\text{note: }\hspace{0.2cm}{\rm exp} [x] = {\rm e}^x.$$
- AWGN channel ⇒ channel frequency response $H_{\rm K}(f) = 1 $ and noise power-spectral density ${\it \Phi}_n(f) = N_0/2$.
Based on the assumptions made here, the following holds for the basic detection pulse:
- $$g_d(t) = g_s(t) \star h_{\rm G}(t) = 2 f_{\rm G} \cdot s_0 \cdot \int_{t-T/2}^{t+T/2} {\rm e}^{- \pi \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} (2 \hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} f_{\rm G}\hspace{0.05cm}\cdot\hspace{0.05cm} \tau )^2} \,{\rm d} \tau \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The integration leads to the following equivalent results:
- $$g_d(t) = s_0 \cdot \big [ {\rm Q} \left ( 2 \cdot \sqrt {2 \pi} \cdot f_{\rm G}\cdot ( t - {T}/{2})\right )- {\rm Q} \left ( 2 \cdot \sqrt {2 \pi} \cdot f_{\rm G}\cdot ( t + {T}/{2} )\right ) \big ],$$
- $$g_d(t) = s_0 \cdot\big [ {\rm erfc} \left ( 2 \cdot \sqrt {\pi} \cdot f_{\rm G}\cdot ( t - {T}/{2})\right )- {\rm erfc} \left ( 2 \cdot \sqrt {\pi} \cdot f_{\rm G}\cdot ( t + {T}/{2} )\right ) \big ]\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Here, two variants of the complementary Gaussian error function are used, viz.
- $${\rm Q} (x) = \frac{\rm 1}{\sqrt{\rm 2\pi}}\int_{\it x}^{+\infty}\rm e^{\it -u^{\rm 2}/\rm 2}\,d {\it u} \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ {\rm erfc} (\it x) = \frac{\rm 2}{\sqrt{\rm \pi}}\int_{\it x}^{+\infty}\rm e^{\it -u^{\rm 2}}\,d \it u \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
⇒ The "Complementary Gaussian Error Functions" provides the numerical values of the functions ${\rm Q} (x)$ and $0.5 \cdot {\rm erfc} (x)$.
The noise power at the output of the Gaussian receiver filter $H_{\rm G}(f)$ is
- $$\sigma_d^2 = \frac{N_0}{2} \cdot \int_{-\infty}^{+\infty} |H_{\rm G}(f)|^2 \,{\rm d} f = \frac{N_0\cdot f_{\rm G}}{\sqrt{2}}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
$\text{From these equations one can already see:}$
- The smaller the cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G}$ of the Gaussian low-pass filter, the smaller the noise rms value $\sigma_d$ and consequently the better the noise performance.
- However, a small cutoff frequency leads to a strong deviation of the basic detection pulse $g_d(t)$ from the rectangular form and thus to intersymbol interference.
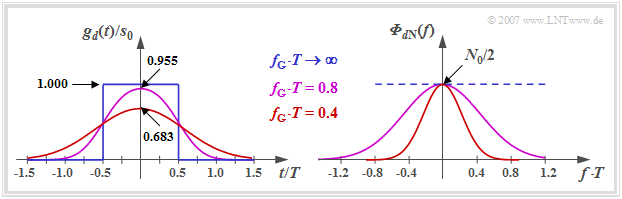
$\text{Example 1:}$ The left graph shows the basic detection pulse $g_d(t)$ at the output of a Gaussian low-pass filter $H_{\rm G}(f)$ with the cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G}$ when an NRZ rectangular pulse (blue curve) is applied at the input.
One can see from this plot:
- The Gaussian low-pass filter $H_{\rm G}(f)$ causes the detection pulse $g_d(t)$ to be reduced and broadened compared to the transmitted pulse $g_s(t)$ ⇒ "'time dispersion".
- The pulse deformation is the stronger, the smaller the cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G}$ is. For example, with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$ (red curve) the pulse maximum is already reduced to $\approx 68\%$.
- In the limiting case $f_{\rm G} \to \infty$ the Gaussian low-pass has no effect ⇒ $g_d(t) = g_s(t)$. However, in this case, there is no noise limitation at all, as can be seen from the right figure.
