Difference between revisions of "Aufgaben:Exercise 3.2Z: Components of the GSM System"
From LNTwww
m (Text replacement - "Category:Exercises for Mobile Communications" to "Category:Mobile Communications: Exercises") |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
}} | }} | ||
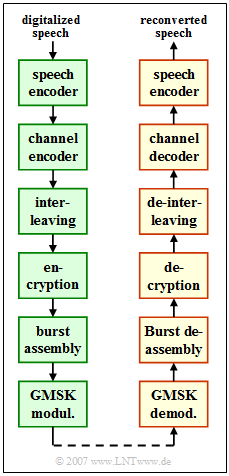
| + | [[File:EN_Bei_Z_3_7.png|right|frame|GSM system components]] | ||
| + | The diagram shows the entire GSM transmission path, with the transmitter on the left and the receiver on the right. | ||
| − | + | The illustration refers only to speech transmission. In GSM data transmission, only the top block $($speech encoder or decoder$)$ is replaced by another channel encoder or decoder $($concatenation of two channel codes$)$. | |
| − | The | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | The two respective lowest system components were already treated in detail in the exercises for the chapter [[Examples_of_Communication_Systems/Radio_Interface|"Radio Interface"]]. | ||
| + | In this exercise, on the other hand, some basic properties are queried from | ||
| + | *Speech encoders and speech decoders, | ||
| + | *convolutional encoder and convolutional decoder, | ||
| + | *interleaver and de-interleaver, and | ||
| + | *encryption and decryption. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | <u>Hint:</u> | ||
| + | *The exercise belongs to the chapter [[Mobile_Communications/Similarities_Between_GSM_and_UMTS|"Similarities between GSM and UMTS"]]. | ||
| + | *Reference is also made to the chapter [[Mobile_Communications/Characteristics_of_GSM|"Characteristics of GSM"]]. | ||
| − | |||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | + | {Which statements are true for speech encoding/decoding? | |
| − | {Which statements | ||
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + | + | + These are source coding components. |
| − | - They are components of channel coding. | + | - They are components of channel coding. |
| − | - | + | - Redundancy is added by the speech encoder. |
| − | + | + | + Redundancy is removed by the speech encoder. |
| − | {Which statements | + | {Which statements are true for the convolutional encoder or decoder? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | - | + | - They are components of source coding. |
| − | + | + | + They are components of channel coding. |
+ Redundancy is added by the convolutional encoder. | + Redundancy is added by the convolutional encoder. | ||
- Redundancy is removed by the convolutional encoder. | - Redundancy is removed by the convolutional encoder. | ||
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true for the interleaver and de-interleaver? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
- The interleaver adds redundancy. | - The interleaver adds redundancy. | ||
| − | + The | + | + The interleaver is used to distribute bundle errors. |
| − | - The interleaver | + | - The interleaver has the most significance for the AWGN channel. |
| − | { | + | {Which statements are true for encryption and decryption? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
+ Both serve data security in the sense of data protection. | + Both serve data security in the sense of data protection. | ||
| − | - These components are | + | - These components are for error correction. |
| − | - | + | - Encryption adds redundancy. |
| − | + GSM | + | + GSM mostly uses symmetric encryption. |
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
| + | |||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
{{ML-Kopf}} | {{ML-Kopf}} | ||
| + | '''(1)''' Correct are the <u>answers 1 and 4</u>: | ||
| + | *The goal of speech coding is data compression and thus redundancy reduction. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*This is a typical task of source coding. | *This is a typical task of source coding. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | '''(2)''' Correct are the <u>answers 2 and 3</u>: | ||
| + | *Convolutional coding is a form of channel coding by which the receiver (convolutional decoder) is enabled to detect and possibly correct errors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The channel encoder adds (meaningful) redundancy for this purpose, while the speech encoder removes irrelevant redundancy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Often both components are implemented together or at least closely coordinated. This is then referred to as "joint source and channel coding". | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''(3)''' Only <u>answer 2</u> is correct: | ||
| + | *The convolutional decoder has major problems when the transmission errors are clustered rather than they are statistically independent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The task of interleaver and de-interleaver is to break up such bunching errors and spread them over a larger time period. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The redundancy is not changed by this procedure. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In the AWGN channel, bit errors occur statistically independently, so interleaver and de-interleaver can be omitted. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '''(4)''' | + | '''(4)''' Correct are the <u>answers 1 and 4</u>: |
| − | *Encryption and decryption & | + | *Encryption and decryption (the counterpart on the receiving side) are used solely to protect user data from unauthorized access. |
| − | *They are not used for error correction | + | |
| − | *A distinction is made between symmetric and asymmetric encryption. GSM | + | *They are not used for error correction, nor do they add redundancy. |
| + | |||
| + | *A distinction is made between symmetric and asymmetric encryption. GSM predominantly uses the first variant. | ||
Latest revision as of 17:26, 30 January 2023
The diagram shows the entire GSM transmission path, with the transmitter on the left and the receiver on the right.
The illustration refers only to speech transmission. In GSM data transmission, only the top block $($speech encoder or decoder$)$ is replaced by another channel encoder or decoder $($concatenation of two channel codes$)$.
The two respective lowest system components were already treated in detail in the exercises for the chapter "Radio Interface".
In this exercise, on the other hand, some basic properties are queried from
- Speech encoders and speech decoders,
- convolutional encoder and convolutional decoder,
- interleaver and de-interleaver, and
- encryption and decryption.
Hint:
- The exercise belongs to the chapter "Similarities between GSM and UMTS".
- Reference is also made to the chapter "Characteristics of GSM".
Solution
(1) Correct are the answers 1 and 4:
- The goal of speech coding is data compression and thus redundancy reduction.
- This is a typical task of source coding.
(2) Correct are the answers 2 and 3:
- Convolutional coding is a form of channel coding by which the receiver (convolutional decoder) is enabled to detect and possibly correct errors.
- The channel encoder adds (meaningful) redundancy for this purpose, while the speech encoder removes irrelevant redundancy.
- Often both components are implemented together or at least closely coordinated. This is then referred to as "joint source and channel coding".
(3) Only answer 2 is correct:
- The convolutional decoder has major problems when the transmission errors are clustered rather than they are statistically independent.
- The task of interleaver and de-interleaver is to break up such bunching errors and spread them over a larger time period.
- The redundancy is not changed by this procedure.
- In the AWGN channel, bit errors occur statistically independently, so interleaver and de-interleaver can be omitted.
(4) Correct are the answers 1 and 4:
- Encryption and decryption (the counterpart on the receiving side) are used solely to protect user data from unauthorized access.
- They are not used for error correction, nor do they add redundancy.
- A distinction is made between symmetric and asymmetric encryption. GSM predominantly uses the first variant.