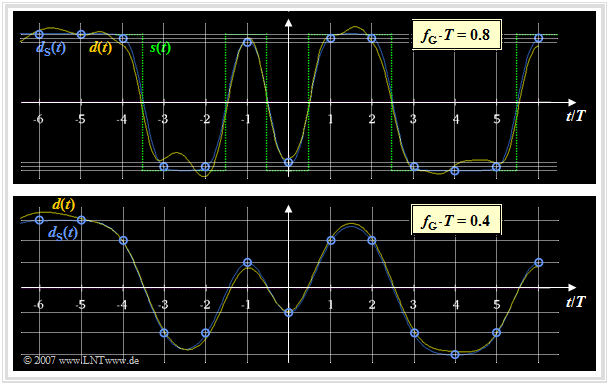
$\text{Example 2:}$ The same preconditions apply as for the last example. The graph shows the detection signal $d(t)$ after the Gaussian low-pass $($before the decision$)$ for two different cutoff frequencies, namely $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.8$ and $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$. We want to analyze these images in terms of intersymbol interference.
In both diagrams are shown:
- the component $d_{\rm S}(\nu \cdot T)$ of the detection signal without considering the noise $($blue circles at the detection times$)$,
- the total detection signal $d(t)$ including the noise component (yellow curve),
- the transmitted signal $s(t)$ as reference signal (green dotted in the upper graph; equally valid for the lower graph).
By comparing these images, the following statements can be verified in terms of Intersymbol Interference $\rm (ISI)$:
- With the cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.8$ (upper graph), only minor ISI result at the detection times $($at multiples of $T)$. Due to the Gaussian low-pass here primarily the corners of the transmitted signal $s(t)$ are rounded.
- In contrast, in the lower image $(f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4)$ the ISI effects are clearly visible. At the detection times $(\nu \cdot T)$, the $($blue$)$ signal component $d_{\rm S}(\nu \cdot T)$ of the detection signal can assume six different values $($compare grid lines drawn$)$.
- The noise component $d_{\rm N}(t)$ – recognizable as the difference between yellow curve and blue circles – is on average larger with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.8$ than with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$.
- This result can be explained by the right graph of $\text{Example 1}$, which shows the PSD of the noise component $d_{\rm N}(t)$:
- $${\it \Phi}_{d{\rm N} }(f) = {N_0}/{2} \cdot \vert H_{\rm G}(f) \vert^2 = {N_0}/{2} \cdot {\rm exp}\left [- \frac{2\pi f^2}{(2f_{\rm G})^2} \right ] .$$
- The integral over ${\it \Phi}_{d{\rm N} }(f)$ – i.e. the noise power $\sigma_d^2$ – is twice as large for $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.8$ (purple curve) than with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$ (red curve).
Definition and statements of the eye diagram
The above mentioned facts can also be explained by the eye diagram.
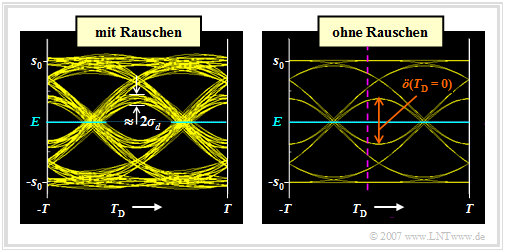
$\text{Definition:}$ The eye diagram (or "eye pattern") is the sum of all superimposed sections of the detection signal $d(t)$, whose duration is an integer multiple of the symbol duration $T$. This diagram has a certain resemblance to an eye, which led to its naming.
$\text{Example 3:}$ We assume a redundancy-free binary bipolar NRZ rectangular signal $s(t)$ and the Gaussian low-pass filter with cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$.
In the graphic shown are the eye diagrams after the Gaussian low-pass,
- left inclusive the noise component ⇒ signal $d(t)=d_{\rm S}(t) +d_{\rm N}(t)$,
- on the right without taking noise into account ⇒ signal $d_{\rm S}(t)$.
This representation allows important statements about the quality of a digital transmission system:
- Only the eye diagram of the signal $d(t)$ can be displayed metrologically on an oscilloscope, which is triggered with the clock signal. From this eye diagram $($left graph$)$, for example, the noise rms value $\sigma_d$ $($⇒ noise power $\sigma_d^2)$ can be read – or rather: estimated.
- The eye diagram without noise (right graph) refers to the signal component $d_{\rm S}(t)$ of the detection signal and can only be determined by means of a computer simulation. For an implemented system, this eye diagram cannot be displayed, since the noise component $d_{\rm N}(t)$ cannot be eliminated.
- In both diagrams of this example, $2^{11}=2048$ eye lines were drawn in each case. In the right graph, however, only $2^5 = 32$ eye lines are distinguishable because the present detection pulse $g_d(t)$ is limited to the time range $\vert t\vert \le 2T$
$($see graph in Example 1 with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$, red curve$)$.
- The inner eye lines determine the vertical eye opening $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})$. The smaller this is, the greater is the influence of intersymbol interference. For a $($ISI-free$)$ Nyquist system the vertical eye opening is maximum. Normalized to the transmitted amplitude, $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/s_0 = 2$ is then valid.
- With symmetrical basic detection pulse, the detection time $T_{\rm D} = 0$ is optimal. With a different value $($for example $T_{\rm D} = -T/10) $, $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})$ would be somewhat smaller and thus the error probability would be significantly larger. This case is indicated by the purple–dashed vertical line in the right graph.
Mean error probability
As with the previous graphs in this chapter, we assume the following:
- NRZ rectangles with amplitude $s_0$, AWGN noise with power-spectral density $N_0$, where
- $$10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm} \frac{s_0^2 \cdot T}{N_0}\approx 13\,{\rm dB}\hspace{0.3cm} \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \frac{N_0}{s_0^2 \cdot T} = 0.05\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Gaussian receiver filter with cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$:
- $$\sigma_d^2 = \frac{(N_0 /T)\cdot (f_{\rm G}\cdot T)}{\sqrt{2}}= \frac{0.05 \cdot s_0^2\cdot0.4}{\sqrt{2}}$$
- $$ \Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} \sigma_d = \sqrt{0.0141}\cdot s_0 \approx 0.119 \cdot s_0 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- Let $g_d(\nu \cdot T) \approx 0$ be valid for $|\nu| \ge 2$. The other basic detection pulse values are given as follows:
- $$g_0 = g_d(t=0) \approx 0.68 \cdot s_0,$$
- $$g_1 = g_d(t=T) \approx 0.16 \cdot s_0,$$
- $$g_{-1} = g_d(t=-T) \approx 0.16 \cdot s_0\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
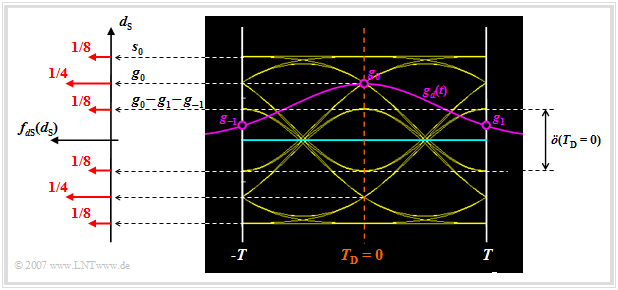
Let us now analyze the possible values for the signal component $d_{\rm S}(t)$ at the detection times:
- Of the total $32$ eye lines, four lines intersect the ordinate $(t = 0)$ at $g_0 + 2 \cdot g_1 = s_0$. These lines belong to the amplitude coefficients "$\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.1cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} {\it +\hspace{-0.05cm}1},\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$". Here, the "middle" coefficient $a_{\nu = 0}$ is highlighted in italics.
- The four eye lines, each representing the coefficients "$\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.1cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} {\it +\hspace{-0.05cm}1},\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.05cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$" result in the signal value $d_{\rm S}(T_{\rm D} = 0) =g_0 - 2 \cdot g_1 = 0.36 \cdot s_0$.
- In contrast, the signal value $d_{\rm S}(T_{\rm D} = 0) =g_0 = 0.68 \cdot s_0$ occurs twice as often. This goes back either to the coefficients "$\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.1cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} {\it +\hspace{-0.05cm}1},\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$" or to "$\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.1cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} {\it +\hspace{-0.05cm}1},\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$".
- For the $16$ eye lines which intersect the ordinate $T_{\rm D} = 0$ below the decision threshold $E = 0$, exactly mirror-image relations result.
The possible values $d_{\rm S}(T_{\rm D})$ and their occurrence probabilities can be found in the above graph on the left side in the (discrete) probability density function $\rm (PDF)$ of the noise-free detection signal samples:
- $$f_{d{\rm S}}(d_{\rm S}) = {1}/{8} \cdot \delta (d_{\rm S} - s_0)+ {1}/{4} \cdot \delta (d_{\rm S} - 0.68 \cdot s_0)+ {1}/{8} \cdot \delta (d_{\rm S} - 0.36 \cdot s_0)+ $$
$$\hspace{2.15cm} + \hspace{0.2cm} {1}/{8} \cdot \delta (d_{\rm S} + s_0)+{1}/{4} \cdot \delta (d_{\rm S} + 0.68 \cdot s_0)+{1}/{8} \cdot \delta (d_{\rm S} + 0.36 \cdot s_0)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Thus, the (average) symbol error probability of the of the ISI-afflicted system can be given. Taking advantage of the symmetry, one obtains with $\sigma_d/s_0 = 0.119$:
- $$p_{\rm S} = {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \frac{s_0}{ \sigma_d} \right)+ {1}/{2} \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \frac{0.68 \cdot s_0}{ \sigma_d} \right)+{1}/{4} \cdot {\rm Q} \left( \frac{0.36 \cdot s_0}{ \sigma_d} \right)$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm}p_{\rm S} \approx {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm Q}(8.40) +{1}/{2} \cdot {\rm Q}(5.71)+ {1}/{4} \cdot {\rm Q}(3.02)\approx {1}/{4} \cdot 2.20 \cdot 10^{-17}+ {1}/{2} \cdot 1.65 \cdot 10^{-9}+ {1}/{4} \cdot 1.26 \cdot 10^{-3} \approx 3.14 \cdot 10^{-4} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
$\text{On the basis of this numerical example one recognizes:}$
- In the presence of intersymbol interference, the (average) symbol error probability $p_{\rm S}$ is essentially determined by the inner eye lines.
- The computational cost of determining $p_{\rm S}$ can become very large, especially if the ISI comes from very many basic detection pulse values $g_\nu$.
$\text{Example 4:}$
- If the pulse values $g_{-5}, \text{...} \ , g_{+5}$ are different from zero and $E \ne 0$, an averaging over $2^{11} = 2048$ eye lines is necessary to determine the error probability $p_{\rm S}$.
- If, on the other hand, only the pulse values $g_{-1}, \ g_0, \ g_{+1}$ are different from zero and, in addition, the symmetry with respect to the threshold $E = 0$ is taken into account, the effort is reduced to averaging over four terms.
- If, in addition, the symmetry $g_{-1} = g_{+1}$ applies as with the above numerical values, then the symmetry with respect to $T_{\rm D}$ can also be exploited and averaging over three terms is sufficient.
Worst-case error probability
In the past, a variety of approximations for the average error probability have been given, among others: Bitte dieses Kapitel sehr kritisch checken
$\text{Definition:}$ As a very simple approximation for the actual error probability $p_{\rm S}$, the worst-case error probability (German: "ungünstigste Fehlerwahrscheinlichkeit" ⇒ subscript: "U") is often used:
- $$p_{\rm U} = {\rm Q} \left( \frac{\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/2}{ \sigma_d} \right) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
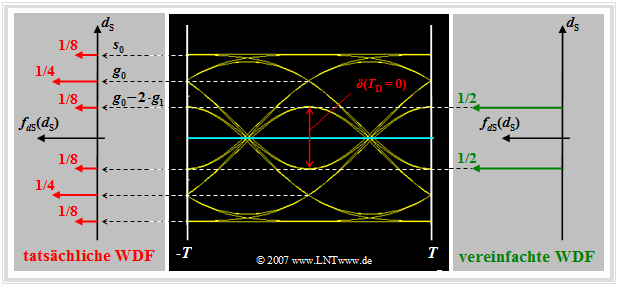
For their calculation, the "worst-case symbol sequences" are always assumed. This means:
- The actual probability density function $\rm (PDF)$ of the samples $d_{\rm S}(T_{\rm D})$ (left graph: six red Dirac delta functions) is replaced by a simplified PDF with only the inner Dirac delta functions (right graph: two green Diracs).
- For the half vertical eye opening, with the basic detection pulse values $g_\nu = g_d( T_{\rm D}+ \nu \cdot T)$ generally holds:
- $$\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/{ 2}= g_0 - \sum_{\nu = 1}^{n} \vert g_{\nu} \vert- \sum_{\nu = 1}^{v} \vert g_{-\nu} \vert \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
This equation can be interpreted as follows:
- $g_0 = g_d( T_{\rm D})$ is the so-called "main value" of the basic detection pulse. For Nyquist systems $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})/{ 2}= g_0$ is always valid. In the following (mostly) $T_{\rm D}= 0$ is set.
- The first sum describes the ISI influence of the $n$ "trailers" $($German: "Nachläufer" ⇒ variable $n)$ of preceding pulses. Tacitly assumed is $g_\nu = 0$ for $\nu \gt n$.
- The second sum considers the influence of the $v$ "precursors" $($German: "Vorläufer" ⇒ variable $v)$ of following pulses under the condition $g_{-\nu} = 0$ for $\nu \gt v$.
- If all precursors and trailers are positive, the two worst-case symbol sequences are "$\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.1cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.05cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} {\it +\hspace{-0.05cm}1},\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.05cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} -\hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$" and "$\text{...}\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.1cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} {\it -\hspace{-0.05cm}1},\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm}1,\hspace{0.05cm} +\hspace{-0.05cm}1\hspace{0.05cm} \text{...}$" (coefficient $a_{\nu = 0}$ is in italics in each case). These specifications apply, for example, to the Gaussian receiver filter considered here.
- If some basic detection pulse values $g_{\nu\ne 0}$ are negative, this is taken into account in the above equation by the magnitude formation. This results in other "worst–case" sequences than those just mentioned.
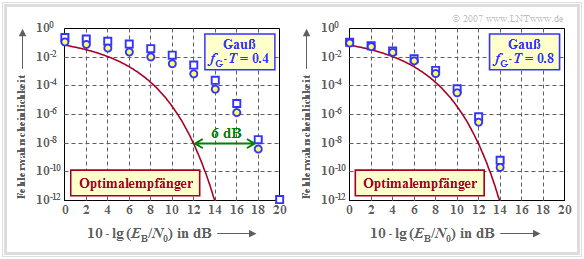
$\text{Example 5:}$ The graph shows the error probabilities of the AWGN channel as a function of the (logarithmized) quotient $E_{\rm B}/N_0$, namely
- the average error probability $p_{\rm S}$ with a Gaussian receive filter (blue circles),
- the worst-case error probability $p_{\rm U}$ with Gaussian receiver filter (blue rectangles),
- the smallest possible error probability according to the section "Optimal binary receiver" (red curve).
Here, the energy per bit is equal to $E_{\rm B} = s_0^2 \cdot T$ (NRZ rectangular transmitted pulses).
The left graph is for the (normalized) cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$, the right one for a broader band receiver filter with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.8$. The results can be interpreted as follows:
- The worst-case error probability $p_{\rm U}$ is always an upper bound for the actual symbol error probability $p_{\rm S}$. The smaller the influence of the intersymbol interference (large cutoff frequency), the closer $p_{\rm S}$ and $p_{\rm U}$ are to each other. For the optimal receiver $p_{\rm S} = p_{\rm U}.$
- For Gaussian receiver filter with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T \ge 0.3$, the intersymbol interferences are caused by the neighboring pulses alone $(g_2 = g_3 = \text{...} \approx 0)$, so that a lower bound can also be given for $p_{\rm S}$:
- $${p_{\rm U} }/{ 4} \le p_{\rm S} \le p_{\rm U} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
- The strong intersymbol interference of a Gaussian receiver filter with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.4$ leads to the fact that compared to the optimal receiver a $6 \ \rm dB$ larger $E_{\rm B}/N_0$ must be applied (four times the power), so that the error probability does not exceed the value $10^{-8}$.
- However, the horizontal distance between the blue $p_{\rm S}$ curve (marked by circles) and the red comparison curve is not constant. At $p_{\rm S} = 10^{-2}$ the distance is only $4 \ \rm dB$.
- The right graph shows that with $f_{\rm G} \cdot T = 0.8$ the distance to the comparison system is less than $1 \ \rm dB$. In the next section it is shown that with a Gaussian receiver filter the (normalized) cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} \cdot T \approx 0.8$ is the optimum.
Optimization of the cutoff frequency
For system optimization and system comparison, it turns out to be convenient,
- instead of worst-case error probability $p_{\rm U}$
- to use the worst–case signal–to–noise power ratio (S/N ratio):
- $$\rho_{\rm U} = [\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D})]^2/ \sigma_d^2.$$
In the case of Gaussian perturbation, the following relationship exists:
- $$p_{\rm U} = {\rm Q} \left( \sqrt{\rho_{\rm U}} \right) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
The mean symbol error probability $p_{\rm S}$ can also be formally expressed by a S/N ratio via the Q function:
- $$\rho_d = \left[{\rm Q}^{-1} \left( p_{\rm S} \right)\right]^2 \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
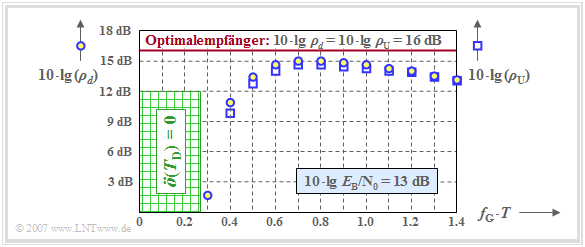
The graph shows the two quantities $\rho_d$ and $\rho_{\rm U}$ in logarithmic form depending on the normalized cutoff frequency $f_{\rm G} \cdot T$ of a Gaussian receiver filter, where $10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm} E_{\rm B}/N_0 = 13 \ \rm dB$ is the basis.
- The circles outlined in blue are for $10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm} \rho_d$ ⇒ "mean" detection SNR,
- The blue outlined squares mark $10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm} \rho_{\rm U}$ ⇒ "worst-case" SNR.
For comparison, the result for the "optimal binary receiver" is also plotted as a red horizontal line. For this one holds:
- $$\rho_d = \rho_{\rm U} = {2 \cdot E_{\rm B}}/{ N_0}\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm} \rho_d = 10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm} \rho_{\rm U} \approx 16\,{\rm dB} \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
One can see from the plot:
- The optimization criterion $\rho_d$ leads to the optimal cutoff frequency $f_\text{G, opt} \cdot T = 0.8$. A smaller cutoff frequency results in stronger intersymbol interference (smaller eye opening), a larger cutoff frequency results in a larger noise rms value $\sigma_d$.
- Such a Gaussian receiver filter with $f_\text{G, opt} \cdot T \approx 0.8$ leads to the signal-to-noise ratio $10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm} \rho_d \approx 15 \ \rm dB$ and thus to the error probability $p_{\rm S} \approx 10^{-8}$. For comparison: For the optimal receiver (impulse response matched to the transmitter), the results are $10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm} \rho_d \approx 16 \ \rm dB$ and $p_{\rm S} \approx 10^{-10}$.
- However, the graph also shows that the much simpler optimization criterion $ \rho_{\rm U}$ $($or $ p_{\rm U})$ leads approximately to the same optimal cutoff frequency $f_\text{G, opt} \cdot T = 0.8$. For this cutoff frequency, we obtain $10 \cdot {\rm lg}\hspace{0.1cm} \rho_{\rm U} \approx 14.7 \ \rm dB$ and the worst-case error probability $p_{\rm U} \approx 3 \cdot 10^{-8}$.
- If the cutoff frequency $f_\text{G} \cdot T < 0.27$, the vertical eye opening will always be $\ddot{o}(T_{\rm D}) = 0$. This is called a closed eye. As a consequence, some worst-case pulse sequences would always be wrongly decided even without noise. A systematic error occurs.
- Further investigations have shown that the optimization criterion $ \rho_{\rm U}$ is sufficient even with smaller $E_{\rm B}/N_0$. Thus, for a distortion-free channel ⇒ $H_{\rm K}(f) = 1$, the optimal cutoff frequency of the Gaussian low-pass always results in $f_\text{G, opt} \cdot T \approx 0.8$, at least in a realistic approach.
All statements of this chapter can be reproduced with the interactive applet "Eye diagram and eye opening".
Exercises for the chapter
Exercise 3.2: Eye Pattern according to Gaussian Low-Pass
Exercise 3.2Z: Optimum Cut-off Frequency for Gaussian Low-pass